Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=26845719
Points: 1
# Comments: 0
The Human Index
As the Dow comes close to a brand-new all-time high (the document close was 11,722.98), currently would certainly be a great time to pause from the monetary information discovered on your tvs, in your papers, (as well as of course) also on your computer systems.
A brand-new high is a vacant heading. I’m not contacting inform you that; you currently understand that. What you might not completely value is simply exactly how approximate an index the Dow Jones Industrial Average actually is.
Just regarding one of every 3 supplies in the Dow is entailed in what may be taken into consideration an old-line commercial (hefty production, removal, and so on) service. A great deal of the Dow parts are included in absolutely various companies such as customer items, wellness treatment, and also innovation.
Today, the level to which the ordinaries shares of the thirty firms relocate with each other might have even more to do with their shared category as “Dow” supplies than with the future potential customers of the hidden services.
On April 8, 2004 some modifications were made to the Dow. These weren’t the very first adjustments– and also they will not be the last. Such adjustments include in the approximate nature of the index, particularly in the temporary.
Typically, the modifications have actually been encouraged much more by that ought to go than with that ought to can be found in. Disposed of Dow parts can typically criticize a passing away sector for their leave. Often, a quickly diminishing market cap assisted.
The April 2004 modifications included 3 areas in the index and also 6 supplies.
Separations: AT&T (T), Eastman Kodak (EK), and also International Paper (IP).
Arrivals: Verizon (VZ), American International Group (AIG), and also Pfizer (PFE).
Please note that AT&T is currently back in the Dow. In November 2005, SBC Communications, which was itself birthed from the 1984 divestiture arrangement in between AT&T as well as the Justice Department, altered its name to AT&T after getting that firm.
None of these supplies has actually made out specifically well. Considering that the adjustments, they’ve all generally underperformed the S&P 500. With the exemption of Kodak (as well as Verizon for an extremely brief time), none of the supplies have actually taken care of to trade over the share cost they contended the moment of the reshuffle
Is this simply a coincidence?
Generally, reshuffling an index with human treatment is most likely to generate weird (and also unanticipated) coincidences.
The Dow is made up of a tiny number of business. Generally, they were prominent supplies prior to they got in; however, clearly, being included to the Dow just boosts capitalist passion in their ton of money.
The outcome? An extremely human index.
What you might not completely value is simply exactly how approximate an index the Dow Jones Industrial Average truly is.
Just regarding one of every 3 supplies in the Dow is included in what could be thought about an old-line commercial (hefty production, removal, and so on) service. A great deal of the Dow elements are included in completely various companies such as customer items, health and wellness treatment, as well as innovation. On April 8, 2004 some adjustments were made to the Dow. Normally, they were prominent supplies prior to they got in; however, undoubtedly, being included to the Dow just enhances capitalist passion in their lot of money.
Every Amazon seller knows how difficult it is to track and measure the impact of external advertising channels on sales. It doesn’t matter how you are driving clicks to your Amazon page; once consumers land on the website, it’s anyone’s guess what happens.
Thankfully, that’s not the case anymore. Amazon Attribution makes it possible for certain sellers to track what happens to every user they send to the platform. In this post, I’ll explain everything you need to know about Amazon Attribution, including:

Amazon Attribution is a new tool that promises to grow your Amazon business by improving experiences away from the Amazon platform.
Specifically, the tool provides analytics insight into how non-Amazon marketing channels like search, social media, display, PPC, and email marketing impact sales on Amazon. It can also track traffic sent to a different website that ultimately converts on Amazon.
Access to Amazon Attribution is available through either the platform’s self-service console or through tools that already integrate with the Amazon Advertising API.
Amazon Attribution is currently available for free, which is great news for e-commerce owners.
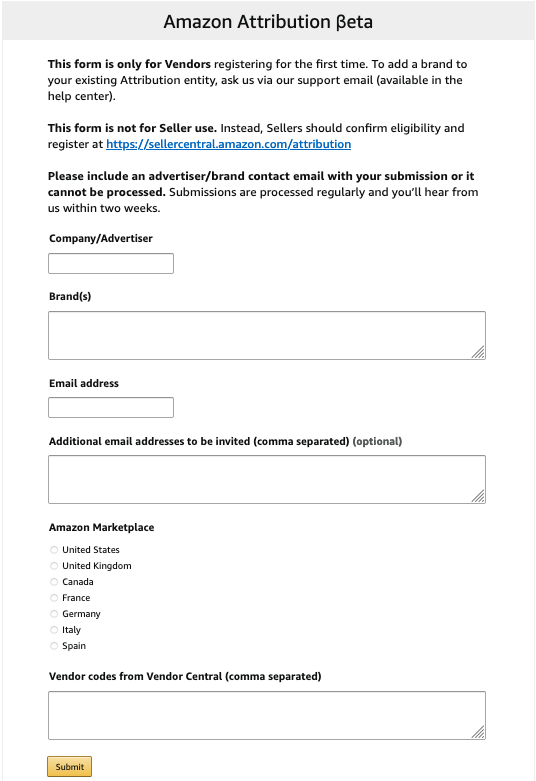
Amazon Attribution is currently only available to sellers enrolled in Amazon Brand Registry and Vendors in the U.S., Canada, the U.K., Germany, Spain, France, and Italy. That may change in the future, so keep your eyes peeled if you are in other locations.
Amazon Attribution lets you track a range of metrics that can impact e-commerce sales, including:
Amazon Attribution uses parameterized URLs—essentially a tracking URL. When users click on the link and go to your store, Amazon can track precisely what they do.
It’s a bit like a combination of Facebook’s Pixel and Google Analytics. Everything users do once they click on your ad is tracked, and you can see it all in an easy-to-use dashboard.
Amazon Attribution isn’t just a URL tracking tool. It has several key features marketers will want to leverage.
Amazon Attribution significantly increases the number of sales funnel data brands have access to. You’re not just limited to conversion data. Instead, Amazon lifts the curtain on how consumers interact with your product on their platform, providing metrics like clicks, detailed page views, and how many times customers add your product to their basket.
You can see campaign performance as and when it happens. Real-time reporting means marketers can optimize their marketing campaigns faster than ever before.
Because of the wealth of metrics Amazon Attributes provides, marketers can understand how the users they send to their store behave once they get there. Do they add the product to their basket as soon as they land on a page? Do they find a different product they prefer? Do they not buy anything at all? Amazon Attribution lets you answer all those questions and more.
Amazon Attribution lets marketers create different tags for every marketing channel. Facebook Ads, Google AdWords, blog posts, social media posts, it doesn’t matter. You can make hundreds of tags so you always get granular detail on the performance of every channel.
It’s not an overstatement to say Amazon Attribution could be a transformational tool for sellers and vendors. Before the tool was created, tracking off-Amazon marketing campaigns was an absolute nightmare.
There was simply no way to differentiate traffic from separate marketing channels. It was all dumped together.
Let’s say you made 500 sales, and you know that your own Amazon ads generated 100 of them. That leaves 400 sales that could have come from any marketing channel or even through an organic Amazon listing.
Do you see what a problem that is for marketers trying to find the best channel? There’s no way they can tell.
Amazon Attribution changes everything completely. Now marketers and brands will be able to see precisely where each sale comes from, and that comes with a bunch of benefits.
“Why use Amazon Attribution in the first place?” I hear some of you ask. There are several reasons eligible brands should start using Amazon Attribution immediately. Here’s my top three.
It’s not always easy to calculate the ROI of your non-Amazon marketing efforts, especially if you use multiple channels. Amazon Attribution allows sellers to see exactly which advertising efforts drive the most sales and provide the highest ROI. With a clear picture of what’s working and what’s not, store owners can focus on their most profitable channels.
Amazon Attribution lets you understand how users interact with your store and the broader Amazon ecosystem. If traffic from one demographic converts better than others, you can optimize your existing campaigns to drive more users that do convert and fewer of those that don’t.
Some sellers may find the concept of sending external traffic to Amazon strange, but it’s becoming increasingly important. Amazon is becoming increasingly dominant in e-commerce. At the same time, the price of sponsored ads on the platform continues to rise.
When you understand which marketing channels are most effective and how consumers interact with your products on Amazon, you can start to make real, data-backed decisions. The kind of decisions that will help you sell more on Amazon For some that could be investing more in a specific marketing channel. For others, it could be adjusting the price of their products.
What’s more, new sellers are signing up to Amazon every day. Oberlo recently reported that a million new sellers are joining Amazon every year. With so much competition, external traffic can be a vital lifeline to help sellers survive.
External traffic helps you sidestep the competition for listings on Amazon and drive traffic directly to your storefront. There’s no need to pay for sponsored ads on Amazon when you drive traffic directly to your products.
External traffic can seriously increase the number of sales your store makes. This can have a huge impact on your overall sales. Sales velocity is one of the ranking factors Amazon uses in its A9 algorithm, so the more sales you’re making, the higher your products will rank in the future.
The insights from Amazon Attribution can help you learn more about your customers than ever before. You may find that one product doesn’t convert as well as you thought it did, for instance. Or that customers prefer one product over another.
You won’t just be improving your Amazon store’s performance, either. These kinds of insights can improve your business outside of the Amazon platform, too.
The first step to getting started with Amazon Attribution is filling out a signup form and logging in to your account.
Once your account has been approved and set up, you can start matching products to the campaigns you’re tracking:
Amazon Attribution is an incredible tool, but unfortunately, it’s not available to everyone who sells on the platform. Luckily, there are several alternatives you can use instead.
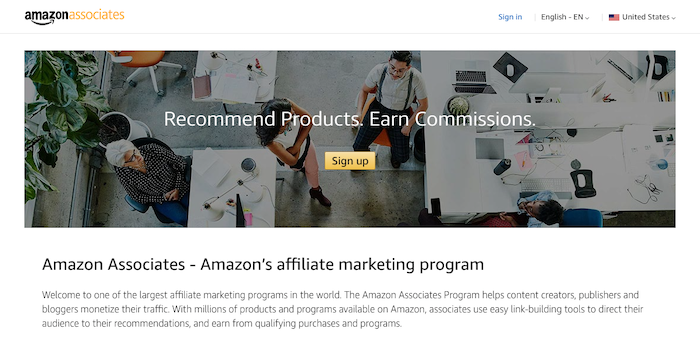
Amazon Associates tracking links were the most popular way to track external traffic to the store platform before Amazon Attribution. With Associates tracking links, you get paid a commission every time a customer converts.
Unfortunately, this tracking solution is nowhere near as in-depth as Amazon Attribution. You’ll only be able to see which items users bought, not their behavior on the site before conversion. Plus, Amazon Associates only get one tag. That means it can be hard to differentiate between traffic sources.

Pixelfy.me is a URL shortener and tracker built specifically for Amazon sellers. You can create and track every kind of Amazon link, including Supreme, Brand, Canonical, Store Front, Add-to-Cart URLs, and many more.
Pixelfy.me can track almost everything apart from conversions. While that’s not as comprehensive as Amazon Attribution, Pixelfy.me does let you pixel users to retarget them in the future.

The Amazon Super URL Tool is part of the AMZ Tracker suite of tools. It does not offer sellers more insight into the way users shop their store, but it can significantly improve the quality of inbound traffic and boost sales as a result.
The platform’s special URL shortener makes Amazon believe visitors have searched for specific keywords on Amazon instead of going directly to the listing. Amazon should rank your products higher for these keywords, as a result, which can lead to more sales.
Amazon Attribution is the best way to track how off-site traffic performs on the Amazon platform. If you run external marketing campaigns for your Amazon store and are serious about optimizing your Amazon store, then Amazon Attribution is a must.
Not only can you optimize your marketing campaigns, but you can also increase conversions, too.
Creating Attribution tags is easy. Just follow my advice above or contact my team if you want an Amazon marketing agency to do the work for you.
How many external marketing campaigns are you currently running to Amazon?
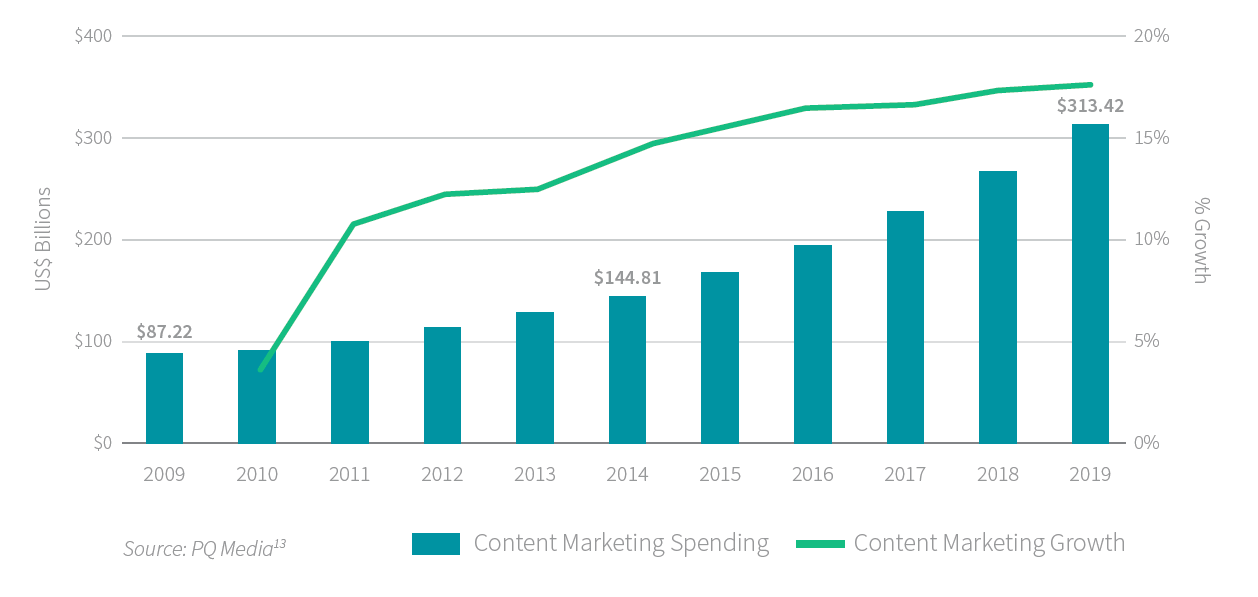
It doesn’t matter if you run a tiny mom-and-pop shop or a mega-billion dollar corporation; content marketing works.
