
Product Life Cycle: What It Is, the 5 Stages, & Examples
If you work with sales, knowing about the Product Life Cycle model is almost mandatory.
The model describes the stages a product goes through in its journey from creation to discontinuation.
Why do you need to know this?
Because products in different stages demand different strategies, be that for physical products or for services.
Do you think you can attract customers to a new product using the same actions used for products that have been on the market for years?
Best case scenario, it will be a wasted opportunity. At worst, a total failure.
To get to know the stages of the Product Life Cycle, examples, and how to employ this concept, don’t forget to read this article until the end!
What Is the Product Life Cycle?
The Product Life Cycle is a management tool that makes it possible to analyze how a product behaves from its development to its withdrawal from the market, also considering its launch, growth, and sales maturity.
It is like a product journey, or to refer to a more well-known example in marketing, the customer journey.
The mind behind this concept is Theodore Levitt, a German economist who lived in the United States and worked in the celebrated Harvard Business School.
Levitt proposed a five-stage model that he named the Product Life Cycle.
The stages are development, introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
Before I explain each of them, it’s interesting to understand why Levitt thought defining this model would be useful.
During his research, he discovered something that seems obvious but hadn’t been mapped until then: the characteristics of a product change a lot during its life cycle.
All the strategies around it need to consider the specific issues and characteristics of each of these stages.
This applies to sales and marketing, but also to product development and decision-making in the management sphere.
For example, when is the right moment to invest so a product explodes in the market?
When is time to step on the brakes and maybe even replace an item that was very successful on another occasion?
These are the questions you can answer with a Product Life Cycle analysis.
The 5 Stages of the Product Life Cycle
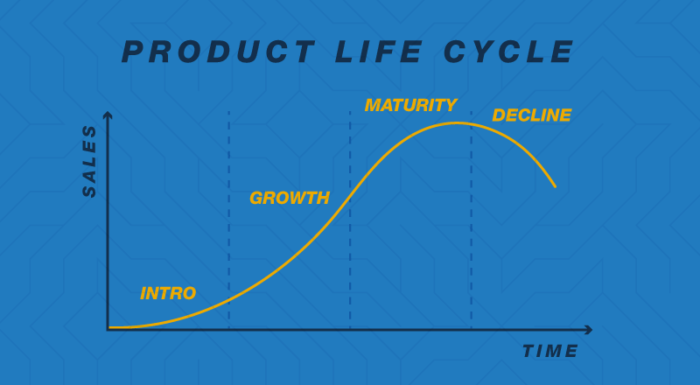
It’s time to explore more deeply the Product Life Cycle model.
Now that we know the stages, we will see what are the characteristics of each of them, and also the best practices to achieve your marketing goals.
1. Development Phase of the Product Life Cycle
Product development is always a very sensitive stage.
The project is still able to be iterated. You can have great expectations for it, but before the product starts generating revenue, you still need to improve your proposal, carry out tests, validate the hypotheses, and make necessary changes.
This stage is naturally integrated into the process of startup companies but is not restricted to them.
For example, an automobile manufacturer does not launch a new car without first having a consistent project and studying its insertion and acceptance in the market.
To present a real example, you might have seen the collection of leggings for dogs the Walkee Paws brand released at the end of 2018.

We can imagine that this launch was preceded by careful planning, which resulted in the shape of the pieces, the material used, and the patterns selected.
When a product is in development, it doesn’t require sales efforts, but promotion should already have begun.
Imagine the success potential of a marketing campaign from Walkee Paws announcing this novelty to dedicated dog lovers.
It could involve fun posts on social networks, generating curiosity and encouraging engagement.
There may also be press releases, billboards, or even interactive actions on the streets, among other types of marketing.
The fact is that the company must consider all this even during the development stage.
2. Introduction Phase of the Product Life Cycle
The Walkee Paws example is about the introduction.
That’s when the product goes through all development stages and is considered ready to be launched in the market.
Every day we are introduced to new items in this stage of the cycle.
For big brands, TV is a choice for promotion.
Proof: you only need to turn on the TV for a few minutes to see ads for a new flavor of soda, a different motorcycle model, a smartphone that promises new and superior features, etc.
It is no accident that this stage of the Product Life Cycle is the one that demands the most marketing investment from the company.
In fact, it is not uncommon to get negative financial results at this stage, even if sales have already started.
This is also a result of the production costs related to product distribution.
