
Technical SEO Audits: Tips For Successful Implementation
According to BrightEdge, 68 percent of all online experiences start with a search engine, and 53 percent of website traffic corgomes from organic search.
Yet, only 0.78 percent of these searchers click results on the second page of Google.
That means if you’re not showing up on the front page of the SERPs, you aren’t getting traffic.
It’s clear why SEO is a top priority for marketers. In fact, 61 percent say it’s their main focus when it comes to inbound marketing.
If you can get your client’s website to the top of user search, you’ll have a much easier time improving their ROI.
Of course, mastering SEO is no easy task.
There are so many things to consider, from on-page SEO to off-page SEO, copy, content, and even technical SEO.
A truly effective SEO strategy includes all of these strategies, plus regular optimization to ensure consistent returns.
This post dives deep into technical SEO and how you can use it to increase organic traffic, show up in search, and improve your overall site experience.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is an area of SEO that covers optimizations that improve search engine ranking by making your site easier for search engines to crawl. For example, improving site load time, checking robot.txt files, and making redirects work properly.
Essentially, it’s the process of ensuring your website can be seen, crawled, and ranked by search engines.
Search engines, such as Google, give preference to websites that meet their webmaster guidelines. The basic principles state your website content should be accurate, easy to access, and user-friendly.
If your website loads slowly, has an unresponsive design, or lacks a secure connection, your content will not meet these guidelines.
This is where technical SEO comes in, as it can help you improve the technical characteristics of your website to improve organic traffic.
Why Is Technical SEO Important?
Imagine you wrote the most amazing content in the world. It’s content that everyone should read.
People would pay buckets of money just to read it. Millions are eagerly waiting for the notification that you’ve posted this new, incredible content.
Then, the day finally comes, and the notification goes out. Customers excitedly click the link to read your article.
Then, it takes over 10 seconds for your web page to load. Readers are annoyed and they don’t want to wait.
For every second that it takes for your web page to load, you’re losing readers and increasing your bounce rate.
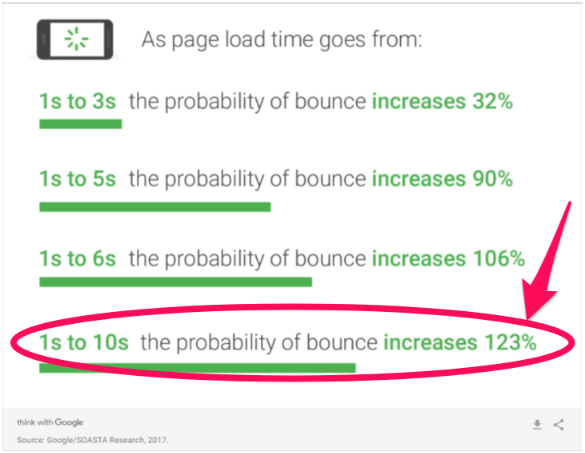
It doesn’t matter how great that piece of content is—your site isn’t functioning well, and you’re losing precious traffic.
That’s just one example of why technical SEO is so critical.
Without it, Google and other search engines are incapable of finding, crawling, and indexing your site.
If search engines can’t access your site, you can’t rank and you become one of the 90.63 percent of websites that get no organic search traffic from Google. Yikes.
Even if your site can be found, user experience issues, like page load times and confusing navigation, can still negatively impact SEO.
Other issues like mobile optimizations, duplicate content, and site security can cause search engines to rank your site lower.
Elements of Technical SEO
While crawling and indexing are important factors in SEO, there are many more aspects to consider when performing a technical SEO audit. These include:
- mobile optimization
- page load speed
- link health
- duplicate content
- schemas
- crawl errors
- image issues
- site security
- URL structure
- 404 pages
- 301 redirects
- canonical tags
- XML sitemaps
- site architecture
At a minimum, a technically sound website should be secure, quick to load, easy to crawl, have clear and actionable navigation, and not contain any duplicate links or content.
It should also have systems in place to engage users even if they do hit a dead end, such as content created for 404 errors and 301 redirect pages.
Finally, a site should have structured data to help search engines understand the content. This can come in the form of schema graphs and XML sitemaps.
When conducting a technical SEO audit, be wary of over-optimizing your website. Too many improvements can work against your best intentions and actually damage your SEO rankings.