Just look at the way the content marketing industry has exploded in recent years.
In this article, I’m not just going to sing the praises of content marketing. Instead, I’m going to take a deep dive into something that most people don’t talk about: a tiny slice of content marketing called H1 tags.
Truth be told, most SEOs, content marketers, web developers, and marketers know a little bit about H1s. That can be a problem though; we’re so used to hearing about H1s, using H1s, and talking about H1s, that we don’t stop and think about how to write them in a way that appeals to users and search engines.
You’re different though. You’re reading this article, and are going to learn the exact method for producing great H1s that will take your content marketing to the next level.
The H1 is an HTML tag that indicates a heading on a website.
Let me unpack that.

If you were to create an H1 in HTML, it would look like this:
<h1> Hi, My Name is Header One! </h1>
You can take a look at this yourself. Open up any web page (preferably a good quality blog) and follow these instructions.
First, make sure you’re on a web page.
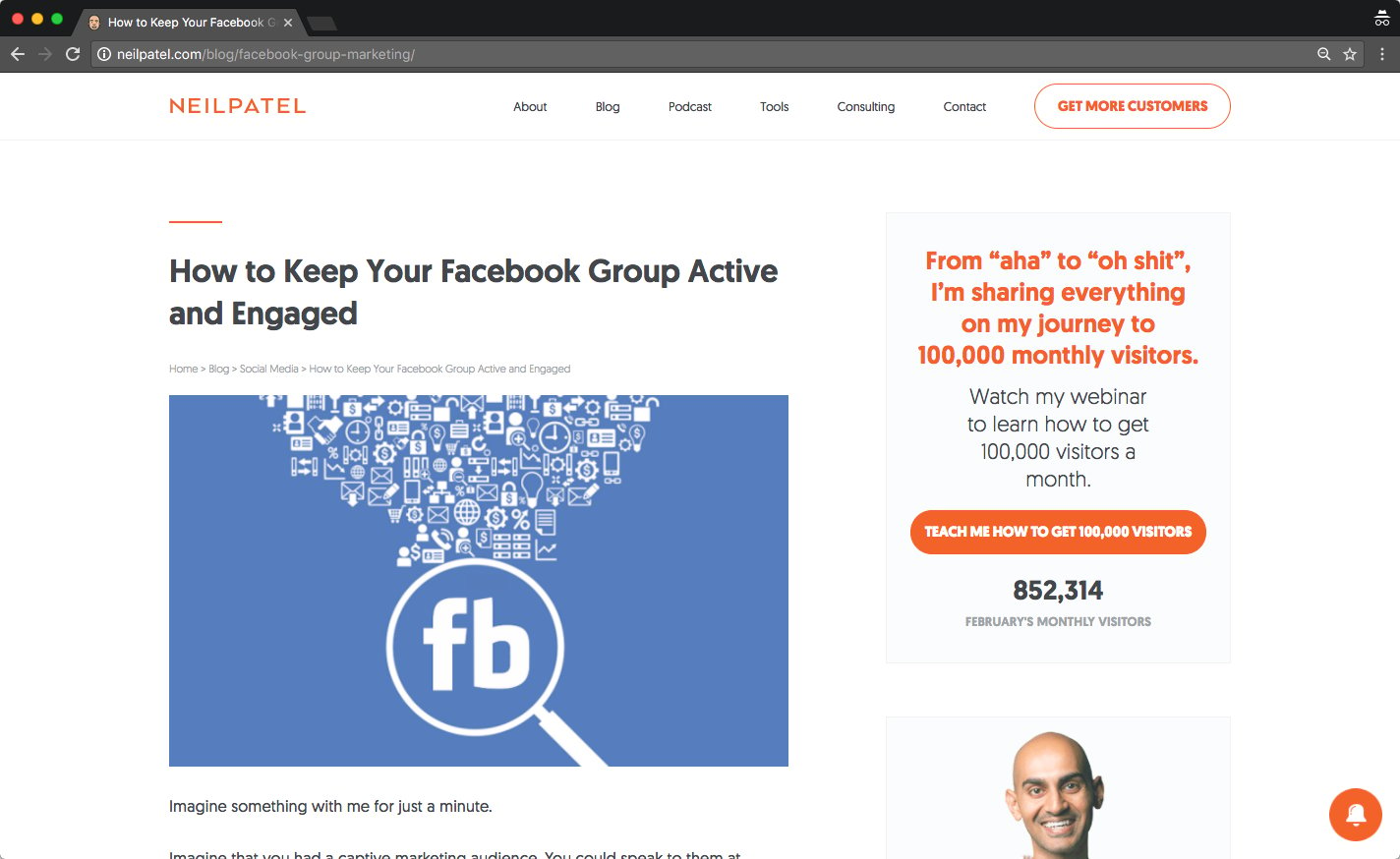
Next, view the source code.
To do this, I use a keyboard shortcut for Chrome (Mac): command + Option + u (do not press the plus sign, you just hold command, option, and u at the same time).
The commands you use to open source code will vary depending on the browser and processor you use.
You can also click View → Developer → View Source (in Chrome):
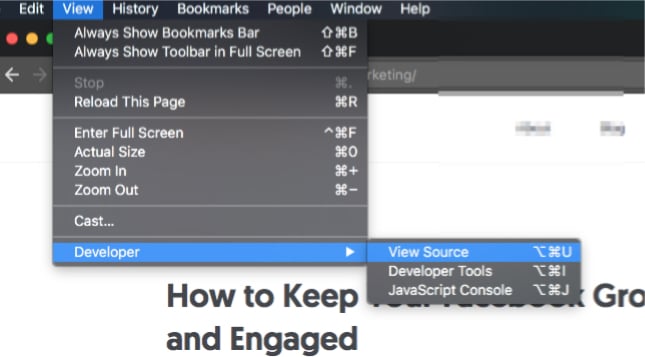
This is what you’ll see when you view the source code:
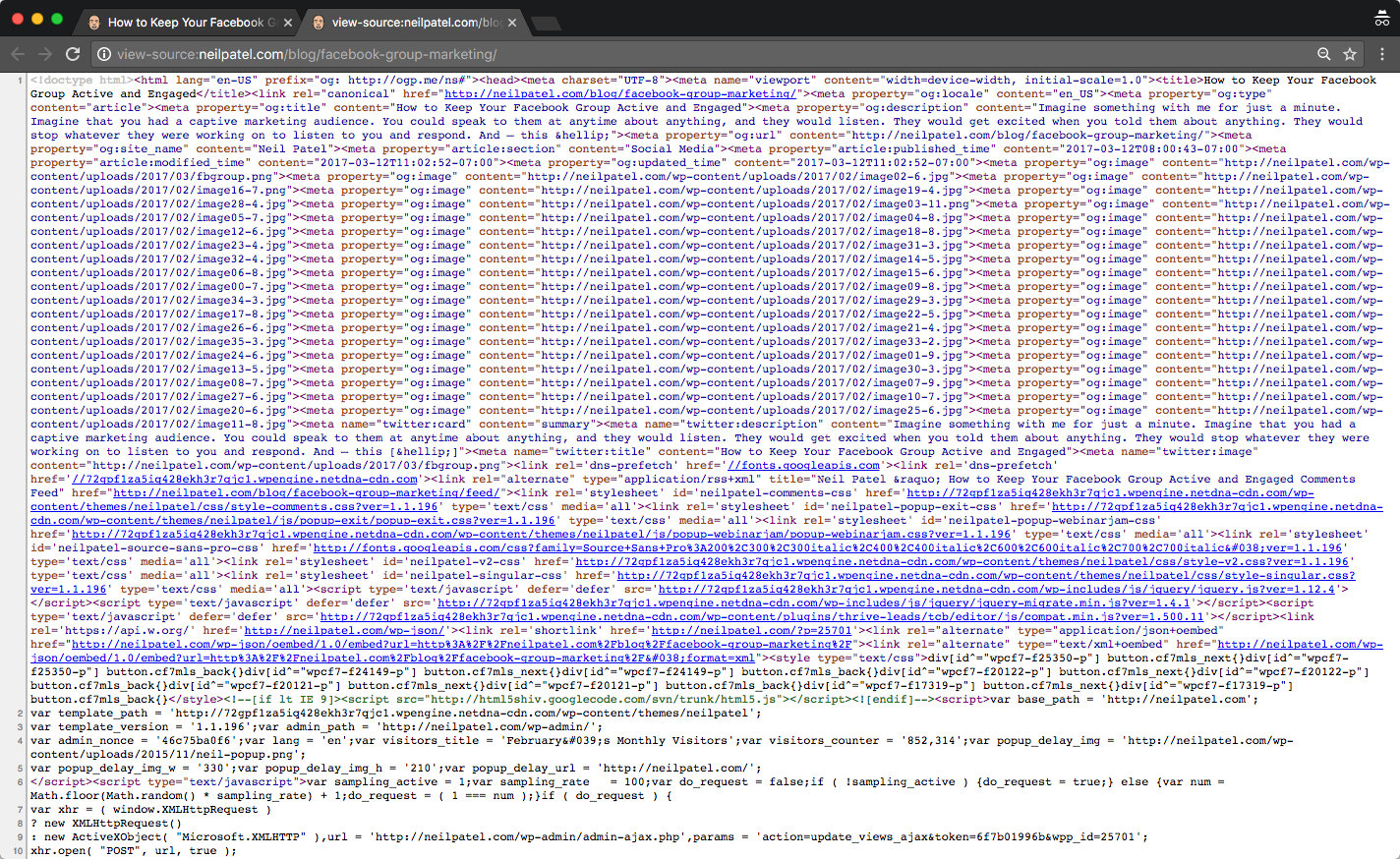
Next, search for the h1 tag.
Press CTRL + F to open the search feature on your browser. Again, I’m using Chrome, but most browsers use this function.
When I press CTRL + F, I see a small search bar in the upper-right corner of the browser window.
Type “h1.”
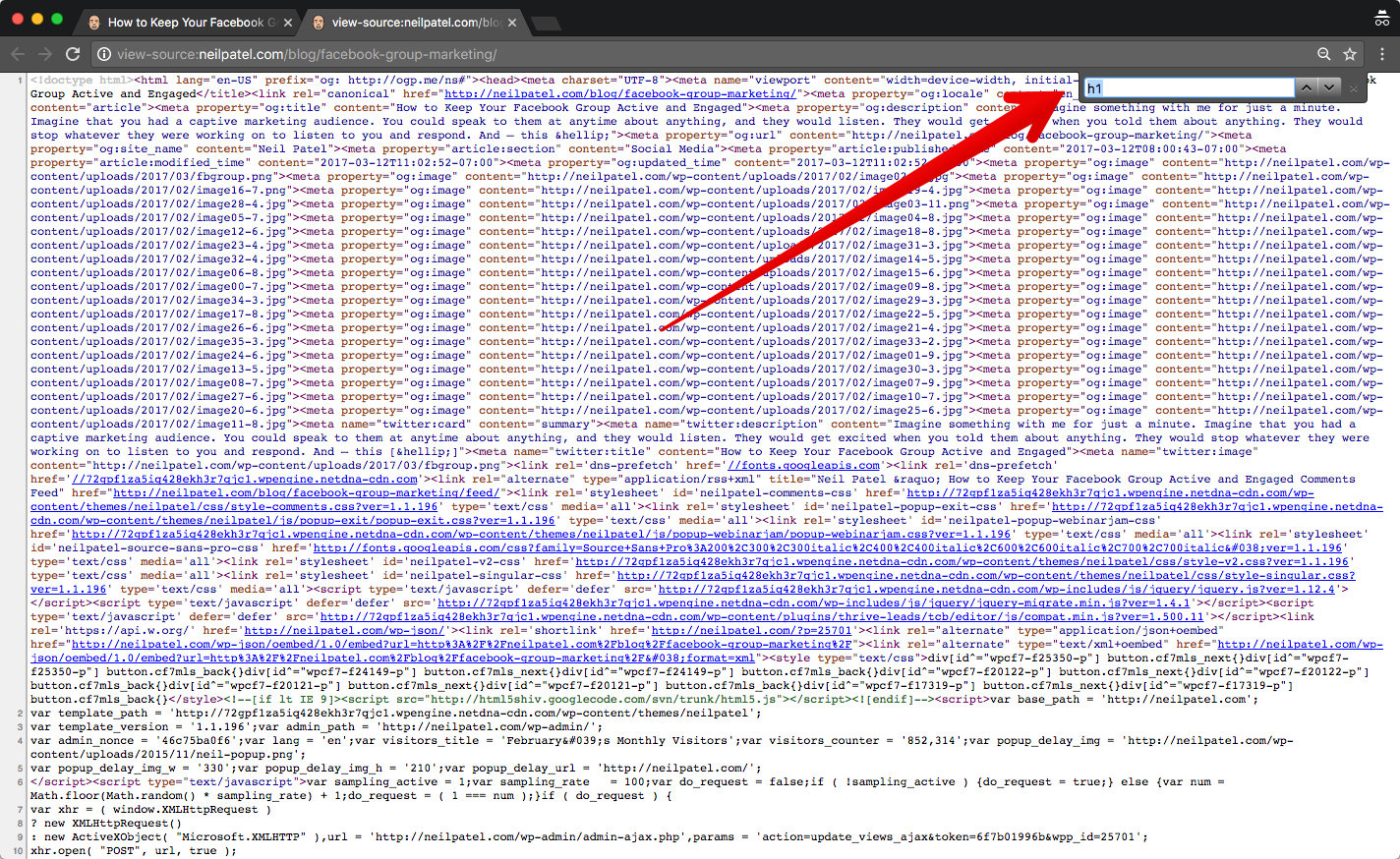
Then, press Enter.
