
What Type of Links Does Google Really Prefer?
We all know that links help rankings. And the more links you build the higher you’ll rank.
But does it really work that way?
Well, the short answer is links do help with rankings and I have the data to prove it.
But, you already know that.
The real question is what kind of links do you need to boost your rankings?
Is it rich anchor text links? Is it sitewide links? Or what happens when the same site links to you multiple times? Or when a site links to you and then decides to remove the link?
Well, I decided to test all of this out and then some.
Over the last 10 months, I decided to run an experiment with your help. The experiment took a bit longer than we wanted, but we all know link building isn’t easy, so the experiment took 6 months longer than was planned.
Roughly 10 months ago, I emailed a portion of my list and asked if they wanted to participate in a link building experiment.
The response was overwhelming… 3,919 people responded, but of course, it would be a bit too hard to build links to 3,919 sites.
And when I say build, I’m talking about manual outreach, leveraging relationships… in essence, doing hard work that wouldn’t break Google’s guidelines.
Now out of the 3,919 people who responded, we created a set of requirements to help us narrow down the number of sites to something more manageable:
- Low domain score – we wanted to run an experiment on sites with low domain scores. If a site had a domain score of greater than 20, we removed it. When a site has too much authority, they naturally rank for terms and it is harder to see the impact that a few links can have. (If you want to know your domain score you can put in your website URL here.)
- Low backlink count – similar to the one above, we wanted to see what happens with sites with little to no backlinks. So, if a site had more than 20 backlinks, it was also removed from the experiment.
- No subdomains – we wanted sites that weren’t a Tumblr.com or a WordPress.com site or subdomain. To be in this experiment, you had to have your own domain.
- English only sites – Google in English is more competitive than Google in Spanish, or Portuguese or many other languages. For that reason, we only selected sites that had their main market as the United States and the site had to be in English. This way, if something worked in the United States, we knew it would work in other countries as they tend to be less competitive.
We decided to cap the experiment to 200 sites. But eventually, many of the sites dropped off due to their busy schedule or they didn’t want to put in the work required. And as people dropped off, we replaced them with other sites who wanted to participate.
How the experiment worked
Similar to the on-page SEO experiment that we ran, we had people write content between 1,800 and 2,000 words.
Other than that we didn’t set any requirements. We just wanted there to be a minimum length as that way people naturally include keywords within their content. We did, however, include a maximum length as we didn’t want people to write 10,000-word blog posts as that would skew the data.
Websites had 2 weeks to publish their content. And after 30 days of it being live, we looked up the URLs within Ubersuggest to see how many keywords the article ranked for in the top 100, top 50 and top 10 spots.
Keep in mind that Ubersuggest has 1,459,103,429 keywords in its database from all around the world and in different languages. Most of the keywords have low search volume, such as 10 a month.
We then spent 3 months building links and then waited 2 months after the links were built to see what happened to the rankings.
The URLs were then entered back into the Ubersuggest database to see how many keywords they ranked for.
In addition to that, we performed this experiment in batches, we just didn’t have the manpower and time to do this for 200 sites all at once, hence it took roughly 10 months for this to complete.
We broke the sites down into 10 different groups. That’s 20 sites per group. Each group only leveraged 1 link tactic as we wanted to see how it impacted rankings.
Here’s each group:
- Control – with this group we did nothing but write content. We needed a baseline to compare everything to.
- Anchor text – the links built to the articles in this group contained rich anchor text but were from irrelevant pages. In other words, the link text contained a keyword, but the linking site wasn’t too relevant to the article. We built 3 anchor text links to each article.
- Sitewide links – they say search engines don’t care for sitewide links, especially ones in a footer… I wanted to test this out for myself. We built one sitewide link to each article.
- Content-based links – most links tend to happen within the content and that’s what we built here. We built 3 content-based links to each article.