What Is an SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is the process of evaluating your website to see how well it is performing on search engines.
SEO audits are a great way to create actionable plans to outperform your competitors, identify opportunities within your website, find and fix exit points, and create better customer experiences.
You should perform technical SEO audits, on-page SEO audits, and off-page SEO audits regularly.
As you go through your audit, you’ll find places where you can improve or optimize your website performance to improve performance and keep site visitors happy.
You may not be able to fix every error at once, but you can figure out what’s going wrong and make a plan to fix it.
What Are the Key Elements of a Technical SEO Audit?
There are three key factors to look at during an SEO audit:
- back-end factors, such as hosting and indexing
- front-end factors, such as content, keywords, and metadata
- link quality and outside references
Sometimes, you won’t have the time to address each pain point. So, when deciding which audit insights are worth taking action on, use the 80/20 rule.
The most important part of your site’s SEO is the part that your incoming traffic actually sees.
That’s all washed away if your site isn’t mobile-friendly, though.
With the introduction of the mobile-first index, you need to make sure you understand how your site performs on mobile to ensure proper placement on SERPs.
What does the mobile-first index mean?
Due to 52.2 percent of global web traffic coming through mobile, Google has adjusted its algorithm to crawl the mobile version of websites.
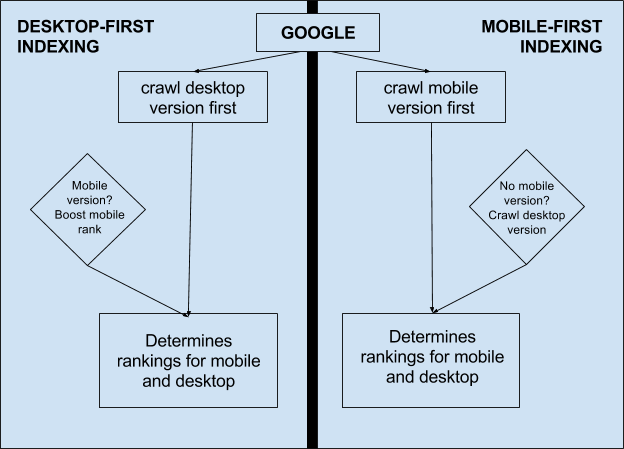
It boils down to this—if your site doesn’t perform well on mobile devices, you are not just losing traffic; your site also looks bad to Google. That can result in lower rankings, and even less traffic.
How to Perform a Technical SEO Audit
SEO guidelines are constantly changing. Every time a major search engine significantly updates its algorithm, SEO has to adapt.
The good news is the frequency of changes in technical SEO tends to be lower.
After all, it’s not like search engines or readers will suddenly decide they’re okay with slower speeds.
If anything, you will see the average acceptable speed continue to drop. Your site simply has to be faster if you want to keep up with SEO demands.
Your website has to be mobile-friendly. This is only going to become more important over time, too.
It has to work without errors, duplicate content, and poor images.
Search engines also have to be able to crawl it successfully.
These things are all crucial to your success on search engines and site visitors. If you want to prioritize your SEO efforts, make sure you tackle the technical aspects first.
1. Crawl Your Website
The most important part of the SEO audit is the crawl.
Before you do anything else, start a crawl of your website. You can use Ubersuggest to make it a simple process. Here’s how you do it:
- Step 1: Enter your URL and click “Search.”
- Step 2: Click “Site Audit” in the left sidebar.
- Step 3: Run the scan. Upon completion, you’ll see this:
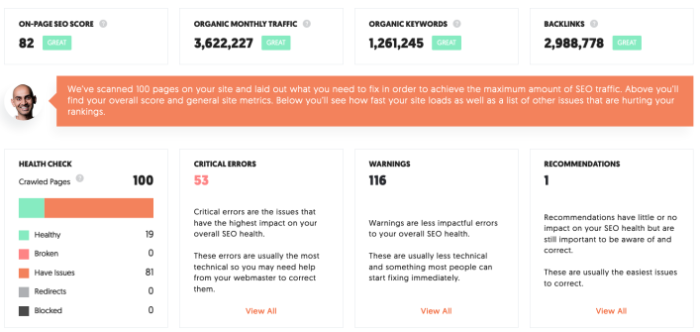
Crawling is useful for identifying problems such as duplicate content, low word count, unlinked pagination pages, and excess redirects. Ubersuggest will even rank issues in order of importance, so you can focus on what matters most.