Chrome highlights the h1 on this page.
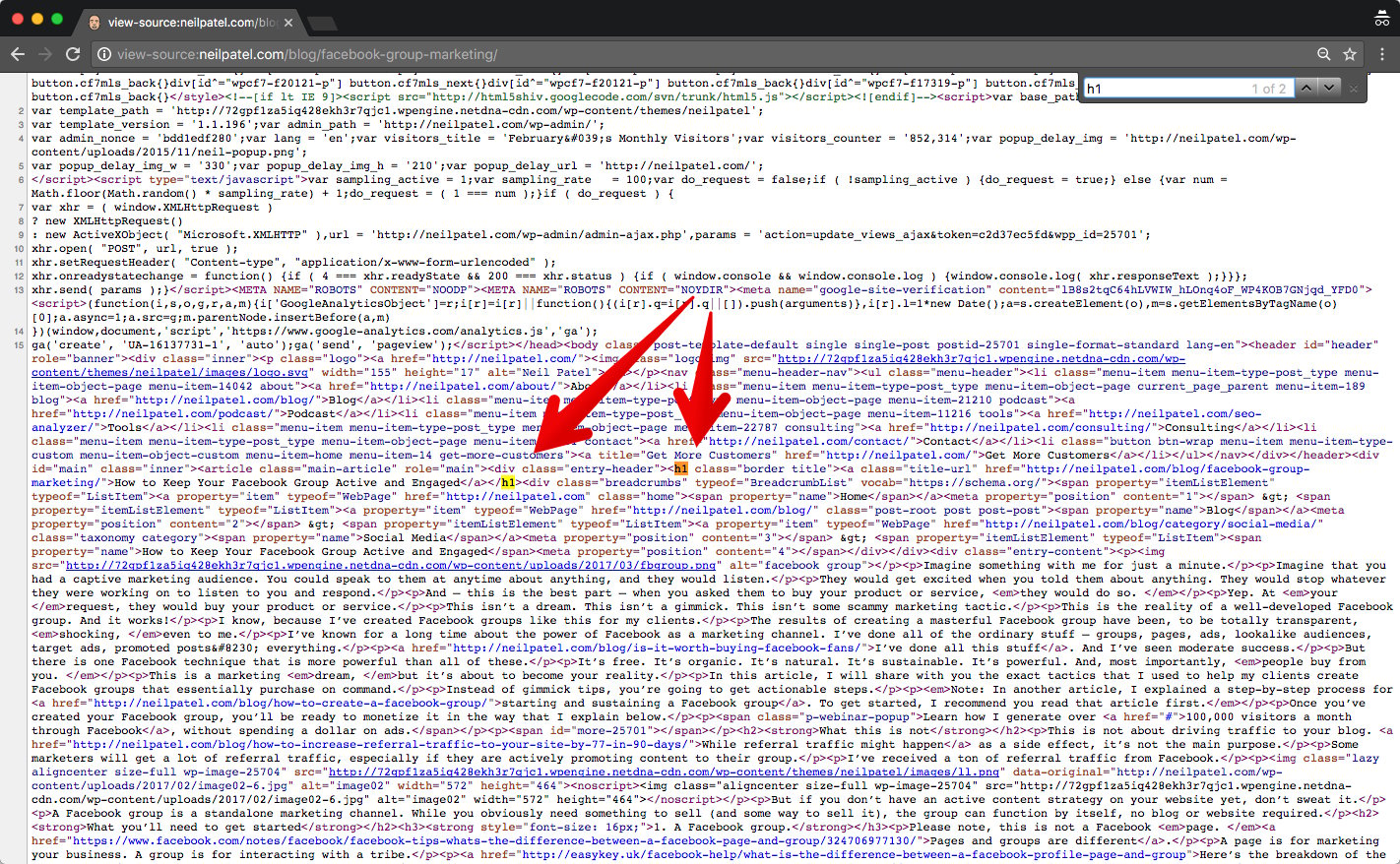
There’s a bit of intervening code between the start tag and the end tag, but the tag is there.
The copy within the h1 tag is “How to Keep Your Facebook Group Active and Engaged.”
That’s it. It seems pretty simple, but the h1 has a big impact, as you’ll find out in the next section.
First, I’ll tell you a story. A little while back, business was humming along as usual. I was doing my thing, running my blog, and writing my articles.
My blog traffic had been pretty good overall, but I decided to get another set of eyeballs on it to help identify improvements. One of these improvements was to update an H1 on one of my articles. Within three days, the page had 85% more organic traffic. Plus, it had gone from page 3 of the SERPs to page 1, position eight!
All because I changed the H1.
I’m not the only one who’s experienced such a dramatic change. In fact, my bump in search traffic is nothing compared to a local car parts store in Houston, TX, who changed their page titles and H1s. The result?
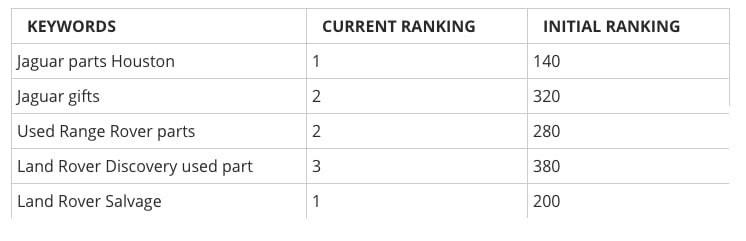
I don’t want to sound like a snake-oil salesman with a bunch of anecdotes, so let me give you the cold, hard facts about h1s and SEO.
H1s have always been a major ranking factor.
There have been plenty of trends in SEO that have come and gone, but H1s have never lost their significance.
In Moz’s most recent search ranking factors survey, title tags are listed as the second most important ranking factor. Although it’s not always the case, many use the same title tag. and H1.
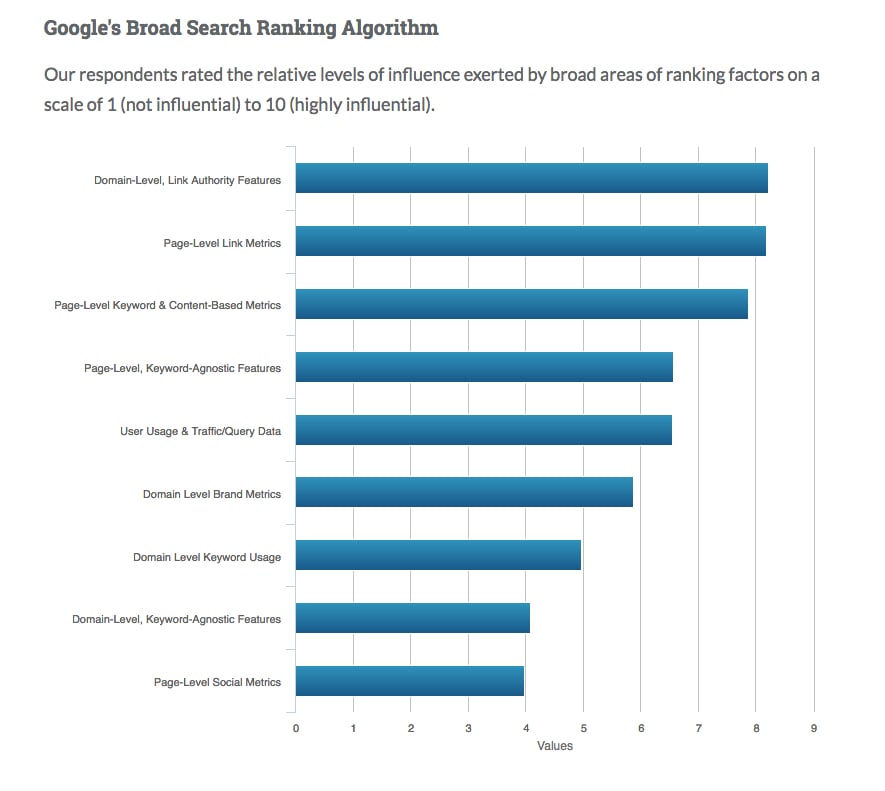
H1s are usually the most visually notable content on the page and are probably the most important SEO feature.
And at first, it might not seem like H1s are an “SEO” feature at all, because it’s more about the user than about the technical optimization of the page, right?
Right! That’s the direction that SEO has taken in recent years. SEO is more about user optimization than it is about search engine optimization.
Don’t skip over this idea of users noticing the H1. It matters.
H1s are one of the most potent on-page SEO and UX elements that you have in your arsenal.
Now, let’s figure out how to use them.
H1s aren’t a big secret. The fact is, just about anyone who knows anything about SEO or HTML uses them.
So why did I even write this article? It’s because most people use them incorrectly.
Until recently, even I didn’t realize just how wrong I had been when I was writing H1s. After turning the corner and making a discovery, my knowledge of H1s hit the roof, and my website traffic changed as a result.
Here are the rules of H1 creation.
Every page needs only one H1 tag. There is no reason to use more than a single H1 tag.
Why not? If one is good, wouldn’t two or sixteen be even better?
Search engines will crawl multiple H1s on a page, sure, but the logical priority of an H1 semantic tag means that you’re focusing your SEO efforts on one keyword phrase or sentence, as opposed to many.
The presence of more than one H1 won’t necessarily confuse the search engine, but it could dilute the SEO power of a single H1.
Google may also consider your page over-optimized if you use more than one H1, and may penalize you as a result.
At the most basic level, the H1 should describe what the content is all about.
If your H1 is too short, you’re wasting valuable space; if it’s too long, you’re diluting the power of the tag.
However, if you’re using the same H1 and title tag for a page, you should pay more attention. Best practices say titles should be between 40 to 60 characters so you can fit in the most keywords. However, when you start to reach the 50-60 keyword range, your click-through rate can start to decrease. As a result, try to stick to the 30-40 character range.
Your H1 should be the most important visual element on the page.
Why is this important?
Keep in mind that an H1 is a semantic element, not a visual element, and it’s important to keep this distinction. Web designers don’t need to add style elements by using semantic tags such as the H1, H2, etc.
However, in the real world, style and semantic elements do mix. Following design and development best practice mean the most significant semantic tags are also the most important visual elements.
Size matters in web design, and semantic tags matter in web development. Conjoining them in SEO makes sense.
For a good example of this formatting, check out the blog at Smart Passive Income. Pat Flynn’s H1 is definitely strong.
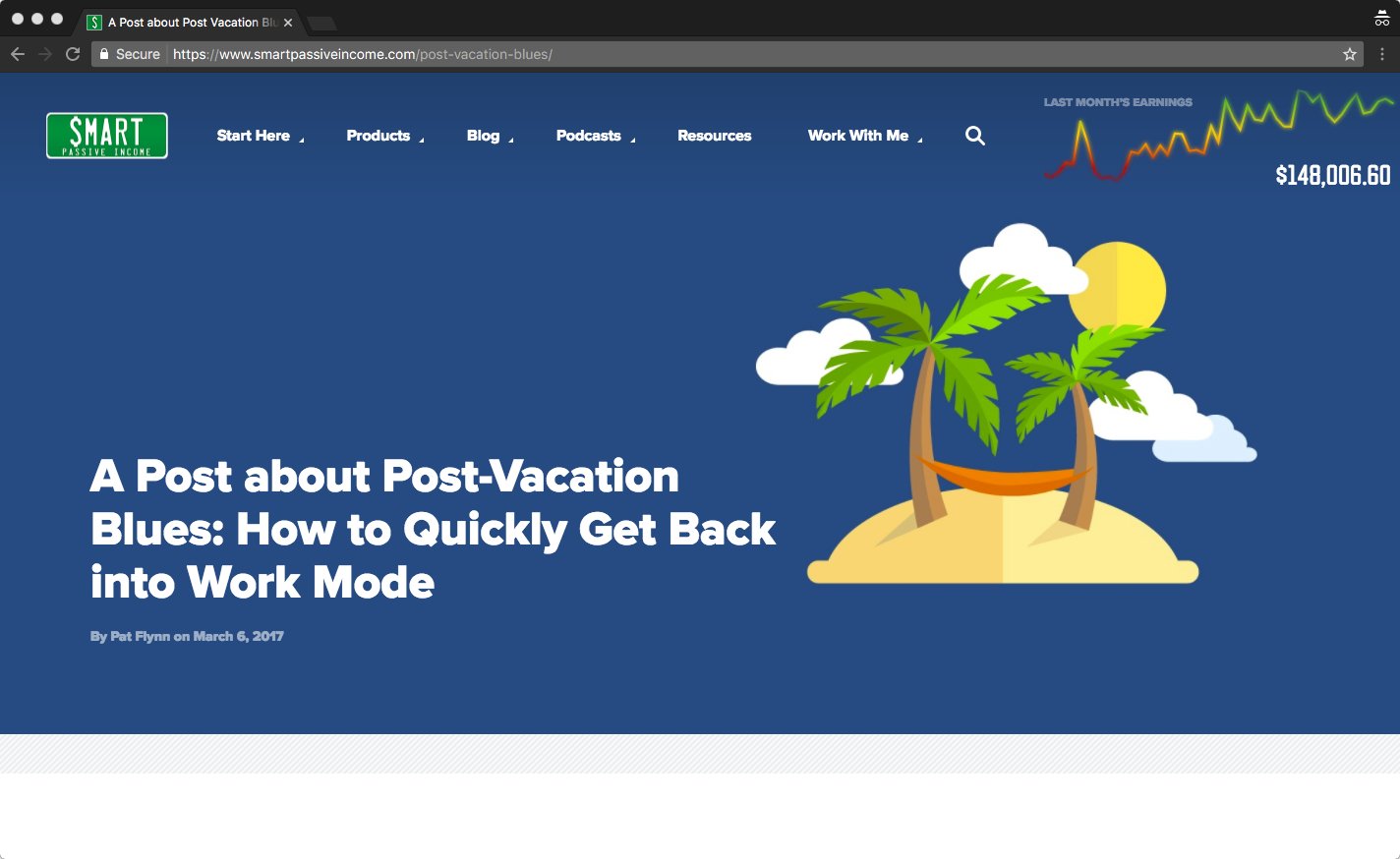
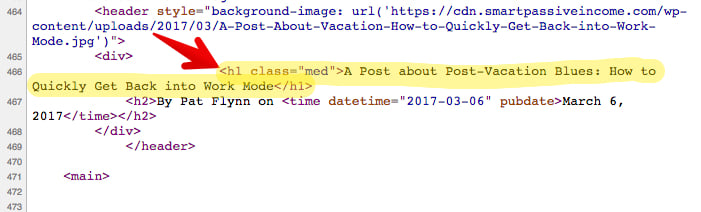
When I check out the source code, this is what I see:
Here’s another good example from Ramit Sethi.