To reduce the damage, it is imperative to define the target audience and persona that represents the ideal customer profile for your products.
This exercise makes it possible to optimize your marketing investments, using the right platforms to convey the best message and reach the exact audience you want.
A good practice is to bet on inbound marketing and, by means of relevant content, ensure the user discovers the company and what it offers
This strategy is also how potential consumers are persuaded to confirm sales.
3. Growth Phase of the Product Life Cycle
If the Product Life Cycle works as it should, the next step is the growth stage.
The main characteristics of this stage are scalable sales and the maintenance of the amounts invested in marketing.
It is not possible to predict precisely when it happens, because that depends a lot on the details of the product and the market it’s in.
But it is worth repeating: if you follow the plan correctly, you are likely to reach your goals even if it takes a while.
So don’t get discouraged before you get to the growth stage.
Your investments must continue, either because of expanding your participation in the market or keeping production/output up with your sales rates.
This applies to sales of anything from marketing services, to salespeople training, to physical products.
Many companies fail at this stage and their products’ sales decline without having ever experienced maturity.
You might remember a beer brand that made fun tv ads with a short and chubby actor with a mustache as the protagonist.
For a long time, it was one of the leading brands, and the advertisements generated comments in the only social network in existence back then: word-of-mouth.
The product is still in the market, and there is no news of changes to its formula, but it was swallowed by the strong competition that is peculiar to the industry.
Lower investment in marketing would certainly be high in a list of possible reasons for this change.
So the lesson is clear: if a product is in the growth stage, it is important to have a strategy to keep it there even as new competitors start fighting for its audience.
4. Maturity Phase of the Product Life Cycle
Maturity is the peak, the highest point of the Product Life Cycle.
It’s when the product reaches its maximum potential and sales stabilize.
Once the summit is reached, it is no longer possible to grow, but the company can act to avoid significant setbacks.
The challenge at this stage is to maintain good results over time.
There isn’t a simple way to make this happen.
All the famous brands that come to mind now are where they are today because they invested in this stage.
For example, Coca-Cola doesn’t leave the media even though it “doesn’t depend on marketing.” The company understands that brands are not forever, being subject to market instabilities and behavioral changes in the audience.
Imagine if a competitor developed a new soft drink and people discover that that flavor is essential for their weekend family lunches.
With no visibility, Coca-Cola would lose space in the market, and in that situation, possibly even its place as the leading brand.
5. Decline Phase of the Product Life Cycle
It’s interesting to even imagine the end of Coca-Cola, a company with over 100 years of existence and so much financial success.
But even Coca-Cola will end one day. Maybe not the company, but its main product.
This might take 100, 200, or even 1000 years. It’s impossible to predict.
But every product reaches the end and concludes its life cycle.
When that happens, the company must recognize the painful truth shown in its performance indicators and prepare a replacement product.
If everything contributes to the idea of discontinuing the product, investing heavily in marketing to try to revert the situation tends to be too dangerous.
It might work, of course. But what if it doesn’t?
The company as a whole, and not just the product, may be endangered.
Why It’s Important to Understand the Product Life Cycle
If you’ve made it this far, you hopefully understand the concept of Product Life Cycle and the characteristics of each of its stages.
You should also understand why it’s important to apply this model to your business.
To eliminate any questions, here are the main advantages and benefits of what adherence to the Product Life Cycle model can do:
- allow decision making with better support
- optimize marketing investments
- qualify sales efforts
- offer more control over results
- give better long term strategic planning
- offer better organization and process management
- provide more longevity for products
- give more appropriate preparation to face competition
- leading the market becomes a feasible goal
Does the Product Life Cycle Only Apply to Products?
This is an interesting question about this tool.
If it were restricted to products, the audience who would be able to make use of it would be much smaller.
On one hand, the idea that the Product Life Cycle works better for physical products is correct considering its characteristics.
On the other hand, it’s possible to be creative and think about adaptations of the model.
Let’s take a large company with subsidiaries in different towns as an example.
Each one of these units may be considered a product when applying this Product Life Cycle model; all you have to do is analyze each one’s performance individually.
Another example is a company with many brands, each with their own products.
To understand this better, take a look at the Procter & Gamble website, where you will see that the company has several active brands in the USA market.

In which stage of the cycle is each of these brands?
Are they planning new brands that are currently in the development stage?
To conclude, let’s look at another example.