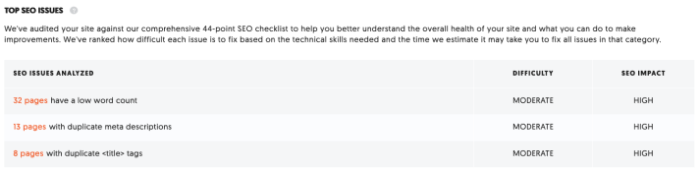
If you find anything here, click on it for more information and advice on how to fix it. For example, our website has 32 pages with a low word count.
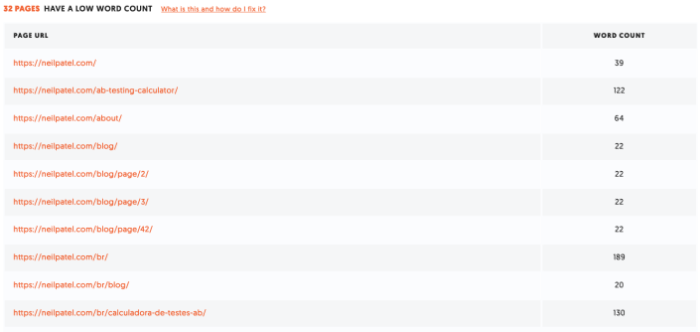
You can then review these pages to determine if you need to add more content.
What does this all mean?
In short, it gives you a glimpse into how the Googlebot is crawling your site.
If you don’t use Ubersuggest for your technical SEO audit, you can also search your site manually. We’ll explain that below.
2. Perform a Manual Google Search
A few Google searches can tell you approximately how well your website is ranking. This will help you figure out where to start your technical SEO audit.
How many of your pages appear in relevant search results?
Does your site appear first when you search for it by name?
Overall, where does your site appear in the results?
To figure out which pages are actually being crawled, you can use a “site:rootdomain” search to see what shows up.
Here’s what this looks like in action:
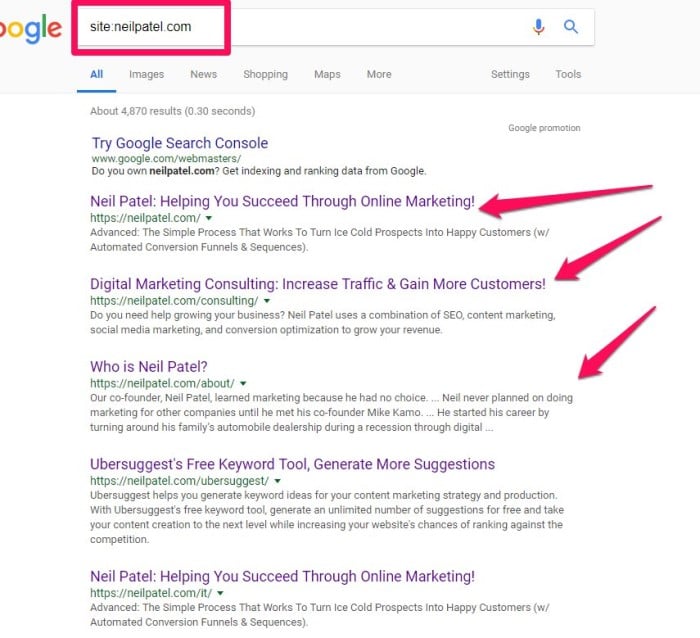
Missing pages don’t automatically mean that your site is un-crawlable, but it’s useful to understand what’s happening behind the scenes.
Your website doesn’t need to be at the very top of your searches, either. By using the site search, it will show you only pages on your own site.
3. Make Sure Only One Version of Your Site Is Browseable
If your website has multiple “versions” of itself, you send search engines a mixed message about how to crawl your site.
Basically, the crawlers don’t know which one is the right one.
If search engines don’t even know how to show your site to prospective traffic, your site’s SEO ranking will be negatively impacted.
This could be a mobile and desktop version warring with each other, or a duplicate “https” version and a non-”https” version.
The impact of HTTP vs. HTTPS on a site’s SEO is debated in the SEO community. Some sites using AdSense saw a decrease in revenue after making the switch to HTTPS.
