Article URL: https://jobs.ashbyhq.com/Cambly?departmentId=58bf36fe-813a-4048-bd36-11bd6f0ee3e2&utm_source=ROe4eDx4yP
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=40107283
Points: 0
# Comments: 0
Article URL: https://jobs.ashbyhq.com/Cambly?departmentId=58bf36fe-813a-4048-bd36-11bd6f0ee3e2&utm_source=ROe4eDx4yP
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=40107283
Points: 0
# Comments: 0
And how can they affect if you can get funding? We tell you all about NAICS Codes. They could be the difference between getting business money or not getting any money.
Federal statistical agencies use the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) . The idea is to classify business establishments. This is to collect, analyze, and publish statistical data, related to the U.S. business economy.
The NAICS was developed under the auspices of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB). Its adoption was in 1997. The intention is to replace the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) system. The U.S. Economic Classification Policy Committee (ECPC) developed it with Statistics Canada and Mexico’s Instituto Nacional de Estadistica y Geografia. The intent was to make business stats easy to compare among North American countries.
NAICS is a 2- through 6-digit hierarchical classification system. It offers five levels of detail. Each digit in the code is part of a series of progressively narrower categories. The more digits in the code, the more classification detail.
The first two digits are the economic sector. The third digit designates the subsector. And the fourth digit designates the industry group. The fifth digit designates the NAICS industry. The sixth digit designates the national industry.
A 5-digit NAICS code is comparable in code and definitions for most of the NAICS sectors. This is across the three countries participating in NAICS. They are the United States, Canada, and Mexico. The 6-digit level lets the U.S., Canada, and Mexico all have country-specific detail. A complete and valid NAICS code has six digits.
NAICS industry codes define businesses based on the primary activities they engage in. Recently, the NAICS changed many of its codes as it updated its philosophy. It no longer sets aside online businesses. Now the NAICS no longer distinguishes businesses by how they deliver goods or services.
There is an older NAICS list of high-risk and high-cash industries. Higher risk industries on the list include casinos, pawn shops, and liquor stores. But it also included automotive dealers and restaurants. But this list is from 2014 and does not appear to have ever gotten any updating.
Per the NAICS, various professionals in the banking industry compiled the list. The idea was to use it as a working guide. But it is not an officially sanctioned list. They do not guarantee the accuracy of this list.
When considering any aspects of a business, risk must be a major factor. There are inherent issues in every single industry. But some businesses are considered to be risky by their very nature. This is the case even if everything else goes off like a hitch and the business is prospering. Risk is inherent within these business types. Even if your business doesn’t feel risky, it could be anyway.
Learn more here and get started with building business credit with your company’s EIN and not your SSN.
The biggest reason why risk matters has to do with funding. There are several industries where lending institutions are hesitant to do business. In those particular cases, there are stricter underwriting guidelines. But at least a company can get funding.
In some industries, no funding is available at all. As a result, those businesses will need to find other solutions for financing. These solutions can include:
Still, a lot of businesses would rather work with lenders. But where are lenders’ ideas of the degree of risk coming from? One clue comes from the CDC.
The Centers for Disease Control looks at risks in small businesses. Part of the calculation of risk comes from occupational injuries. But the other side of the risk coin is occupations which are high in cash transactions. After all, a pawn shop might not have much of a specific risk of injury at all. But the large amounts of cash normally associated with one mean it can be a tempting target for thieves.
These industries (among many others) can get an automatic decline:
Learn more here and get started with building business credit with your company’s EIN and not your SSN.
These industries (among many others) can be subject to stricter underwriting guidelines:
According to the older list, the following codes are among those considered to be high risk:
How do you choose a better code?
Of course you want to be 100% honest when it comes to selecting your NAICS code. But if more than one can apply, you don’t have to choose the one that’s higher risk. So it pays to check and be careful when making your selection.
Also, if only high risk codes apply, there’s nothing wrong with changing your business. Then you may be able to match a related but lower risk code. There is nothing underhanded or dishonest about doing this.
Let’s say your business is automotive transmission repair (NAICS Code 811113). We know this is a high risk code. But 811191 is not on the NAICS list. It covers Automotive Oil Change and Lubrication Shops. So why not offer oil changes and use the lower risk code? It could be the difference between getting funding, or not.
The Internal Revenue Service will use the NAICS code you select. This is to see if your business tax returns are comparable to other businesses in your industry. If your deductions do not reasonably resemble other businesses in your industry, your business could be subject to an audit.
The IRS may label some companies as high-risk when they do not choose the right NAICS code. But if you know how the system works, then you can choose the correct code on your first try.
Learn more here and get started with building business credit with your company’s EIN and not your SSN.
Lenders, banks, insurance companies, and business CRAs all use codes. They tend to use both NAICS and SIC Codes. SIC Codes are the older business classification system. D&B uses both SIC and NAICS Codes.
OSHA uses NAICS Codes for industry identification in its data. These agencies use them to determine if your business is in a high-risk industry. So you could get a loan or business credit card denial based on your business classification. Some SIC codes in particular can trigger automatic turn-downs. You could end up paying higher premiums, and get reduced credit limits for your business.
Will a better NAICS code guarantee funding for your business venture? Of course it won’t. But at least your business will not be automatically turned down before you can make a case for funding.
Industries are defined by codes from the North American Industry Classification System. Codes go up to six digits for the most granular information. Some codes are always associated with high risk. This makes it harder to get business funding. So if more than one NAICS code can apply to your business, pick the one that’s less risky.
The post In Just a Few Minutes of Your Time, Learn All About Avoiding Risky NAICS Codes appeared first on Credit Suite.