Can you guess what his H1 is?
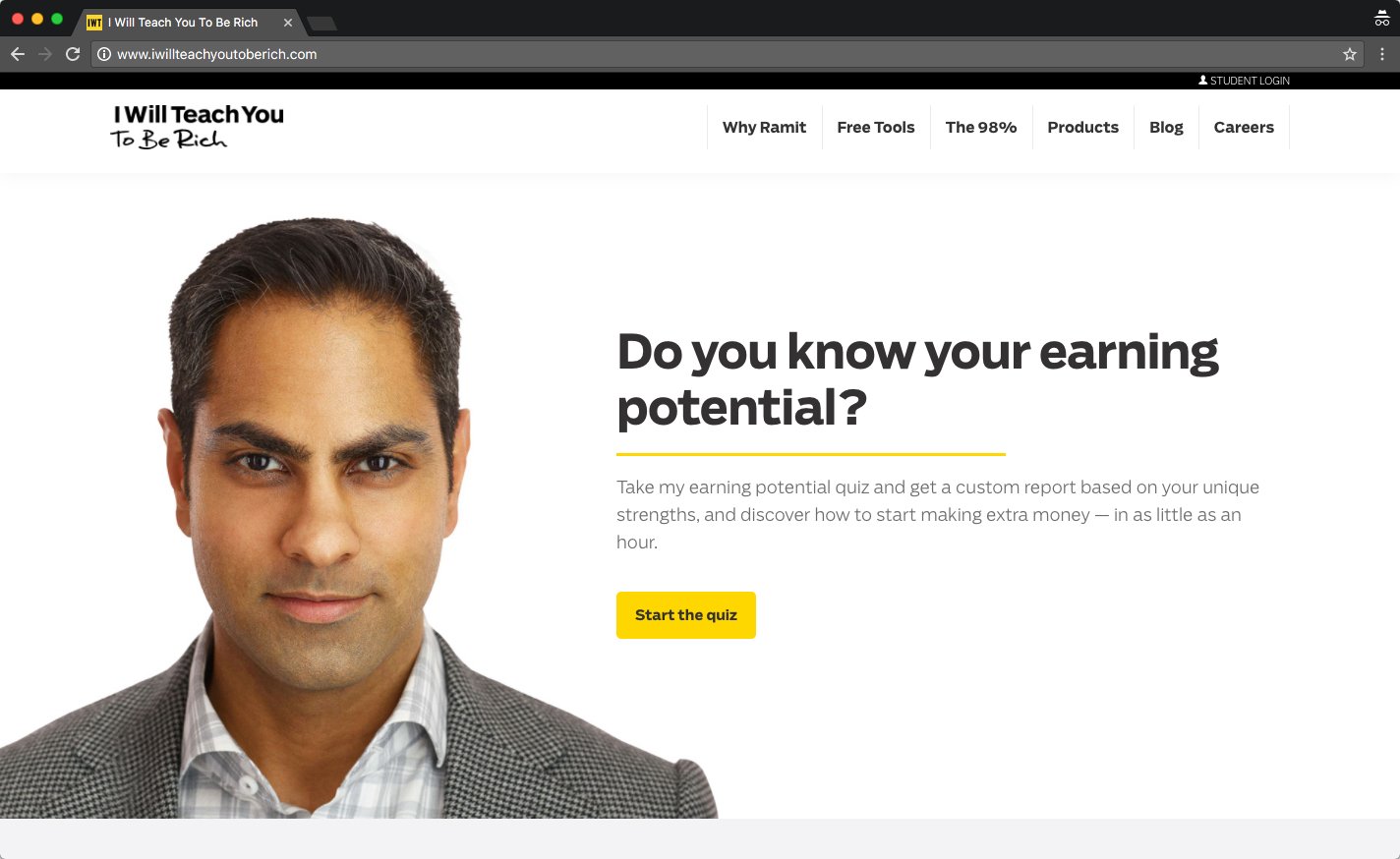
The H1 is “Do you know your earning potential.”
SEO changed massively over the past few years. The biggest change by far has been the influence of user experience (or UX) on SEO.
The best way to consider SEO and UX is with this Venn diagram (to access link, you must download a chrome extension).
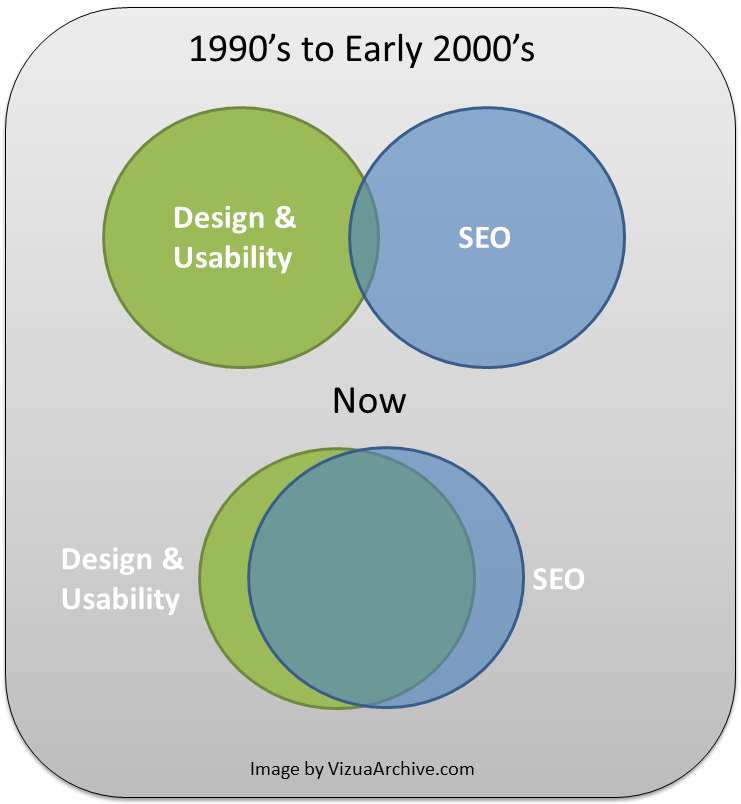
That diagram was published in 2012.
Nearly a decade later, the SEO circle would be a smaller circle within an even bigger Design & Usability circle.
Part of the reason for this is search engines have evolved to such a high degree they can intuit what users want, even as users are searching and browsing.
Keep in mind that due to machine learning, search engines are constantly changing. There are no longer massive SERP upsets due to algorithm shifts.
Instead, there is the continual nuanced adjustment of search ranking factors based on the search and browsing habits of the search engine’s millions of users. In other words, how users interact with your page has a lot to do with how your page will rank; and the H1 is one of the most important elements on your page that influences their interaction.
This is because it’s noticeable. It sends a message. It communicates a sentiment. It makes a promise.
Your H1 should speak to the user in an overt way. It should be formatted and placed carefully so your user understands that it is the title of the page, and explains what the page is about.
Believe it or not, some SEOs used to not recommend using keywords in your H1s. They thought it could be considered keyword stuffing, which Google penalized a long time ago.
Luckily, there’s nothing keyword-stuffing at all about using a keyword in an H1. On the contrary, Google wants you to use a keyword in the H1. It helps their crawlers better understand what your page is all about.
If you don’t use a strong keyword in your H1 tag, then Google can still find out what the page is about, index it appropriately, and give you a nice rank. Why leave out the opportunity to give Google all of the information it needs and wants right in your website source code, though?
It’s better to use a keyword; sometimes a long-tail keyword specifically.
Let me show you a clear example of how this works using a simple keyword, “bandit testing.”
Even though this keyword is not technically long tail, it works well for our purposes, because it’s clear, concise, noticeable, and easy to use in an H1 tag.
This is a page from the Crazy Egg blog.
The article is about bandit testing.
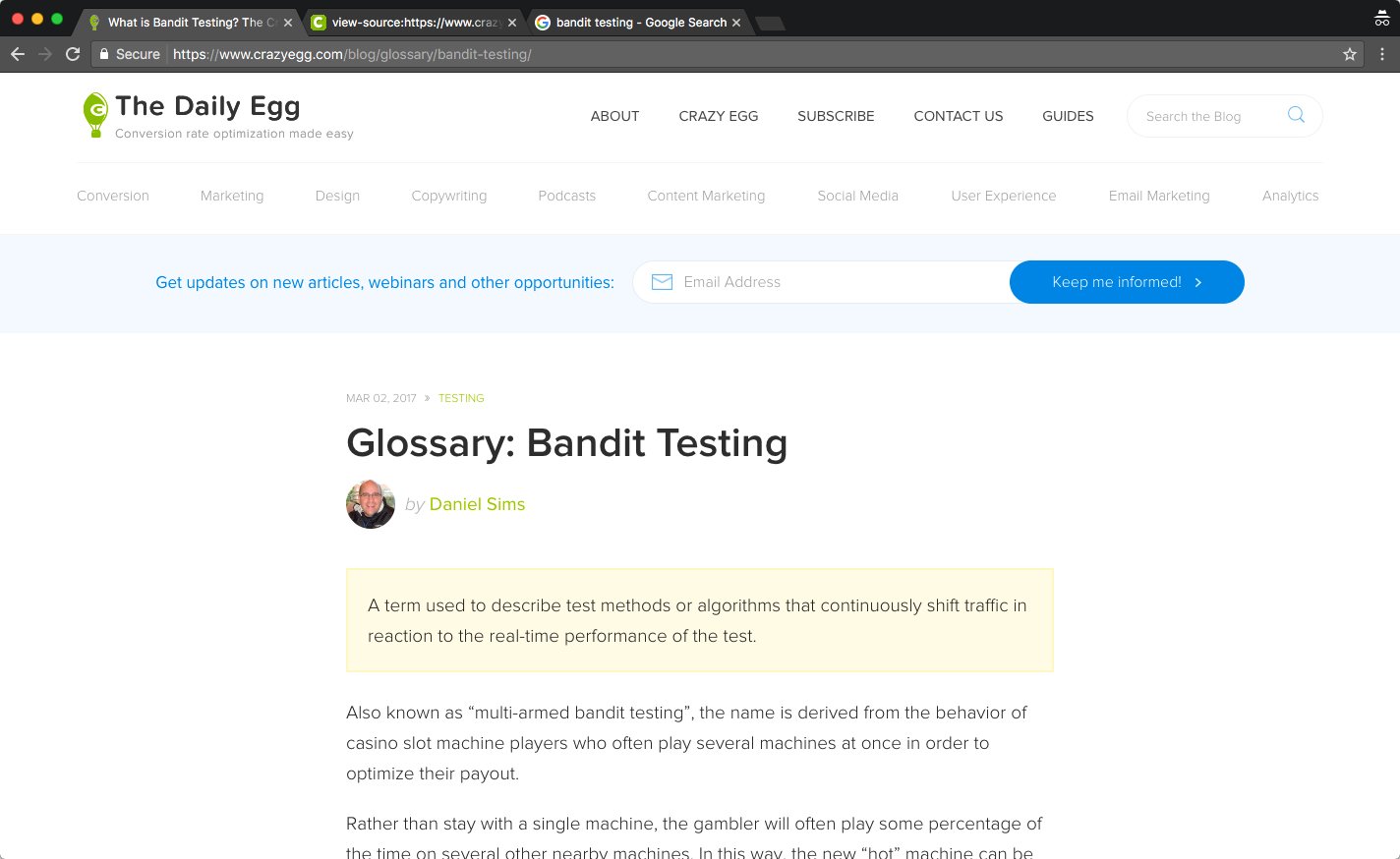
The most noticeable visual element on the page is “Glossary: Bandit Testing.” That’s also the h1.