For example, Crunchify’s revenue decreased 10 percent after switching to an HTTPS site.
However, it seems that websites without SSL protection are being deprecated on Google SEO moving forward.
Google is even taking steps to make it more known which sites have SSL protection and which do not. Chrome is marking pages as “Not secure” to make it clearer.
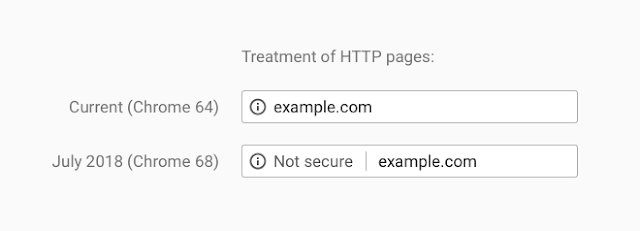
With this change from Google, it seems you will need to make sure that your website only uses “https.”
4. Conduct On-Page Technical SEO Checks
When evaluating your site and the results from your crawl, there are tons of things to check. Don’t get overwhelmed! Start by looking for duplicate pages, headers, and title tags.
If you’ve published a lot of content with similar themes, like me, some seemingly unrelated content will show up in your crawl.
That’s okay. You’re looking for duplicates of the same content.
You can use a tool like Copyscape to assess potential technical SEO problems arising from duplicate content.
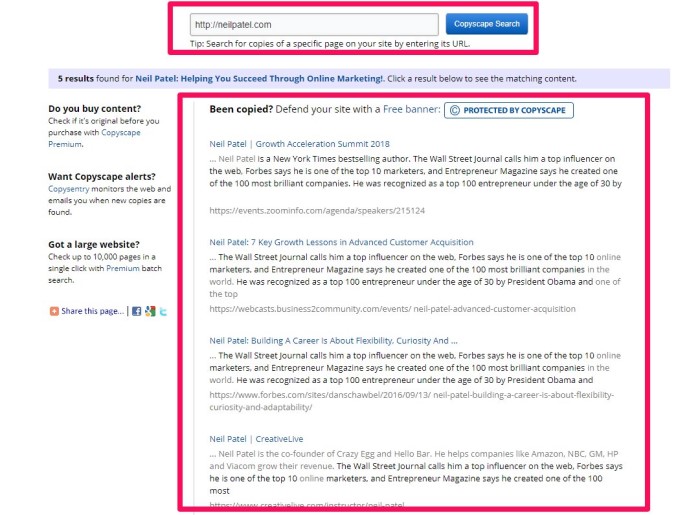
From there, closely examine a few key criteria that Google evaluates in their rankings.
Page Titles and Title Tags
A title tag is an HTML code that tells search engines the title of a page. This information will be displayed on SERPs.
It looks something like this:

You’ll want to make sure these are relevant to the content on your page. The content should also answer the questions your users are asking as fast as possible.
The optimal length for title tags is between 56-60 characters. You can use a pixel width checker to make sure that your title isn’t truncated.
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions don’t directly impact ranking; but they are still incredibly important because it’s the first thing a user sees in the SERPs.
Meta descriptions should be compelling, engaging, and give a taste of what the user will find on the page.
Google recently expanded the limit for descriptions from 160 to 320, which provides even more real estate to draw in a click.
Clear Hierarchy
You’ll want to make sure your content is organized, with a clear hierarchy on the page.
This makes it easy for Google to analyze your site and index it for search.
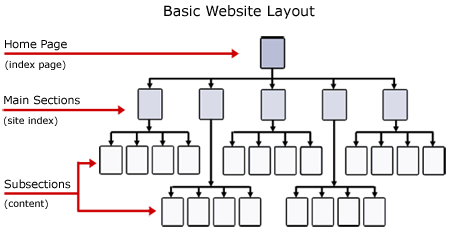
Essentially, you want to make sure the placement of pages makes sense—all your service pages should be under your “services” tab, for example. Make sure users don’t have to click through four levels of pages to find best-selling products. The goal is to make it easy for Google —and users—to find the information or products they are looking for.
Keyword Placement
Every page on your site should have a focus keyword included in the first 100 words.
For example, in this post about social proof, it’s included twice in the first 100 words.