- Multiple links from the same site – these weren’t sitewide links but imagine one site linking to you multiple times within their content. Does it really help compared to having just 1 link from a site? We built 3 links from the same site to each article.
- One link – in this scenario we built one link from a relevant site.
- Sidebar links – we built 3 links from the sidebar of 3 different sites.
- Nofollow links – does Google really ignore nofollow links? You are about to find out because we built 3 nofollow links to each article.
- High authority link – we built 1 link with a domain score of 70 or higher.
- Built and removed links – we built 3 links to articles in this group and then removed them 30 days after the links were picked up by Google.
Now before I share what we learned, keep in mind that we didn’t build the links to the domain’s homepage. We built the links to the article that was published. That way we could track to see if the links helped.
Control group
Do you really need links to rank your content? Especially if your site has a low domain score?
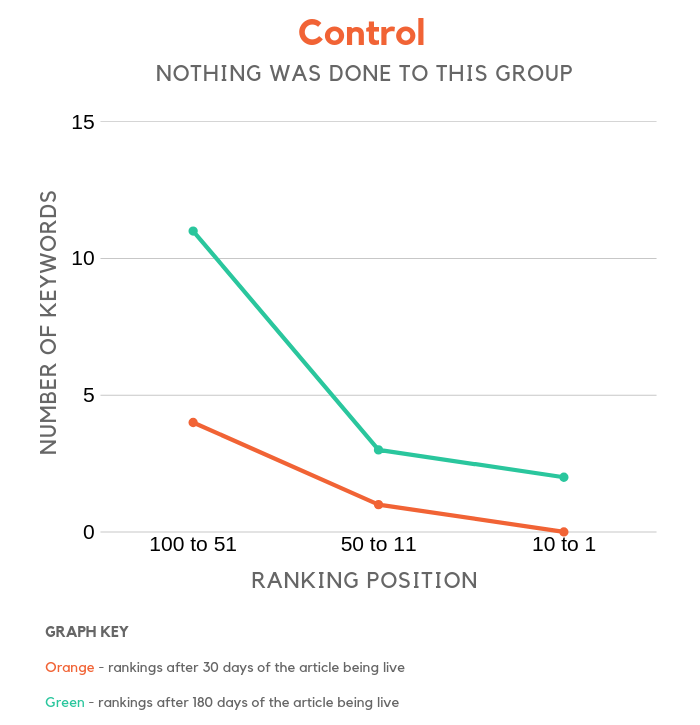
Based on the chart, the older your content gets, the higher you will rank. And based on the data even if you don’t do much, over a period of 6 months you can roughly rank for 5 times more keywords even without link building.
As they say, SEO is a long game and the data shows it… especially if you don’t build any links.
Anchor text
They say anchor text links really help boost rankings. That makes sense because the link text has a keyword.
But what if the anchor rich link comes from an irrelevant site. Does that help boost rankings?
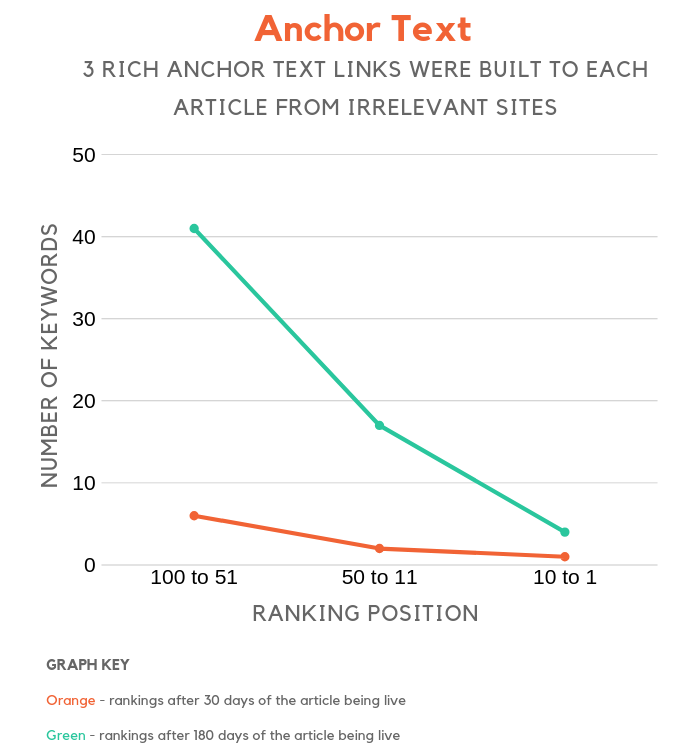
It looks like anchor text plays a huge part in Google’s rankings, even if the linking site isn’t too relevant to your article.