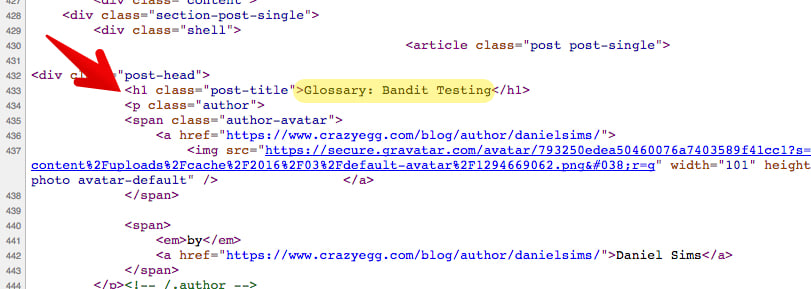
Here are the facts about this page:
Their rank at the time this page was originally published (it has subsequently been updated)? Google page 1, position five! That position was earned only two weeks after publishing the article.
This article takes a more long-tail approach. The keyword in this scenario is “Facebook Video Ad Hacks.”
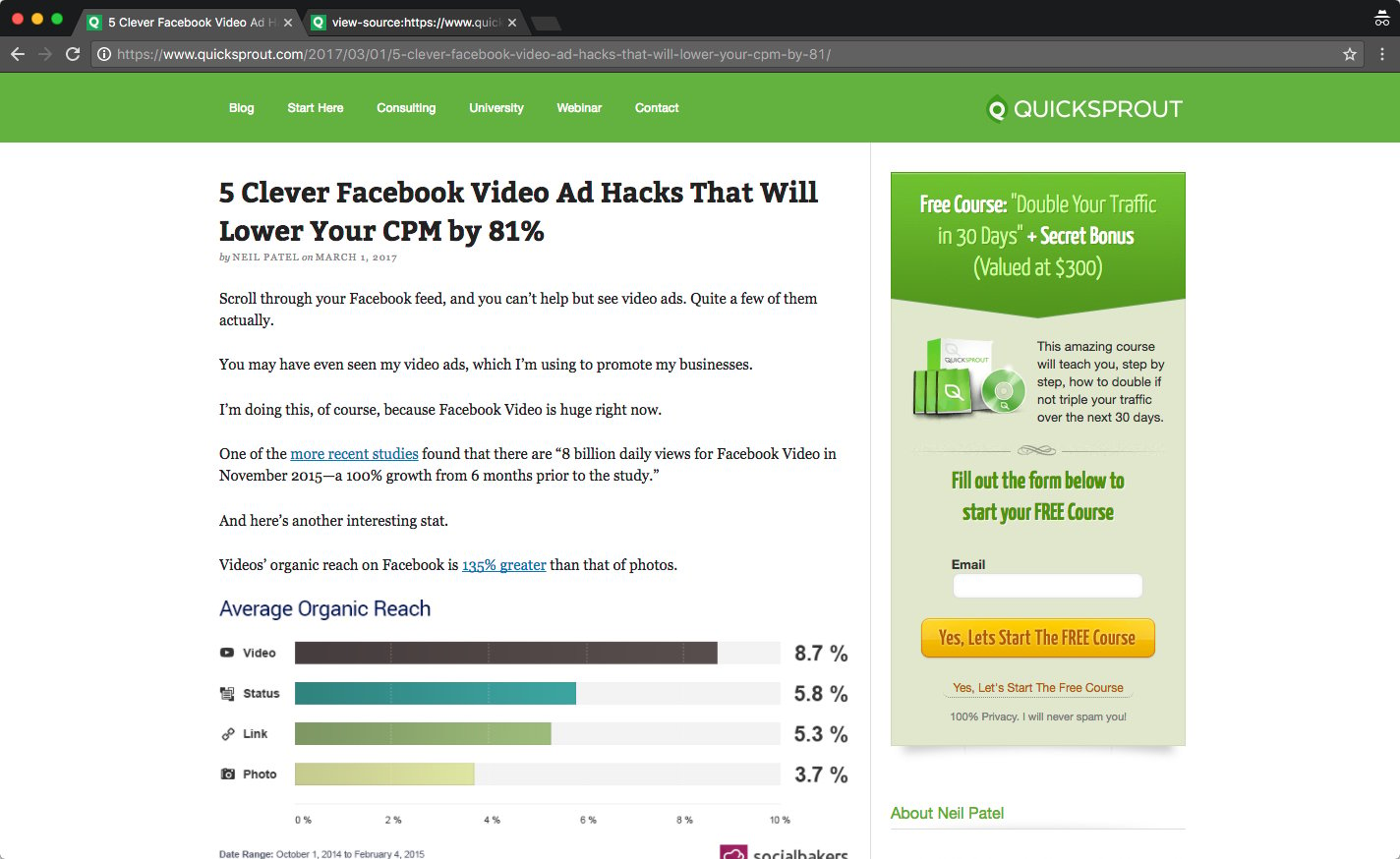
That keyword is included in the blog title, and it is also the H1 tag.
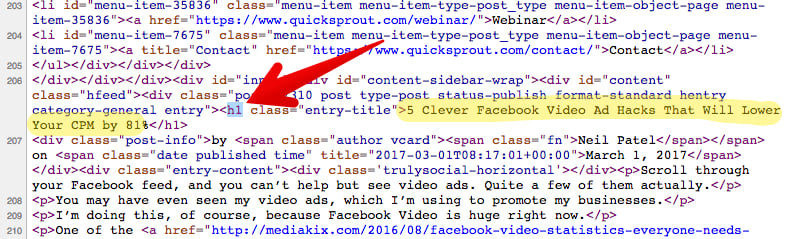
Just two weeks after publishing, the article was on page one, position 5 of Google.
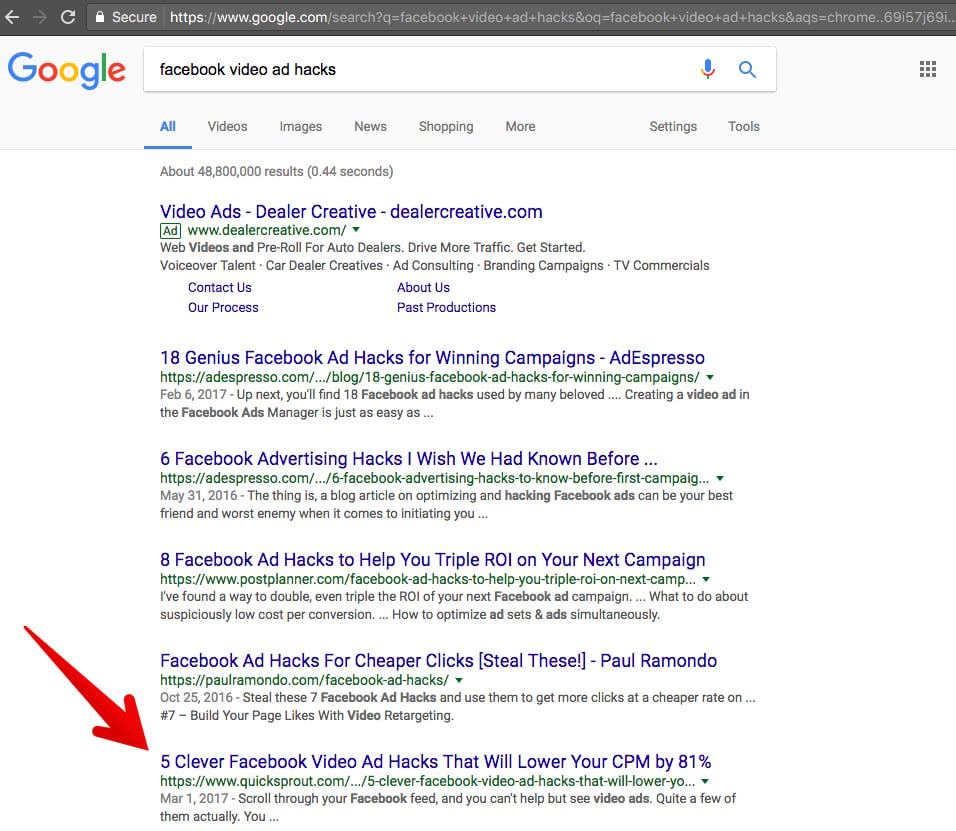
To summarize: yes, I’m recommending that you use a long-tail keyword in your H1 tag.
Follow a few simple rules though:
The phrase “user intent” seems to confuse some people, but it’s really quite simple.
Whenever you write a piece of content, you want to be asking questions like:
What does the user want when they open my article?
What’s their intent?
Your H1 should satisfy that intent.
If someone is googling “risky SEO tactics,” I can probably assume that they are looking for some quick search engine optimization techniques that will boost their rankings.
If I were to write an article on that topic (oh wait, I did!) then I want to answer their intent with my H1.
Here’s how the journey of intent works.
First, the user gets an idea. Then, they search Google for it.
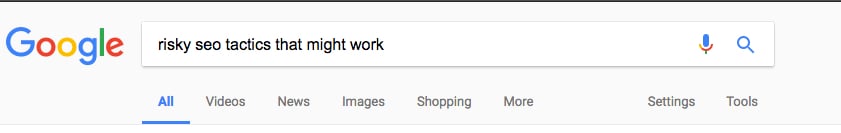
They see this promising result in the SERP.
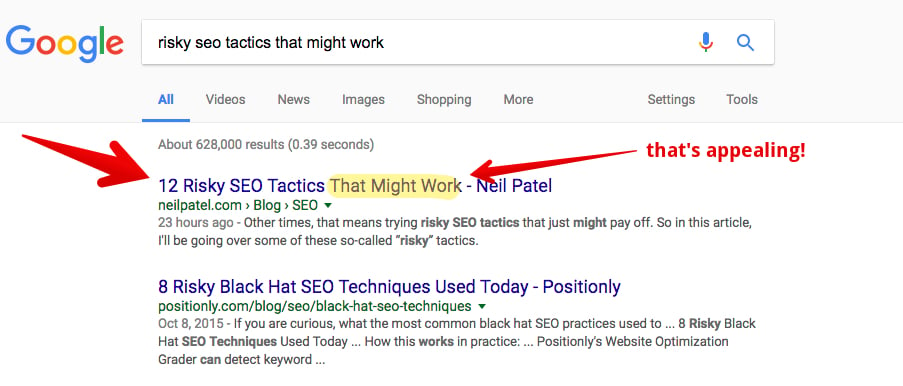
If they click it, they see my blog article on the topic.
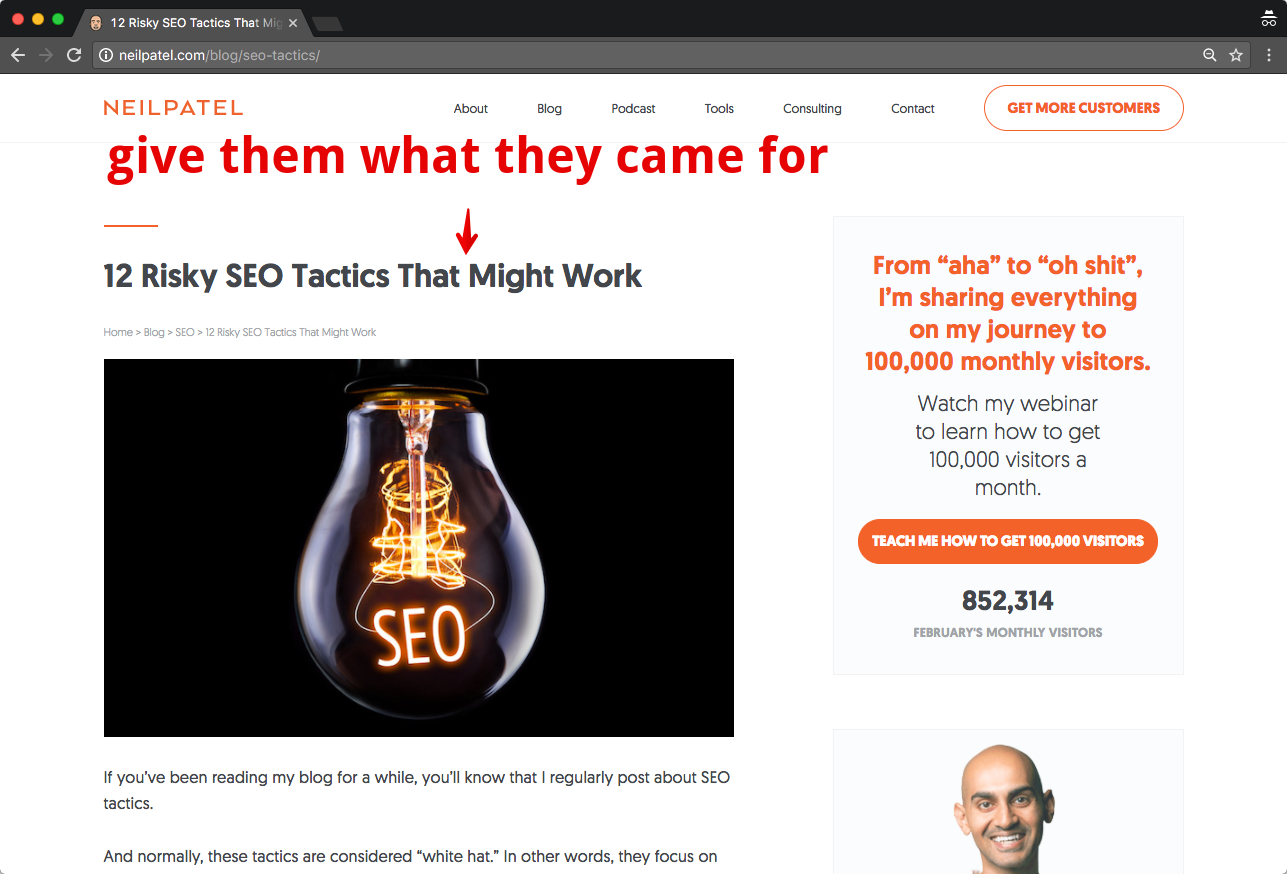
My goal with that H1 tag is to promise them what they came looking for: some straightforward but risky SEO tactics that could boost their traffic.