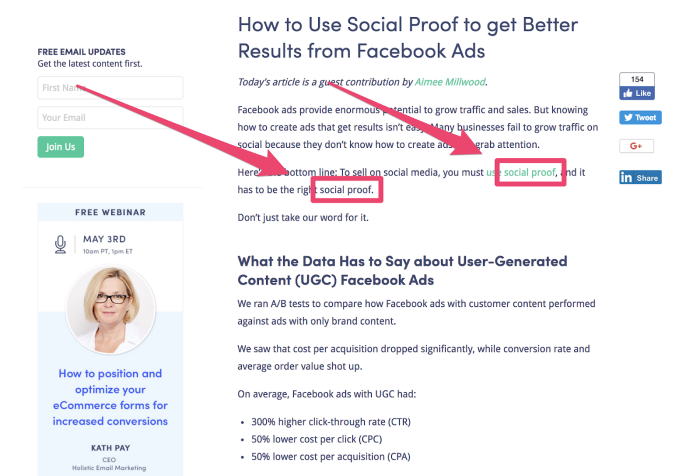
This helps Google understand what the post focuses on—but don’t stop there.
While keyword stuffing will penalize you, you should be strategic about keyword placement.
Include them, when possible:
- title
- alt tags
- URL
- subheadings (h2, h3, etc.)
- meta description
Overall, on-page SEO checks are incredibly important, but they are only one part of your overarching technical SEO strategy. There are also other SEO checks to consider.
5. Manage Your Internal and External Links
Sites with logical hierarchies have improved SEO rankings. That’s why it’s important to check your internal and external links—to make sure visitors can navigate your site intuitively.
Pages might be deleted or moved, which can result in broken links and annoyed site visitors.
Don’t worry; you don’t have to do this manually.
Integrity and Xenu Sleuth can help you identify your broken links on your site. (Note: Integrity only works for Mac.)
While both tools are straightforward to use, I’ll use Integrity as an example.
Once you download it, add your URL in the text bar at the top of the page and click “Go.”
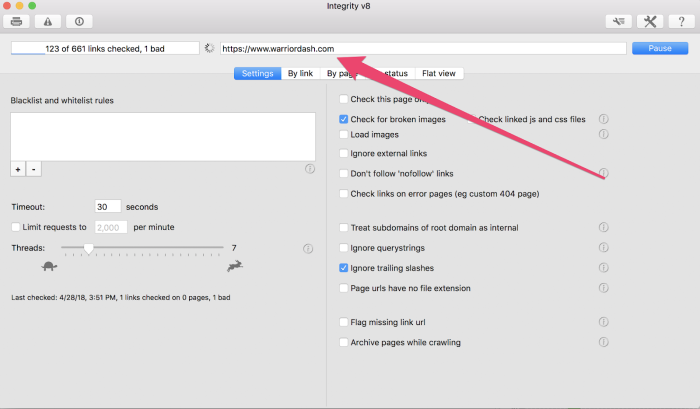
Then the tool will begin testing all the links found on your site and provide you with the results.
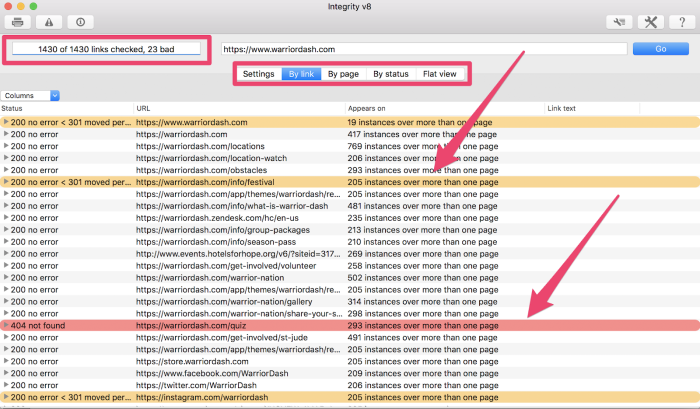
In the top-left corner, you see a snapshot of links and how many are bad.
Depending on the size of your site and how many links you have, you might consider viewing the results by link, page, status, or flat view to understand the results.
You’ll want to change any links marked in red with the “404 not found” label. These dead ends can negatively impact your technical SEO.
Google does score clicks from internal and external links differently, although both have their purpose in improving your SEO.
6. Check Your Site Speed
People are impatient. Google knows this.