Now, I am not saying you should build spammy links and shove keywords in the link text, more so it’s worth keeping in mind anchor text matters.
So if you already haven’t, go put in your domain here to see who links to you. And look for all of the non-rich anchor text links and email each of those site owners.
Ask them if they will adjust the link and switch it to something that contains a keyword.
This strategy is much more effective when you ask people to switch backlinks that contain your brand name as the anchor text to something that is more keyword rich.
Sitewide Links
They say sitewide links are spammy… especially if they are shoved in the footer of a site.
We built one sitewide footer link to each article to test this out.
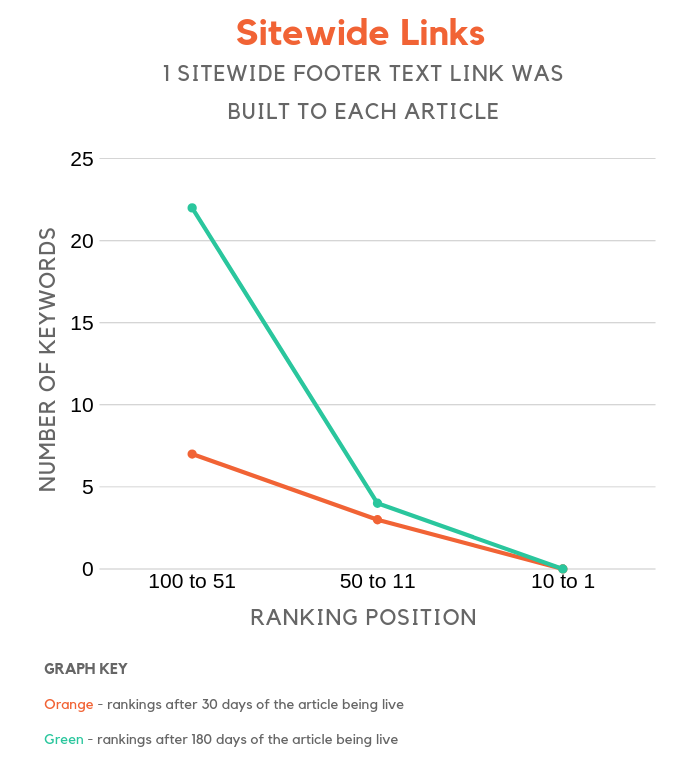
Although sites that leverage sitewide links showed more of an increase than the control group, the results weren’t amazing, especially for page 1 rankings.
Content-based links
Do relevance and the placement of the links impact rankings? We built 3 in-content links that were relevant to each article.
Now the links were not rich in anchor text.