Could services replace products in the model proposed by Theodore Levitt?
Depending on the activity the company performs, this is perfectly possible.
Let’s think about a home renovation company, for example.
It may offer a great variety of construction services, such as installing floors and tiles, painting, plastering, providing electric and hydraulic works, masonry, and more.
When using the Product Life Cycle method, you can observe the life cycle of each of these services to assess the type of investment each of them requires and the possibilities for returns in each case.
Practical Examples of the Product Life Cycle
How does the Product Life Cycle work in practice, in real cases?
We are going to take a look at two cool examples: Havaianas and Coca-Cola.
The Product Life Cycle of Havaianas

- Development: the traditional flip flops were inspired by Japanese sandals made of wood or straw; in Brazil, rubber was selected as the material because it was believed to have the most acceptance with the audience
- Introduction: deliberately or not, its introduction in the market was a great success with classes C, D, and E
- Growth: Havaianas flip flops were in the growth stage for most of their existence, eventually dominating over 90% of the market for flip flops
- Maturity: maturity only came in the ’90s, with new product design, aimed at a different audience, and great marketing investment, especially with the now-classic TV ads that were fun and always starred famous actors
- Decline: up to this moment, there are no signs that Havaianas flip-flops may go through this stage in the short term
The Product Life Cycle of Coca Cola

- Development: very little is known about the development of Coca-Cola and how they created the mysterious formula
- Introduction: by 1886, the year of its foundation, the brand already seemed to have the right project
- Growth: less than ten years after its launch, Coca-Cola was already consumed in all the U.S. states
- Maturity: it’s impossible to say exactly when the brand reached maturity, but it’s safe to say that it has spent most of its history until now in this stage
- Decline: since 2012, the net operating revenue of Coca-Cola has fluctuated towards decreasing; while a small decrease is within what’s expected for the maturity stage, investments in marketing and new products must continue
Product Life Cycle Vs. BCG Matrix
A product is born, grows, declines, and dies.
Isn’t this model the same as that of the BCG Matrix?
If you thought of that, you were very astute.
The BCG Matrix is another amazing management tool, created by the Boston Consulting Group (the model is named after their initials).
The BCG Matrix is very similar to the Product Life Cycle, though there are some differences.
First, there are four instead of five stages: Question Mark, Star, Cash Cow, and Dog.
Second: these curious names relate to specific characteristics of the stage in which the product is, not necessarily analyzing the entire life cycle.
Are you confused? I’ll explain.
Take a look at the table below:
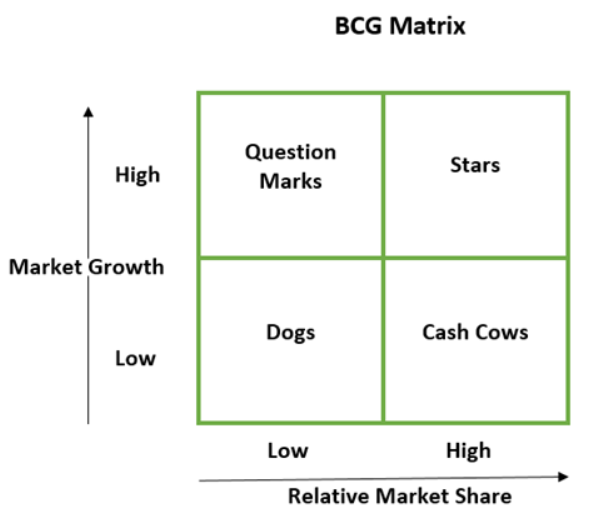
Question marks are new products that don’t have a market yet but have great potential for growth.
Stars, as the name indicates, are at the top: they generate good revenue.
Cash cows are the future of stars: their performance has peaked, but their decline is expected.
And dogs are a problem: products at the end of the line, that no longer sell well and are unlikely to recover their space.
In general, question marks and stars demand marketing investment, cash cows no longer need investment and dogs will not recover even with investment.
Product Life Cycle Conclusion
By now you should understand the Product Life Cycle and the characteristics of each of its five stages. You also learned tips for creating an appropriate strategy for each of them, even if you’re a digital marketer and you aren’t selling physical goods.
If you need digital marketing help throughout any of the stages of Product Life Cycle model, let our agency know.
Now it’s time to dedicate yourself to reach maturity and extend it for as long as possible.
Speaking of which, in what stage is your main product? Leave a comment and share the article!