Your customers don’t want to wait around. The longer your page takes to load, the higher the chance your customer will bounce.
You need to check your site speed, and Ubersuggest can help. Here’s how to get started:
- Step 1: Enter your URL and click “Search.”
- Step 2: Click “Site Audit” in the left sidebar.
- Step 3: Scroll down to “Site Speed.”
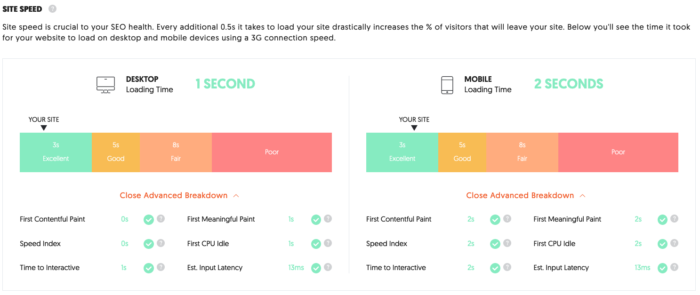
Ubersuggest displays loading time for both desktop and mobile devices. The results above show my site is in the “excellent” range for both.
In addition to loading time, it also tests:
- First Contentful Paint
- Speed Index
- Time to Interactive
- First Meaningful Paint
- First CPU Idle
- Est. Input Latency
Take action if your website scores less than excellent or good.
You might need to optimize your images, minify JavaScript, leverage browser caching, or more.
Ubersuggest will outline just what you need to do to improve site speed.
7. Leverage Your Analytics and Compare Site Metrics
This step determines whether your analytics service (e.g., Google Analytics, Kissmetrics, etc.) is reporting live metric data.
If it is, your code is installed correctly.
If not, your code is not installed correctly and needs to be fixed.
If you’re using Google Analytics, you want the tracker code to be placed above the header of each web page.
Once you have an analytics service up and running, compare the metric data to the results of your earlier “site:rootdomain” search.
The number of pages showing in your metric data should be comparatively similar to the number of pages from the “site:rootdomain” search.
If not, certain pages aren’t properly accepting crawl requests.
Check Your Bounce Rate
Google Analytics can be helpful when assessing your page’s bounce rate.
A high bounce rate means that people aren’t finding what they are looking for on your site. This means you might have to go back and make sure the content is optimized for your audience.
You can check your bounce rate by logging into your Google Analytics account and clicking on Audiences > Overview.
Compare Metrics With the MozBar
In addition, you can use Moz’s tool called The Mozbar to benchmark between pages.
The MozBar is a tool that provides various SEO details of any web page or search engine results page.
The toolbar adds an overlay to your browser and offers a number of features.
For example, MozBar can be used to highlight different types of links that you view.
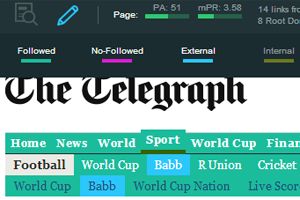
This is useful on its own, but it also lets you compare link metrics on or between pages.
It also comes with robust search tools to make your life easy.
With it, you can create custom searches by location, down to the city.
Page Authority is also supported by the MozBar.
It ranks each specific page from 1 to 100 in terms of how well it will rank on search engine results pages.
When doing a technical SEO audit, tools like this help you quickly take the temperature of your site’s relationship with search engines.
The less guesswork you have to do, the better quality your SEO audit will be.
8. Check Your Off-Site SEO and Perform a Backlink Audit
Backlinks are critical for SEO success.
This way, Google and other search engines will know that your page is particularly relevant and that other users will find it useful.
Remember that hyperlinks are not the only thing crawlers look for in off-site SEO.
Your site is also crawled for brand mentions. This is why it’s crucial to pay attention to what’s happening both on and off your site.
Perform Your Backlink Audit
Use a tool such as Ubersuggest to perform a backlink audit and assess the kind of backlinks pointing to your site. Here’s how:
- Step 1: Enter your URL and click “Search.”
- Step 2: Click “Backlinks” in the left sidebar.
- Step 3: Review the report.