This is how Marc Purtell explains it in SEJ:
In order to have some great, Hummingbird-optimized h1 tags, try to understand what a user may be asking when they are searching for a keyword the page is targeting and format that question on the page with h1 tags.
Let me summarize the rules for creating amazing h1s.
As a bonus, I want to give you an actionable way to put these lessons into practice. I’m going to give you a homework assignment that may boost your organic traffic by 50%. Most can carry out this task in a few days.
I see a lot of people waste a lot of time doing “content audits” on their websites. I’m not against content audits; but instead of doing a full-fledged content audit on your website, I suggest that you do an H1 tag audit first.
H1 audits are quick and easy and have the potential to produce successful results in record times.
You can do this from the Screaming Frog website.
Click “SEO Spider Tool.”

Then click “Download.”
You do not need to purchase a license to use the software. If your website is more than 500 pages, however, it’s a good idea to purchase a license.
When you’ve successfully downloaded Screaming Frog, go ahead and open it.
Depending on the size of your site, this could take a couple minutes or a few hours.
It usually takes less than a minute for Screaming Frog to crawl 500 pages.
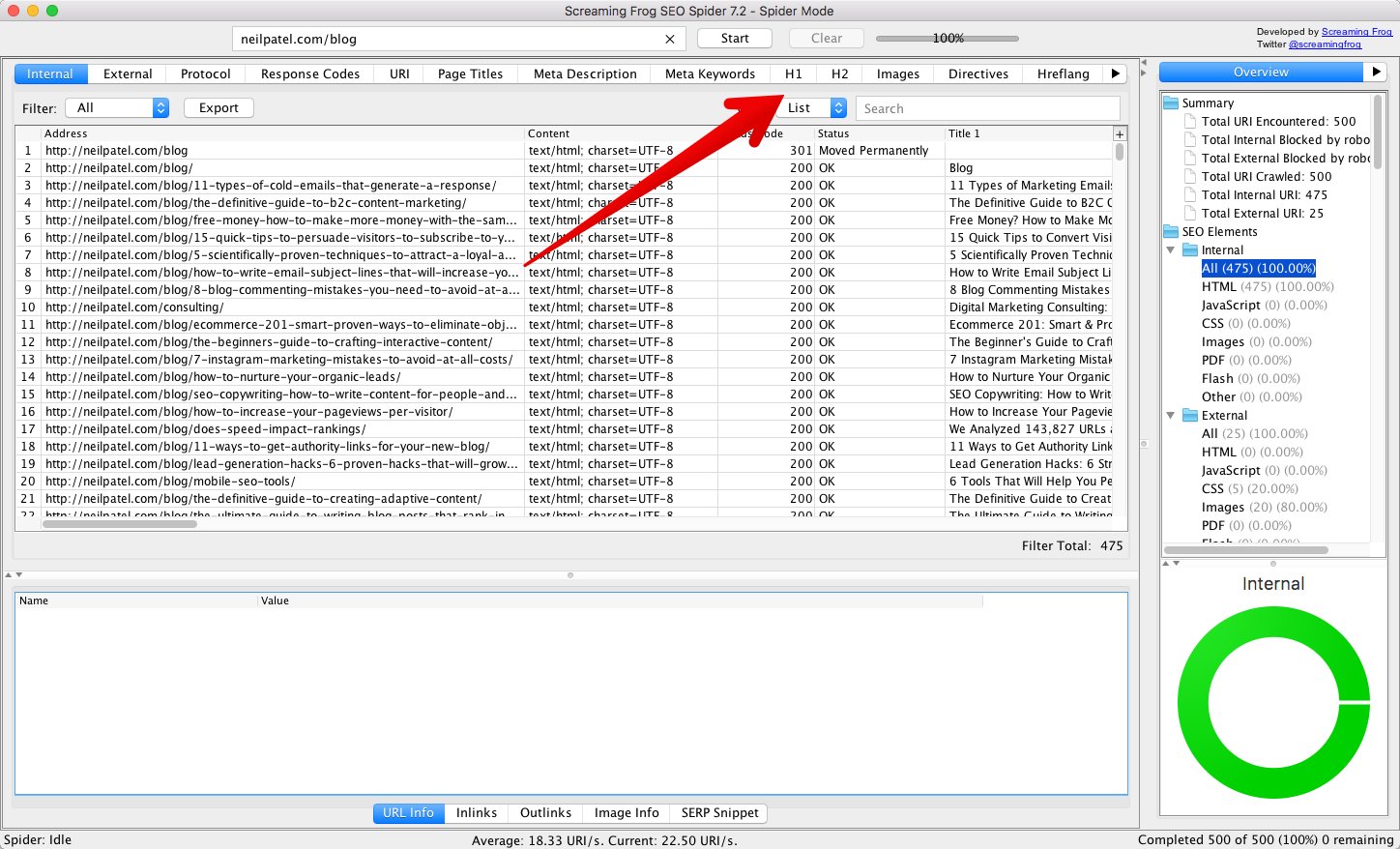
Here, you’ll see a list of all the H1 tags on your website.
Click the filter menu.
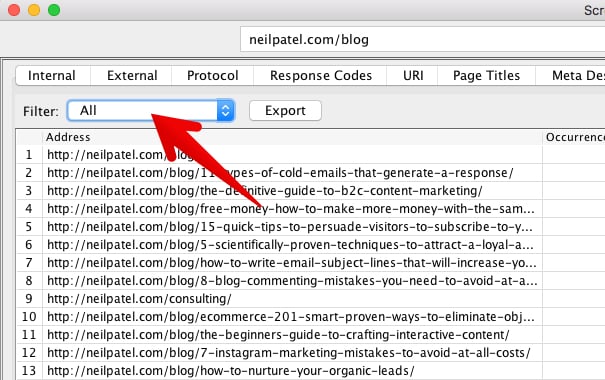
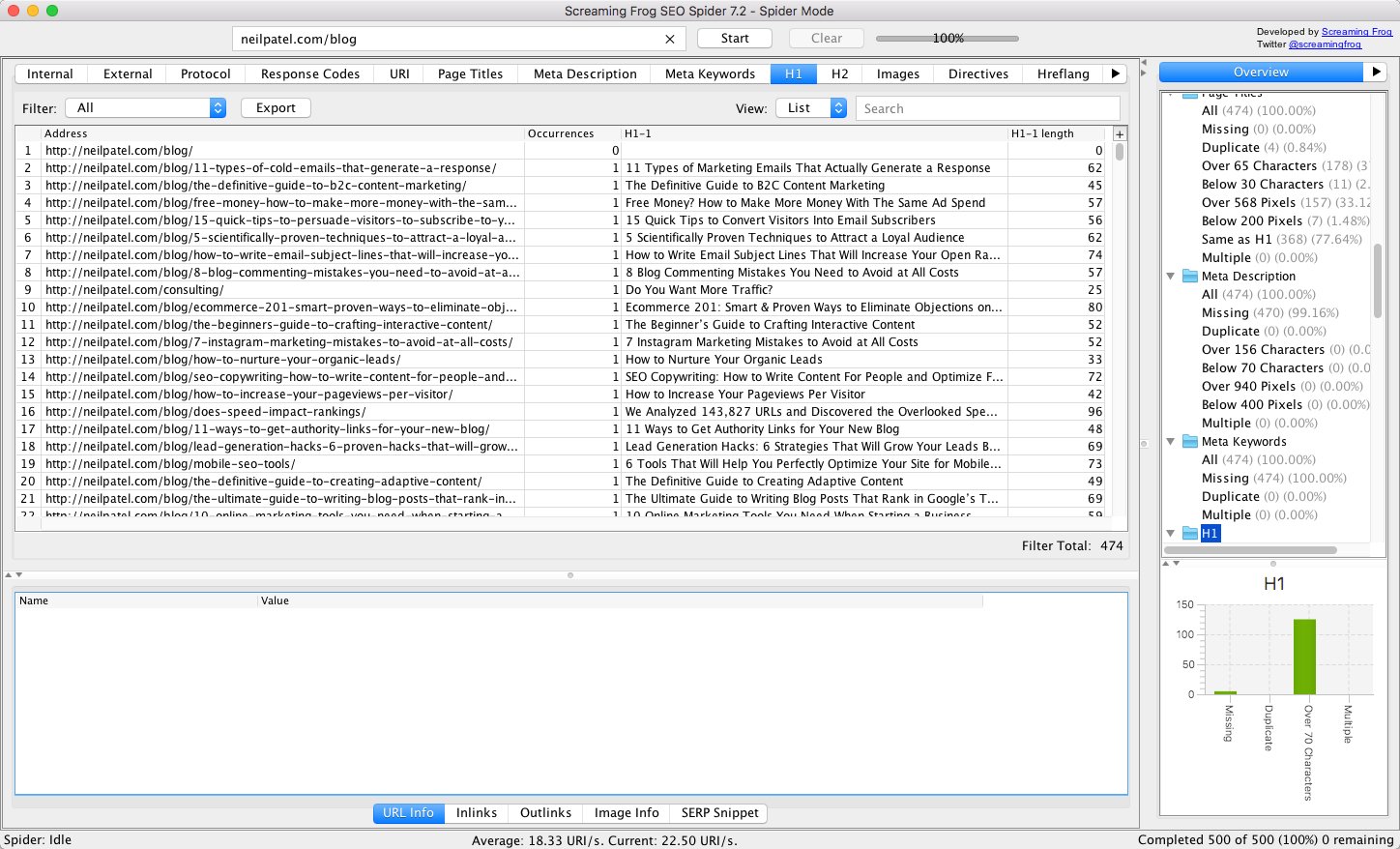
First, search for H1s that are missing by simply selecting “Missing” in the filter field.
You’ll see a list of all the pages on your site that lack an h1 tag.
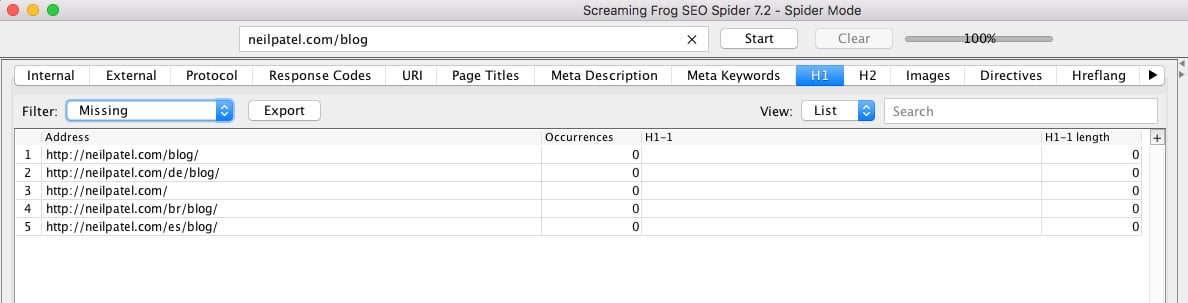
Your first task is to create an h1 for each of these pages.
(Unless, of course, you have a reason not to. My /blog page is a menu page to select the articles that I’m regularly adding and updating there, so I’ve chosen not to include an h1).
Click “Export.”
Find a good place to save the file.
It’s a CSV, so you can open it up in Excel.
Next, filter all the “duplicate” h1s. You can do this by clicking “duplicate” on the filter menu. Again, save this list in a CSV for future reference.
Finally, add a filter all the “multiple” h1s. Again, save the list
Now, go back to the filter menu, and select “All.” Export the list. At this point, you should have four CSV files.
Your task now is to create new h1 tags for each of the categories. Start with the missing ones, move on to duplicate, next multiple, and finally rework all h1s.
If your website is tens of thousands of pages, you may only be able to work on the highest-priority h1 tag project: the missing ones.
However, if you have the time, update all of your h1s to align with the rules that I provided above.
I think you’ll see a big difference in your traffic, your rankings, and your overall site performance.
If you’ve read this article, you know more about h1 tags than most people. More importantly, you know exactly how to use h1s for maximum SEO impact.
If you want help creating better H1s, title tags, content, or even SEO in general, reach out to our agency so we can help.
What are some of your h1 best practice tips?
Article URL: https://www.workatastartup.com/jobs/42988
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=26642396
Points: 1
# Comments: 0
The post Cyble (YC W21) Is Hiring appeared first on ROI Credit Builders.
SEEKING WORK
Location: Romania
Remote: Yes
Willing to relocate: No
Technologies: Go, Javascript, React.js, PHP, Laravel, Symfony, MySQL, Postgres, Git, Linux, HTML, CSS
Résumé/CV: https://www.linkedin.com/in/andrei-boar-7aa32ab7
Email: andrey.boar at gmail com
The post New comment by zuzuleinen in “Ask HN: Freelancer? Seeking freelancer? (April 2021)” appeared first on ROI Credit Builders.
Top 25 Sports Card Blogs Contents [show] ⋅About this list & ranking Sports Card Blogs Sports Collectors Daily The Cardboard Connection Beckett News All Vintage Cards | Vintage Sports Card Blog Cherry Collectables Just Collect Blog | Vintage Sports Cards & Memorabilia News The Knight’s Lance Sports Cards Rock Sports Card Info Upper Deck Blog Matt’s Wonderful […]
The post Top 25 Sports Card Blogs To Follow in 2021 appeared first on Feedspot Blog.
