Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP): The Definitive Guide for Marketers
When it comes to your website, speed matters. The longer your page takes to load, the more traffic you’ll lose.
A few years ago, Google launched its mobile-friendliness update and made page load speed one of its mobile search engine ranking factors. Today, load speed affects your position in the SERPs; so uses may not be able to see your page at all if it loads slowly.
What’s the solution? Accelerated Mobile Pages, or AMP. Well, maybe — there’s actually been pushback on AMP pages in recent years.
What is AMP? Is it still relevant? If you want to dig deeper into AMP and learn how to use it to grow your online marketing strategy, you are in the right place.
What Are Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)?
The AMP plugin was born out of a collaboration between tech giants like Google and Twitter.
In simple terms, Accelerated Mobile Pages is an open-source project designed to optimize faster mobile pages. It’s like taking a page that’s already mobile-friendly and making it load quicker, by stripping it down to basics.
If AMP isn’t already part of your marketing strategy, you should consider it.
Webmasters, marketers, and SEOs have analyzed how AMP can affect mobile web pages. They found AMP can have a huge impact on mobile search engine rankings, though Google maintains this isn’t directly factual.
In a roundabout way, however, it might be true. According to Google, the AMP plugin increases page load speed, and site speed is a confirmed ranking factor.
Faster mobile pages + readable content = better user experience
In a nutshell, pages that are AMP-optimized load faster and therefore rank better than other mobile web pages.