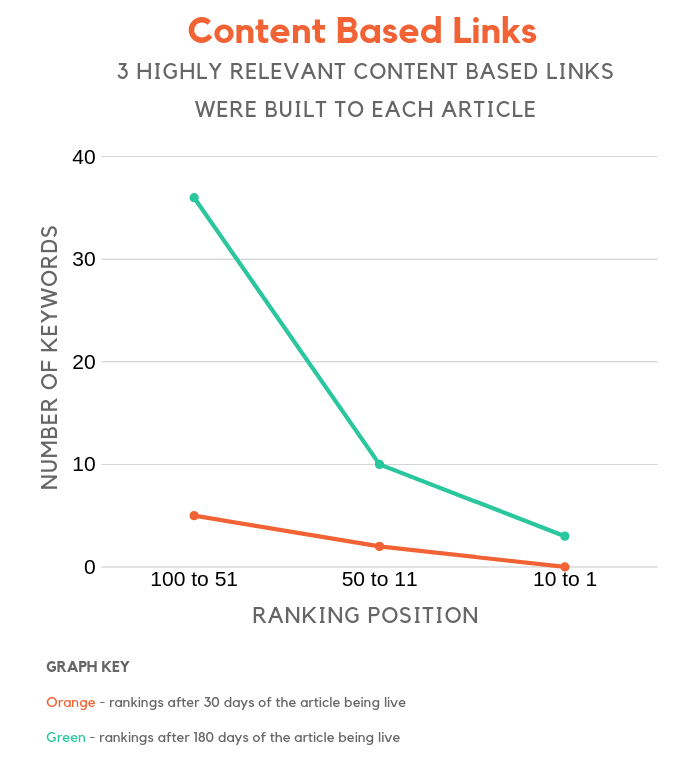
Compared to the baseline, rankings moved up to a similar rate as the sites who built rich anchor text links from irrelevant sites.
Multiple site links
I always hear SEOs telling me that if you build multiple links from the same site, it doesn’t do anything. They say that Google only counts one link.
For that reason, I thought we would put this to the test.
We built 3 links to each article, but we did something a bit different compared to the other groups. Each link came from the same site, although we did leverage 3 different web pages.
For example, if 3 different editors from Forbes link to your article from different web pages on Forbes, in theory, you have picked up 3 links from the same site.
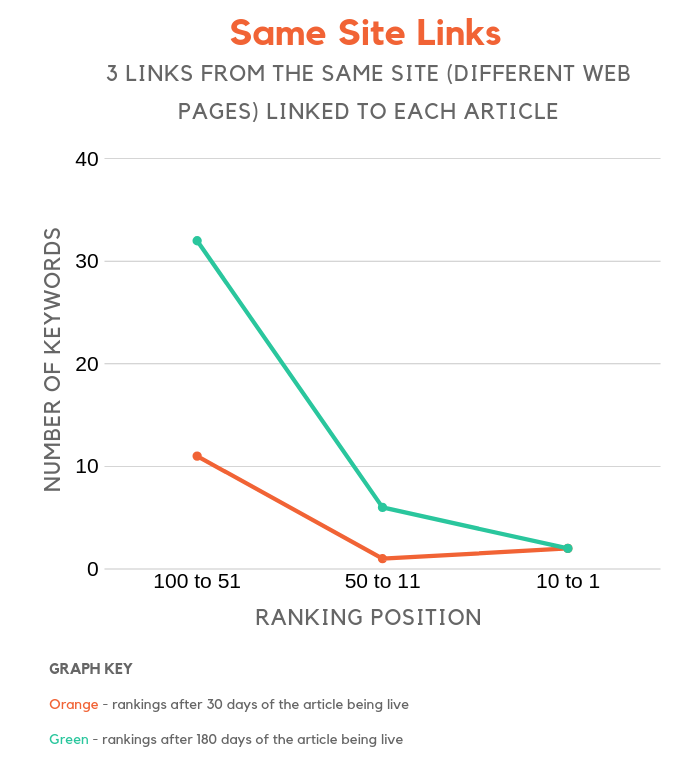
Even if the same site links to you multiple times, it can help boost your rankings.
One link
Is more really better? How does one relevant link compare to 3 irrelevant links?