The post Top 25 Sports Card Blogs To Follow in 2021 appeared first on ROI Credit Builders.
Pages on the internet don’t last forever.
Some disappear overnight without warning. Other times, servers go down, or maybe you’re simply curious what your website or someone else’s looked like ten years ago.
So how do you re-access this information?
You need a web cache viewer.
It’s a tool that helps you recover backups or snapshots of websites.
In this guide, we’ll go through some of the best web cache viewer tools to help you turn back time to find missing information or even spy on your competitors.
A web cache viewer lets you see the older version or snapshot of any website, called a cache page. A cached page is a snapshot of the raw HTML and content of a page.
For example, when Google indexes your website, it takes a screenshot of what it looks like at the time and indexes it.
There are several tools to view an archived page, such as Google’s cache feature on search results and websites like the Wayback Machine dedicated to saving the internet’s history.
A web cache viewer is a valuable tool to have in your back pocket. Here are a few times you might want to use this handy tool.
Need to get information from a page with a pesky 404 error? A web cache viewer can help you see the last archived version before it went offline.
If a website went through a major makeover, you could use the cached version to revert the site to what it used to look like. This is particularly helpful for doing competitor analysis. For example, if a competitor suddenly overtook your site in the search results, you can look at older versions of their site to see what they changed.
Not seeing the SEO results you want? Did you know page caching can improve your site speed by reducing server load time by up to 80 percent? Viewing the cached version shows you what Google sees when it crawls your page. If your website is not cached, it can increase your page load times and drastically affect your bounce rate.
If the web page is slow or unresponsive, you can use the cached version to see a snapshot of the site the last time Google indexed the page. Although a cached page won’t always have up-to-date information, it can help you save time.
It’s helpful to know when the last time Google bots successfully visited your page, especially if you’re making changes to your site.
By viewing the cached version, you can see if a page is unresponsive, how it is being cached, and if there is anything you need to un-do.
While viewing cached versions sounds like an admin nightmare, several tools make the process easy, simple, and fast.
Not using Chrome extensions? You’re missing out.
Google’s Chrome extensions are programs you can install to your browser to change its functionality.
For example, you can add extensions that:
The Web Cache Viewer Chrome extension makes it easy for you to view a snapshot of the page you’re visiting. This is useful if you come across a 404 error and want to revert to the older version to see the information.
The Web Cache Viewer extension will:
Which option should you use? The Wayback Machine or Google Cache?
It comes down to what result you want from the tool.
For example, if you want to check Google is caching your site, or you need to view the last cached page of a site, Google Cache is the best option for you.
However, if you want to turn back the wheels of time and dig through a website’s past, you’ll want to use the Wayback Machine.
Got five minutes? That’s all you need to set up the extension and start using its caching functionalities.
Here’s what you need to do.
Step 1: Install the Web Cache Viewer onto your Chrome and activate the extension.
Step 2: Go to the target URL of your choice, right-click on the page, and scroll down to “View Cached Version.”
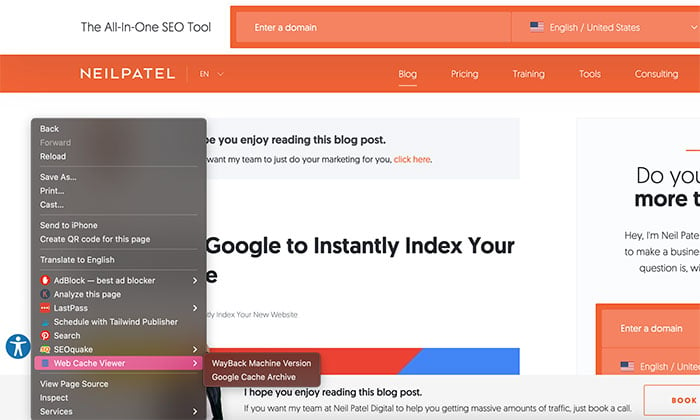
Step 3: Select either the Google Cache or Wayback Machine option.
After choosing, the extension will show you the Wayback Machine URL for the page or show you the last Google cached version.
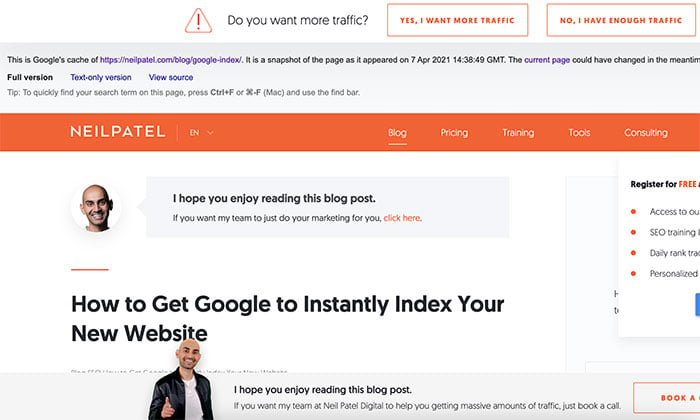
Each time Google crawls a web page, it creates a backup, which becomes part of Google’s cache.
Step 1: Do a Google search on your computer for the page you want to find.
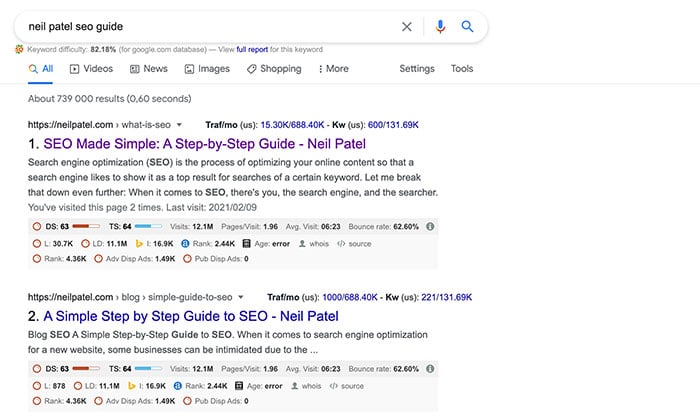
Step 2: When the search results load, click on the down arrow next to the site’s URL and select “Cached.”
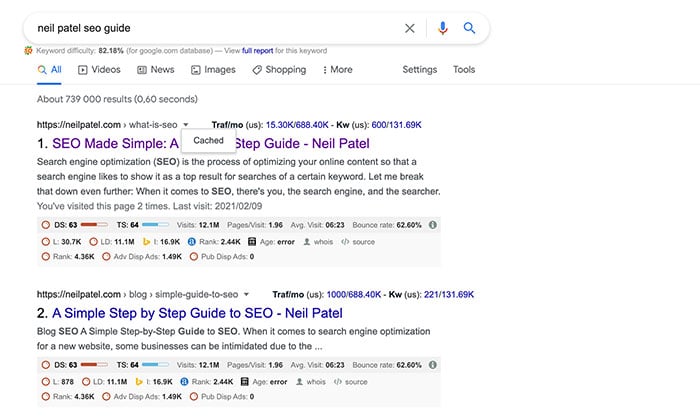
Step 3: The cached version of the page will load. You can view the “Full Version,” “Text-Only Version,” or “View Source.”
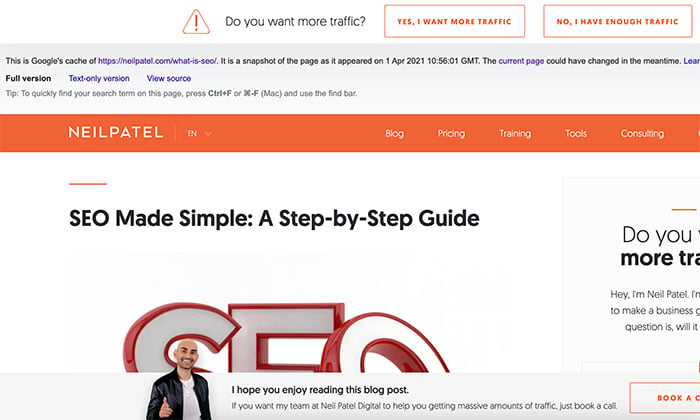
Keep in mind that you won’t be able to navigate to other pages on the site. If you do, it will take you to the live version. You can also access the live page by clicking on the “Current Page” link at the top of the page.
Struggling to find the page you want via search results? If you have the Chrome browser, you can use the address bar to get the cached version of any URL.
Step 1: Open the Chrome browser.
Step 2: Type “cache” in the address bar followed by the URL. For example, “cache:https://neilpatel.com”
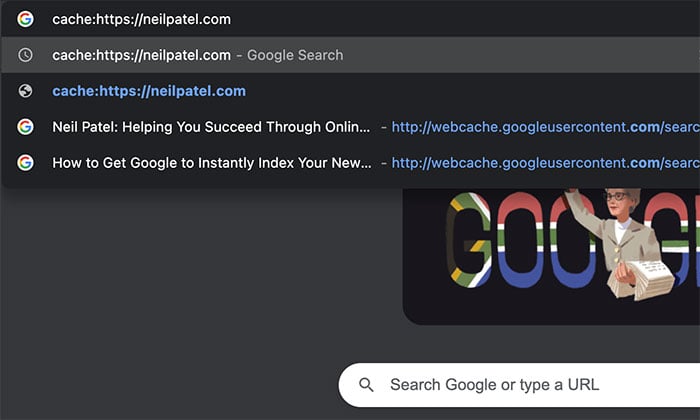
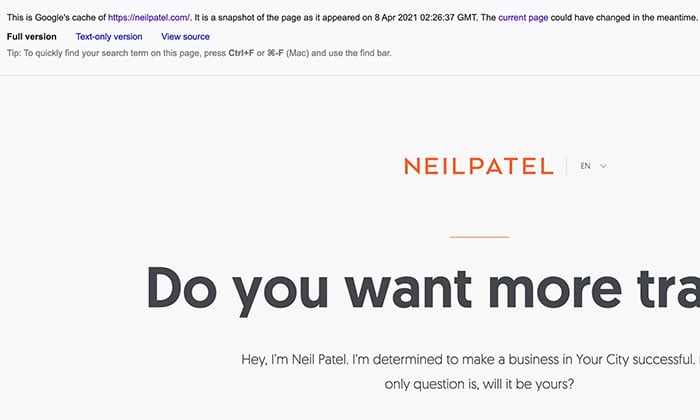
Step 3: The cached version will load, and you’ll have the same three version formats to choose from with the Google search method.
Wish you could travel back in time? Well, you can with Archive.Today.
The website is a time capsule for the internet. It takes a snapshot of a page and stores it forever, even if the original disappears.
The site saves text and graphics and will give you a link to the unalterable record of the web page.
The only catch?
You need to manually submit web pages and can only view entries that have previously been saved.
Step 1: Go to Archive.Today and scroll down to “I want to search the archive for saved snapshots.”
Step 2: Enter the URL you want to search.
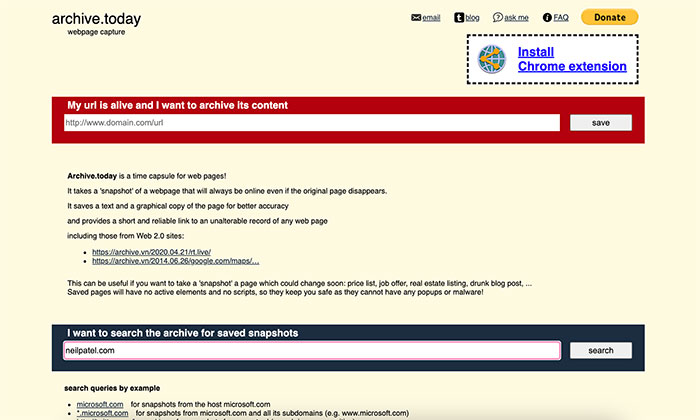
Step 3: A new page will load, and you’ll see snapshots listed from oldest to newest. Click on the one you want to view.
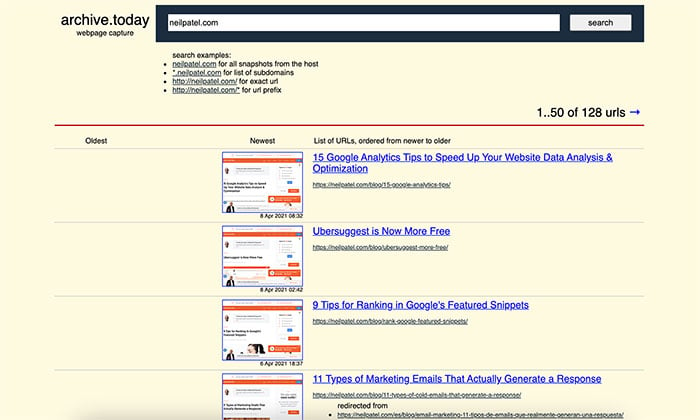
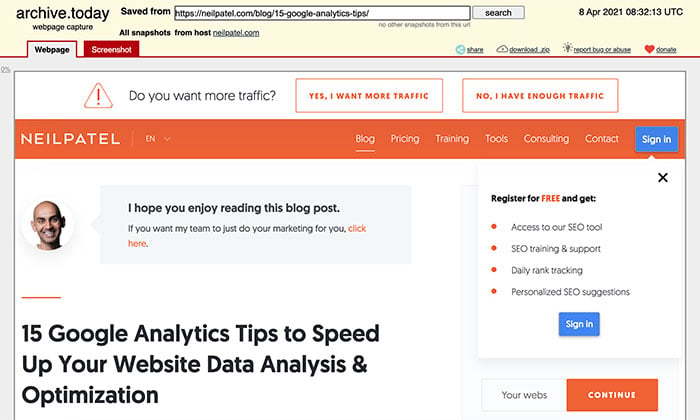
A secure, non-editable version of the page will load. You have the option to download the zip file, share the link, and view the webpage or screenshot.