You can visit the open source initiative platform here.
How Does The AMP Plugin Work?
Paul Shappiro, from Search Engine Land, lays out the three part structure of AMP:
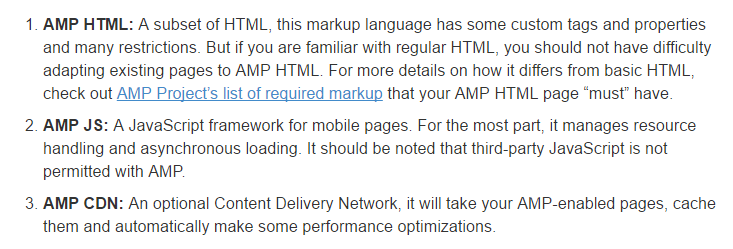
The AMP plugin renders mobile pages faster by cutting back on the HTML coding and rendering only those suitable for mobile users.
This diagram and explanation from Will Critchlow’s Whiteboard Friday make it pretty easy to understand:
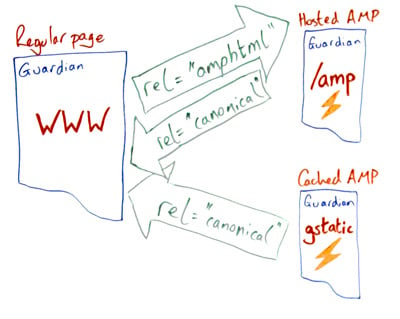
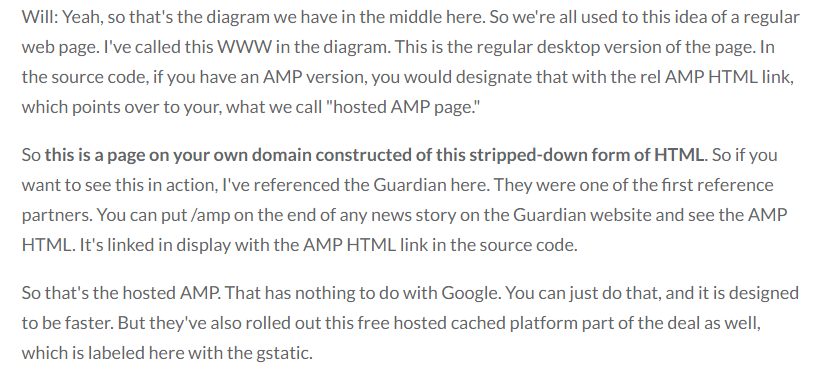
AMP renders your pages using optimized HTML code. The pages are expected to load faster because certain HTML code tag manager aspects that would otherwise slow down the page are eliminated.
If JavaScript is included in your mobile pages, the script won’t be rendered for your Accelerated Mobile Pages.
Here are a few more things you should know:
- With AMP, you have to use a streamlined version of CSS.
- You are only permitted to use the JavaScript library that AMP provides. Since you’re not in control, you may experience lazy loading. This might be the only downside to AMP.
- For AMP sites to work every time, they must be properly validated.
- For a better experience, custom fonts have to be specially loaded.
- To avoid quirky-looking images, make sure to declare height and width.
- Use AMP-approved extensions if you want to have videos on your page.
- There has been some controversy with AMP, with some experts reporting it lowers ad revenue and makes it harder to spot “fake news” articles.
When you integrate the AMP plugin and use it to improve your mobile pages, what should matter to you most is speed and readability, not share-ability. Your social share buttons may not even display properly since the majority of them are developed using JavaScript.
Benefits of Accelerated Mobile Pages
There’s a significant correlation between site speed, page views, and mobile search engine rankings.
One thing that you have to remember is that whenever a particular web page loads up quickly, mobile browser users will view more pages on the site, thereby reducing bounce rate.
When bounce rate is reduced and onsite experience increases, Google will reward the page.
Truth be told, there are many benefits to optimizing with the AMP plugin. Here’s the top four:
1. Insanely Fast-loading Web Pages That Users Love
Speed is the lifeblood of your mobile browser page. Great content is important, but unless your pages are accessible, users won’t read them.
AMP helps you to achieve that.
Remember the way and rate at which people consume content (e.g., articles, blog posts, videos, and podcasts) has changed dramatically. People browsing the internet want their content to load quickly as they jump from site to site, usually consuming many different kinds of content in quick succession or even at once.
If your mobile pages are as slow as a snail, you won’t get mobile browsers that land on your site to convert into customers. AMP gives you dramatic page speed increases that will help you keep users who click on your site from clicking away.
2. Improved Mobile Search Engine Rankings
There’s a strong relationship between site speed and conversion rate. If users are happy on a fast-loading site, they’re more likely to subscribe to a list or purchase a product.
Although a lot is still expected of AMP, Google hasn’t yet made it a ranking factor.
Since AMP works closely with mobile pages, it may never be used as an independent ranking factor; it has nothing to do with the desktop version of pages.
That said, since sites that are mobile-friendly are rewarded with higher rankings in organic mobile search results, pages developed with AMP tend to rank higher than non-AMP pages in the mobile results pages (MRPs).
3. Flexible Ad Support
Most people started a website or blog in order to make money and to possibly replace their day job.
Looking at the desktop and mobile browser versions of a site’s pages, it’s easy to conclude if there are too many distractions.
These distractions, such as the header image, navigational menu, sidebar, social share buttons, forms, popups, and other unnecessary elements, can lower your conversion rate.
With AMP, you can get rid of distractions on your mobile browser pages.
That’s because not all HTML code tags are executed, you use a streamlined version of CSS, and JavaScript is out of the question (mostly).
That means that you can make money more easily from your ads.
When you click on an Accelerated Mobile Page, it’ll load nearly instantaneously, even before you’re done clicking.
When displaying ads from a third party on your Accelerated Mobile Pages, make sure that you deliver ads that load quickly but also grab the user’s attention and deliver immense value.
As you already know, this content marketing approach is the easiest way to increase your influence, help users get answers to their questions, and improve ROI on ad spend.
If you’re ready to monetize your AMP-optimized pages, here are some of the most popular ad networks that are currently using the AMP-ads functionality:
- Amazon A9
- AdReactor
- Google Doubleclick
- Flite
- Adform
- Google AdSense
- AOL AdTech
- Taboola
- plista
- Smart AdServer
- Yieldmo
- DotAndAds
4. User Tracking is Simplified
It’s not enough to send traffic to your mobile browser pages. You also have to know how they arrived at your site.
Tracking helps you determine where people came from, which pages they viewed and so on.
Tracking users and site performance is pretty easy on AMP because there are analytical tools in place, where you can study your AMP versions in greater detail.
User behavior can only be influenced when you track it. With AMP, publishers can utilize such tag manager analytics to choose from two tags.
These tags help to automatically track essential data, such as clicks/conversions, video and link tracking, visitor counts, new vs. returning visitors and more.
Other technology solutions companies, such as WordPress, Parse.ly, Chartbeat, LinkedIn, Adobe Analytics, Pinterest and, of course, Twitter, are also already supporting AMP.
How to Set Up Accelerated Mobile Pages
There are several options when you’re looking to optimize your web pages for AMP. If you’re a beginner, the first step is to maintain at least two versions of your content page.
Your original content page would be the mobile browser friendly version that users will see, but you’ll also have the AMP version of that specific page, which will definitely speed things up.
Remember that AMP versions contain basic HTML code, which doesn’t allow form elements and third-party JavaScript.
As marketers, we all want to build our email list. The downside to AMP is that it won’t allow you to easily achieve that.
Moreover, user comments and other activities that users participate in when viewing your content on a mobile page may not be possible with AMP.
Again, the focus is on speed and readability.
To get started with AMP right now, if you’re a WordPress user, then you just need to download and install the WordPress plugin at GitHub.
Simply click on the “Download Zip” button.
Note that you can install the AMP plugin through your WordPress dashboard, just as you would any other plugin. It’s pretty straightforward.
Once you’ve successfully installed and activated the plugin, all that you have to do is append “/amp/” to your blog post pages. Here’s how it looks on a mobile browser:

Here’s the AMP version of this page on The Guardian:

If you don’t have a friendly permalink, then you can append this “?amp=1” instead.
Don’t forget to validate and tweak at Google Search Console. That way, you can help Google pick up your AMP versions faster.
Accelerated Mobile Pages FAQ
AMP pages strip down pages to their essentials, which helps improve page load time. They do this using a three step configuration.
When most of your site traffic comes from mobile devices or you want to lower your bounce rate.
AMP doesn’t appear to be going away, but there has been some controversy. Google recently announced it will not AMP pages for news sites to show up in top stories, so it does seem to be less important.
They can be helpful, but are not essential for SEO. Optimizing for page speed and mobile experience can be done in several ways.
Accelerated Mobile Pages Conclusion
AMP is powerful, but some marketers say it is losing steam. As an upgrade to mobile-friendly pages, it can help you meet Google’s expectations for site speed.
While there is still a focus on AMP, don’t forget to use proven mobile marketing strategies. That’s the best way to attract mobile customers and grow your business.
Before you leave, I have a question for you: Have you accelerated your mobile pages for speed and readability? If not, what’s stopping you?