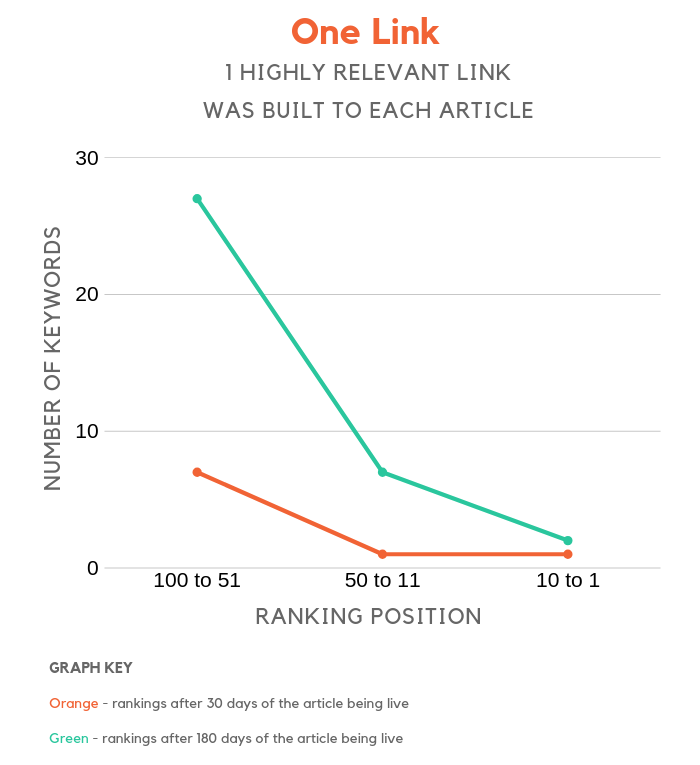
It’s not as effective as building multiple links. Sure, it is better than building no links but the articles that built 3 relevant backlinks instead of 1 had roughly 75% more keyword placements in the top 100 positions of Google.
So if you have a choice when it comes to link building, more is better.
Sidebar links
Similar to how we tested footer links, I was curious to see how much placement of a link impacts rankings.
We looked at in-content links, footer links, and now sidebar links.
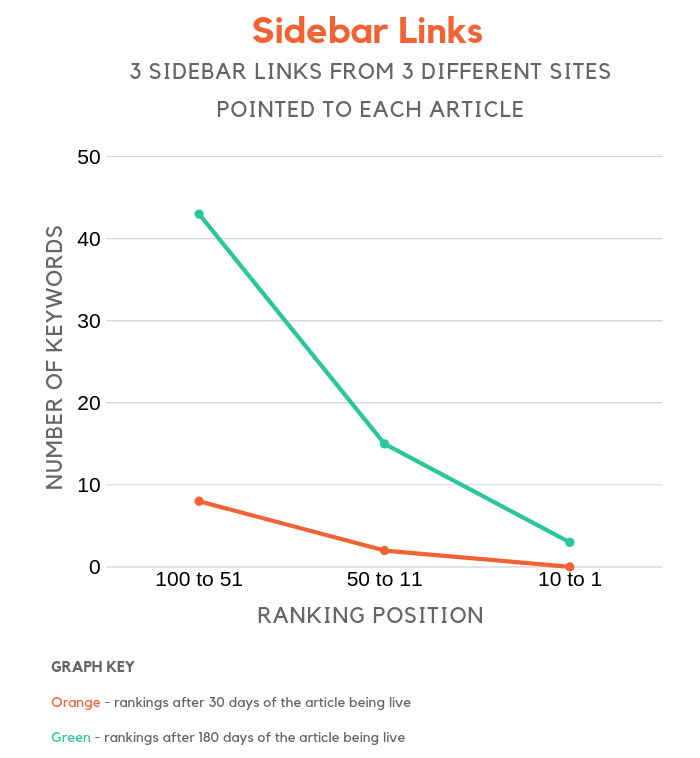
Shockingly, they have a significant impact in rankings. Now in order of effectiveness, in-content links help the most, then sidebar links, and then sitewide footer when it comes to placement.