The Internet Archives runs the Wayback Machine. It’s a non-profit building a digital library of the internet’s history.
You can explore more than 553 billion cached web pages, and the site hosts an archive of text, video, audio, software, and images.
Step 1: Go to Archive.org and enter the URL or keyword you want to view in the Wayback Machine search bar.

Step 2: A search results page will load. Click on the URL of the page you want to view.
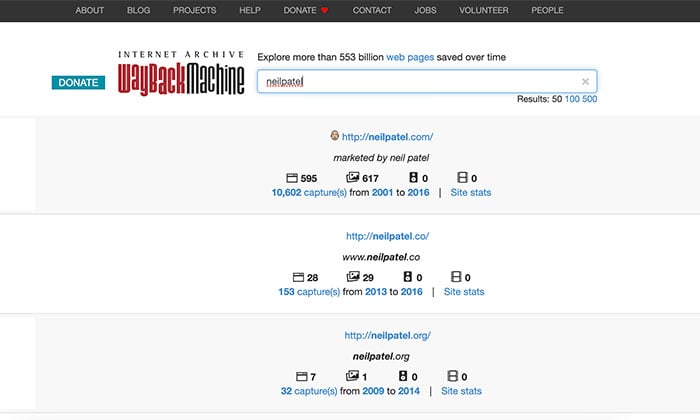
Step 3: Use the calendar at the top of the page to see what the website looked like during a specific time period.
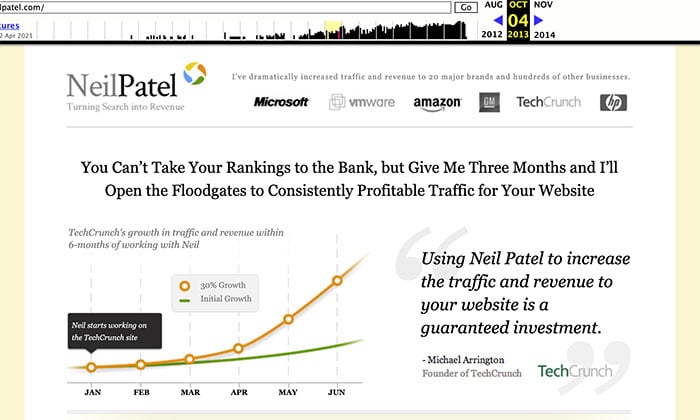
For example, if you search neilpatel.com, you can see what my blog was like in 2013!
Don’t want to log onto the Wayback Machine every time you want to view a cached page? Download the Chrome extension.
If your site is not on the Wayback Machine, you can manually submit your URL, and it will automatically create a snapshot for you. This is useful if you want to track how your site evolves through the years.
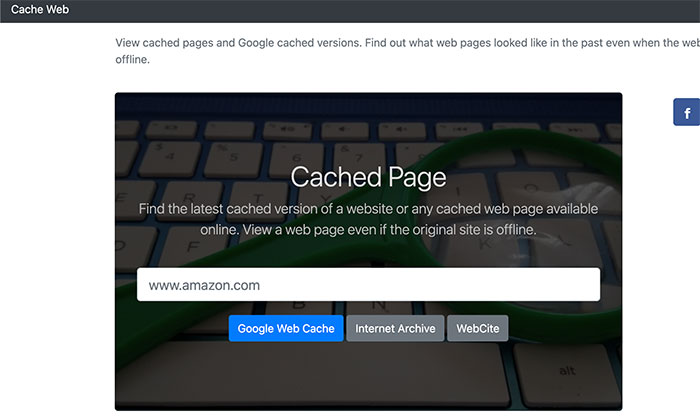
Cachedpage.co is a website that consolidates a few of the tools I’ve mentioned already.
Once you type the URL of the page you want to view, you have three options to choose from:
Select the one you want to use, and Cached Page will redirect you to those respective sites.
It doesn’t do any caching itself, so this site is only useful if you want to save time hopping between caching tools.
As you can see, a web cache viewer is an important SEO and marketing tool to have in your online arsenal.
It can quickly help you find information removed from the internet, see how your site has changed over the years, and tell you if Google isn’t indexing your site correctly.
While there are many tools available, remember to keep intent in mind. Do you only want to view the last cached version of a page, or do you need to go further back into time?
Your answer will help you find the right solution to your caching problem.
What’s your favorite web cache viewer tool, and how to use it?
With over 55 million listeners, Amazon Music is one of the leading music streaming platforms out there. Wouldn’t it be great if you could find a way to reach these subscribers and share your products with them.
Well, you can, and it’s all thanks to Amazon audio ads. Through Amazon’s free, ad-supported tier, you can create short, engaging audio ads to reach a whole new audience base. Let me walk you through how it works.
Think of Amazon audio ads like radio ads.
They’re commercials between 10 and 30 seconds long, and you can use them for any marketing campaign, from promoting brand awareness to hyping up a new product.
You don’t need to sell products on Amazon to use this service, either, which makes it accessible for more businesses.
The ads themselves play between songs. You can’t choose your slot preference, but there’s great reach available anyway. Listeners can tune in through their Echo devices, or they’ll hear your ad when they use the Amazon Music app on Android, FireTV, and iOS.
How much do these ads cost? Well, Amazon charges for audio ads on a cost-per-thousand-impressions (CPM) basis, so you pay each time a thousand people see your ad.
You need to spend at least $15,000 per month on Amazon audio ads to use the service. However, according to Amazon, the average minimum budget is about $25,000 per month, so you might want to bear this in mind.
Audio ads are nothing new, but there are two main reasons why Amazon’s audio ads may be worth a try.
First, think about the potential reach. The Amazon Echo is America’s most popular smart speaker, for one thing, and as I’ve mentioned, there are over 55 million Amazon music subscribers and counting!
Secondly, ad-supported streaming subscriptions aren’t going anywhere any time soon. According to Amazon, 68 percent of Americans rely on free streaming subscriptions, so there’s surely an audience for your campaigns.
The best part, though? You’re engaging with audiences in a creative, exciting new way. In a hugely competitive marketplace, Amazon audio ads may give you an edge over your rivals.
Can any business use Amazon audio ads? Sure.
Are these ads suitable for every business, though? No.
For starters, consider your budget. $15,000 per month is pretty steep, so small or niche businesses might find the cost isn’t justified.
Next, think about your overall marketing strategy. Do you plan on using any other Amazon advertising product? The ads might work best when used alongside other Amazon marketing tools to build a stronger, more cohesive presence on the platform.
Finally, think about your brand. Although you don’t need to sell through Amazon to create an ad, you might find Amazon audio ads make more sense if you’re already an Amazon seller and want to direct people to buy from your store.
Ready to try Amazon audio ads? Great! Let’s break down the steps involved.
Before you sign up, set out your goals. Why? Because it gives you some creative direction, which you’ll need to write a great script and create compelling visuals to accompany it.
Remember, no two campaigns are alike. Be clear on what you need from your Amazon audio ad before you go live.
Next, reach out to an Amazon ad consultant. They can help you plan, optimize, and launch your audio ad campaigns based on your budget and marketing goals.
To get going, simply click the “Get Started” link on the audio ads page.
Select which country you want to advertise in and choose your monthly budget. Remember, if you want to spend less than $15,000 per month, you can’t launch a custom audio ad campaign.
If you’re OK with the budget requirements, input your company contact details and provide a summary of your marketing needs. A consultant will be in touch to discuss your campaign in more detail.
Even if you can’t access Amazon audio ads for your marketing right now, there’s always a chance that Amazon will introduce a more flexible pricing structure in the future.
Your Amazon audio ad needs both an audio file and a companion banner for when your ads run on devices like FireTV.
The audio file contains the ad itself. Remember, it must be somewhere between 10 and 30 seconds long, and the file size can’t exceed 1 MB.
In terms of format, you can submit either a WAV, OGG, or MP3 file, and the volume should be at least 192 kbps so it’s easily audible.
To be clear, you shouldn’t use suggestive, provocative, or offensive language. It must be suited for a general audience.
Your companion banner (or graphic) shows up while the ad plays. Here are some guidelines for it:
There are some visual guidelines, too.
For starters, you can’t use style tools that make it look like any particular part of the ad is clickable. Here’s an example from Amazon:
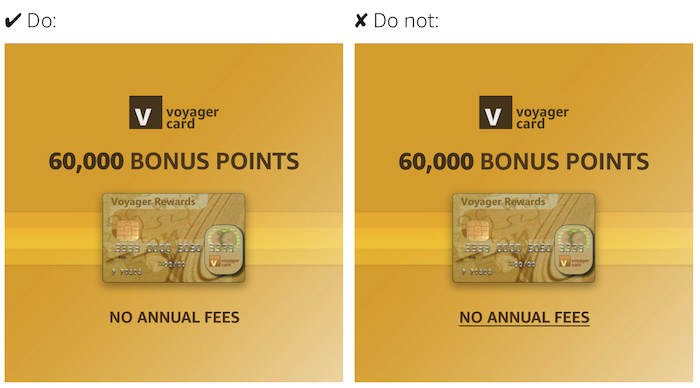
A banner along these lines may be more appropriate because there’s nothing to suggest it’s clickable:

You can also include a URL if you want, but it should be something compact so it doesn’t take over the whole graphic. “Shop now at Amazon.com” or some variation of this is OK.
Finally, make sure the text is clear and legible.
Struggling to put a companion banner together? Don’t worry. Your ad consultant can help you design it, and they’ll offer feedback if something’s not working.
Once you’ve submitted your banner and audio file to your consultant, your ad could go live within three working days.
A call to action (CTA) encourages people to do something after listening to your ad, such as buy your product. Unsurprisingly, every Amazon audio ad should have one! Where should your CTA go, though, and what should it include? Let’s take a look.
First, since you want people to take action after hearing your ad, it’s usually best to place your CTA at the end. Ensure you include your brand name and a specific action for people to take.
Next, keep your CTA short and specific. Don’t leave listeners in any doubt over what they should do and how they can do it.
Finally, avoid using sound effects. You don’t want to lose the message in your CTA behind a jingle!
Let’s say your company’s called Coffee King, and you want people to buy your new Regular Roast. Here are some CTAs you could use.
Remember, if you don’t ask a consumer to do something, how will they know what you want them to do?
Remember, your audio ad can’t be more than 30 seconds long, so every second counts. Here are some tips for making the most of the time you have.
OK, so there’s an art to writing a great script. The good news? It’s something you can learn. Here are some tips:
What’s so great about your product, and why should consumers buy it? Make this the focus of your ad. If you’re running any promotions or exclusive offers, be sure to mention them, too.
You might want to avoid testimonials, though. Too many voices can muddle your recording and distract from your message.
It sounds obvious, but ensure your recording sounds professional.
Does your ad need dramatic sound effects like sirens or horns? Probably not. Jarring sounds can annoy your listener, which isn’t great when you’re trying to nurture them into buying your products.
If you really must use sound effects, use them sparingly, and only if they’re necessary to drive your message home.
Remember, your ad doesn’t play in isolation. It’s playing between songs or other audio ads. Don’t begin with a long pause, and don’t “apologize” for interrupting someone’s music. Since you don’t know when your ad will play, a statement like this could be irrelevant.
Avoid long fade-outs, too. Simply end with your CTA.
Consistency is key. According to Forbes, cross-platform consistency can boost your revenue by 23 percent.
The takeaway? Ensure you’re using consistent language, visuals, and brand messaging across all your marketing campaigns. If your audio ad sounds off-brand, it could deter listeners from shopping with you.
Once your ad campaign is up and running, you need to monitor your key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure it’s working for you. For audio ads, here are the metrics you should track:
Amazon offers tools to help you track these metrics, but you can also use your own tracking tools.
Want to learn more about Amazon audio ads in action? Here are two great success stories to inspire you.
Samsung, the tech industry giant, needed help marketing its Galaxy S10 Lite handset. They opted for audio ads to reach young listeners tuning in to Amazon Music.
According to stats compiled by Amazon, these audio ads generated a 64 percent increase in organic impressions for Samsung and an 18 percent jump in overall product awareness.
All in all, I call this a successful campaign.
This brand took Amazon audio ads to a whole new level.

Berocca is a popular vitamin company with customers around the world. They wanted to identify new ways to reach their diverse audience base and sell their Berocca Boost tablets.
How did they achieve their goal? They used actionable audio ads powered by Amazon Alexa.
What’s great about this campaign is how easy it is for listeners to engage with the audio ad and actually purchase the product.
Amazon audio ads can help you increase your reach, sell more products, and ultimately grow your business. They’re simple to set up, and you can go live in as little as three working days.
That said, Amazon audio ads are not for everyone. If you’re in any doubt as to whether this campaign’s right for you or if you need help with audio marketing more generally, let me help you.
What do you think of Amazon audio ads? How are they helping your business?
Evergreen content engages and educates readers for longer without a huge amount of effort. Once you master the art of writing “timeless” content, you can ensure your articles, e-books, and tutorials stay relevant for years to come. Below, I’m going to show you exactly why evergreen content should be part of every marketer’s content strategy, …
The post How to Create Evergreen Content Right From the Start first appeared on Online Web Store Site.
The post How to Create Evergreen Content Right From the Start appeared first on Buy It At A Bargain – Deals And Reviews.