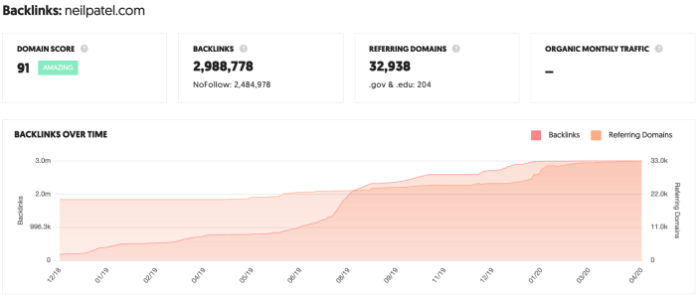
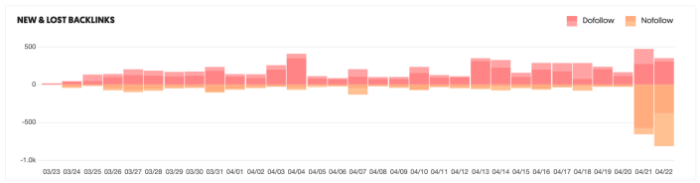
Backlink audits are helpful because:
- You can assess your current link profile and see how it is affecting your site.
- You can identify areas where you can focus on getting more high-value links.
- You can assess your competitors’ number of backlinks and work to outperform them.
Don’t just stop with your site’s backlink audit—you’ll also want to see what the competition is up to.
Analyze Competitor Keywords
Your competitors were busy upping their SEO capability while you were sleeping. Now, they rank higher for your most important search terms.
Ubersuggest can also help with this.
It allows you to see what keywords other sites are ranking for. It also shows what backlinks are going to those sites.
Basically, you want to explore your competitors’ backlinks and see how they compare to your own. Here’s how you do it:
- Step 1: Enter your competitor’s URL and click “Search.”
- Step 2: Click “Keywords” in the left sidebar.
- Step 3: Review the results.
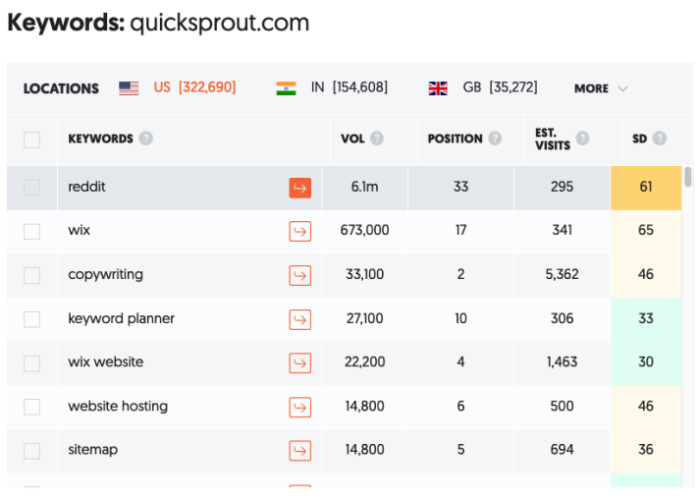
This provides a clear overview of what your competitor’s site is ranking for. In addition to a list of keywords, you can review:
- Volume: the average number of monthly searches for the keyword
- Position: position the URL is ranked in Google search
- Estimated Visits: estimated monthly traffic the webpage gets for the keyword
- SD: estimated competition in organic search, the higher the number, the more competitive the term is
Engage on Social Media
Social media is a conduit for consistent backlinks and engagement. You can use it to support your technical SEO efforts.
You want to figure out which additional social media platforms are frequented by your target audience.
Simply put, social media can improve your SEO by:
- Increasing the number of your backlinks. Those who discover your content on social media might be more likely to link to it.
- Increasing brand awareness, which can help with search queries including your brand’s name.
Social media is an opportunity to increase traffic and mentions beyond what people are searching for on a search engine.
Social media saturation is also simpler than putting together a link-building campaign.
Use the Facebook Sharing Debugger to see what your web content looks like when shared on Facebook.
This tool also allows you to check your Open Graph tags.
Technical SEO: Final Thoughts
There are three different aspects of SEO, and technical SEO is the most important of the three.
It won’t matter how amazing your on-page SEO is if you fail at technical SEO.
It also won’t matter how great you are at off-page SEO if you’re horrible at the technical stuff.
Don’t get overwhelmed by the idea of it being “technical” or complex. Start with the big, critical aspects discussed above and tackle them one problem at a time.
How have you found success with technical SEO on your site?