I wish I tested creating 3 sitewide footer links to each article instead of 1 as that would have given me a more accurate conclusion for what placements Google prefers.
Maybe I will be able to run that next time. 🙁
Nofollow links
Do nofollow links help with rankings?
Is Google pulling our leg when they say they ignore them?
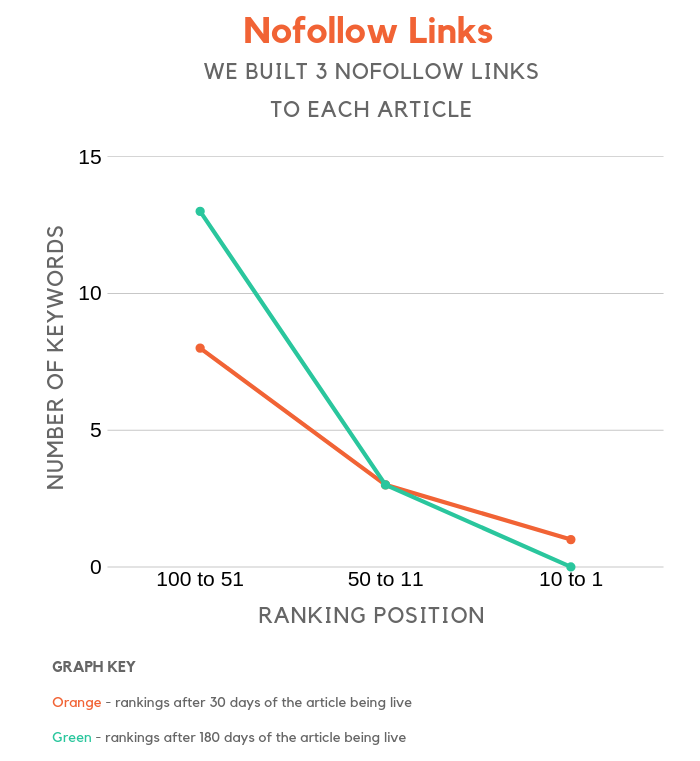
From what it looks like, they tend to not count nofollow links. Based on the chart above, you can see that rankings did improve over time, but so did almost every other chart, including the control group.
But here’s what’s funny: the control group had a bigger percentage gain in keyword rankings even though no links were built.
Now, I am not saying that nofollow links hurt your rankings, instead, I am saying they have no impact.
High authority link
Which one do you think is better:
Having one link from a high domain site (70 or higher)?
OR
Having 3 links from sites with an average or low domain score?
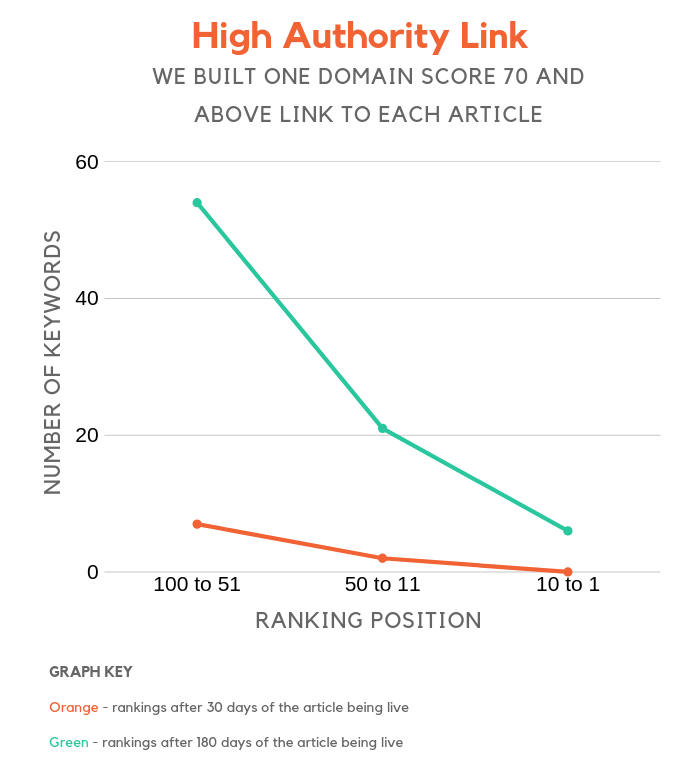
Even though the link from the authority site wasn’t rich in anchor text and we only built 1 per site in this group… it still had a bigger impact than the sites in the other group.
That means high authority links have more weight than irrelevant links that contain rich anchor text or even 3 links from sites with a low domain score.
If you are going to spend time link building, this is where your biggest ROI will be.
Build and removed links
This was the most interesting group, at least that is what the data showed.
I always felt that if you built links and got decent rankings you wouldn’t have to worry too much when you lost links.
After all, Google looks at user signals, right?
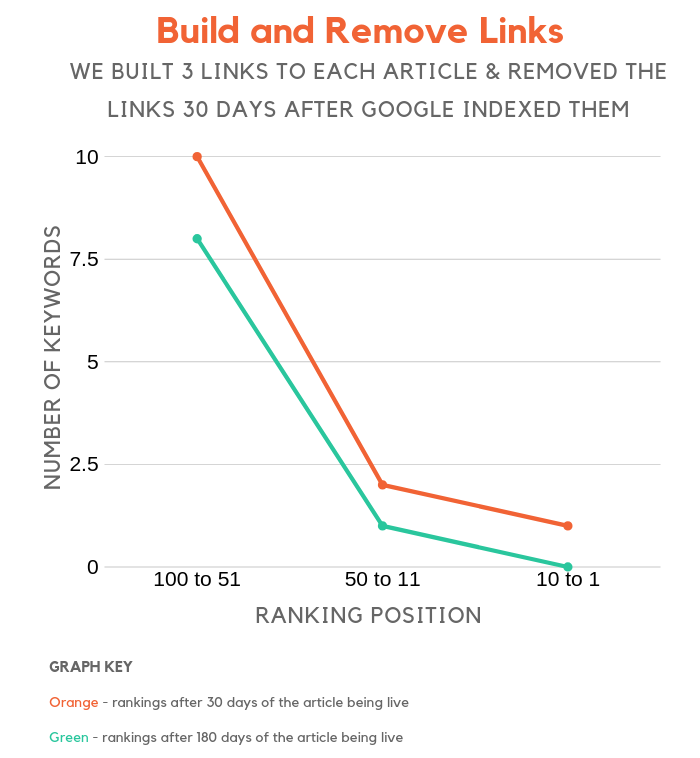
This one was shocking. At least for sites that have a low domain score, if you gain a few links and then lose them fairly quickly, your rankings can tank to lower than what they originally were.
I didn’t expect this one and if I had to guess, maybe Google has something programmed in their algorithm that if a site loses a large portion of their links fast that people don’t find value in the site and that it shouldn’t rank.
Or that the site purchased links and then stopped purchasing the links…
Whatever it may be, you should consider tracking how many links you lose on a regular basis and focus on making sure the net number is increasing each month.
Conclusion
I wish I had put more people behind this experiment as that would have enabled me to increase the number of sites that I included in this experiment.
My overall sample size for each group is a bit too small, which could skew the data. But I do believe it is directionally accurate, in which building links from high domain score sites have the biggest impact.
Then shoot for rich anchor text links that are from relevant sites and are placed within the content.
I wouldn’t have all of your link text rich in anchor text and if you are using white hat link building practices it naturally won’t be and you won’t have to worry much about this.
But if you combine all of that together you should see a bigger impact in your rankings, especially if you are a new site.
So, what do you think about the data? Has it helped you figure out what types of links Google prefers?
The post What Type of Links Does Google Really Prefer? appeared first on Neil Patel.