The post In Just a Few Minutes of Your Time, Learn All About Avoiding Risky NAICS Codes appeared first on Automation For Your Email Marketing Sales Funnel.
The post In Just a Few Minutes of Your Time, Learn All About Avoiding Risky NAICS Codes appeared first on Buy It At A Bargain – Deals And Reviews.
And how can they affect if you can get funding? We tell you all about NAICS Codes. They could be the difference between getting business money or not getting any money.
Federal statistical agencies use the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) . The idea is to classify business establishments. This is to collect, analyze, and publish statistical data, related to the U.S. business economy.
The NAICS was developed under the auspices of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB). Its adoption was in 1997. The intention is to replace the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) system. The U.S. Economic Classification Policy Committee (ECPC) developed it with Statistics Canada and Mexico’s Instituto Nacional de Estadistica y Geografia. The intent was to make business stats easy to compare among North American countries.
NAICS is a 2- through 6-digit hierarchical classification system. It offers five levels of detail. Each digit in the code is part of a series of progressively narrower categories. The more digits in the code, the more classification detail.
The first two digits are the economic sector. The third digit designates the subsector. And the fourth digit designates the industry group. The fifth digit designates the NAICS industry. The sixth digit designates the national industry.
A 5-digit NAICS code is comparable in code and definitions for most of the NAICS sectors. This is across the three countries participating in NAICS. They are the United States, Canada, and Mexico. The 6-digit level lets the U.S., Canada, and Mexico all have country-specific detail. A complete and valid NAICS code has six digits.
NAICS industry codes define businesses based on the primary activities they engage in. Recently, the NAICS changed many of its codes as it updated its philosophy. It no longer sets aside online businesses. Now the NAICS no longer distinguishes businesses by how they deliver goods or services.
There is an older NAICS list of high-risk and high-cash industries. Higher risk industries on the list include casinos, pawn shops, and liquor stores. But it also included automotive dealers and restaurants. But this list is from 2014 and does not appear to have ever gotten any updating.
Per the NAICS, various professionals in the banking industry compiled the list. The idea was to use it as a working guide. But it is not an officially sanctioned list. They do not guarantee the accuracy of this list.
When considering any aspects of a business, risk must be a major factor. There are inherent issues in every single industry. But some businesses are considered to be risky by their very nature. This is the case even if everything else goes off like a hitch and the business is prospering. Risk is inherent within these business types. Even if your business doesn’t feel risky, it could be anyway.
Learn more here and get started with building business credit with your company’s EIN and not your SSN.
The biggest reason why risk matters has to do with funding. There are several industries where lending institutions are hesitant to do business. In those particular cases, there are stricter underwriting guidelines. But at least a company can get funding.
In some industries, no funding is available at all. As a result, those businesses will need to find other solutions for financing. These solutions can include:
Still, a lot of businesses would rather work with lenders. But where are lenders’ ideas of the degree of risk coming from? One clue comes from the CDC.
The Centers for Disease Control looks at risks in small businesses. Part of the calculation of risk comes from occupational injuries. But the other side of the risk coin is occupations which are high in cash transactions. After all, a pawn shop might not have much of a specific risk of injury at all. But the large amounts of cash normally associated with one mean it can be a tempting target for thieves.
These industries (among many others) can get an automatic decline:
Learn more here and get started with building business credit with your company’s EIN and not your SSN.
These industries (among many others) can be subject to stricter underwriting guidelines:
According to the older list, the following codes are among those considered to be high risk:
How do you choose a better code?
Of course you want to be 100% honest when it comes to selecting your NAICS code. But if more than one can apply, you don’t have to choose the one that’s higher risk. So it pays to check and be careful when making your selection.
Also, if only high risk codes apply, there’s nothing wrong with changing your business. Then you may be able to match a related but lower risk code. There is nothing underhanded or dishonest about doing this.
Let’s say your business is automotive transmission repair (NAICS Code 811113). We know this is a high risk code. But 811191 is not on the NAICS list. It covers Automotive Oil Change and Lubrication Shops. So why not offer oil changes and use the lower risk code? It could be the difference between getting funding, or not.
The Internal Revenue Service will use the NAICS code you select. This is to see if your business tax returns are comparable to other businesses in your industry. If your deductions do not reasonably resemble other businesses in your industry, your business could be subject to an audit.
The IRS may label some companies as high-risk when they do not choose the right NAICS code. But if you know how the system works, then you can choose the correct code on your first try.
Learn more here and get started with building business credit with your company’s EIN and not your SSN.
Lenders, banks, insurance companies, and business CRAs all use codes. They tend to use both NAICS and SIC Codes. SIC Codes are the older business classification system. D&B uses both SIC and NAICS Codes.
OSHA uses NAICS Codes for industry identification in its data. These agencies use them to determine if your business is in a high-risk industry. So you could get a loan or business credit card denial based on your business classification. Some SIC codes in particular can trigger automatic turn-downs. You could end up paying higher premiums, and get reduced credit limits for your business.
Will a better NAICS code guarantee funding for your business venture? Of course it won’t. But at least your business will not be automatically turned down before you can make a case for funding.
Industries are defined by codes from the North American Industry Classification System. Codes go up to six digits for the most granular information. Some codes are always associated with high risk. This makes it harder to get business funding. So if more than one NAICS code can apply to your business, pick the one that’s less risky.
The post In Just a Few Minutes of Your Time, Learn All About Avoiding Risky NAICS Codes appeared first on Credit Suite.
It is time to learn about your Equifax credit report.
But let us start with some definitions and background on business credit.
This is credit in the name of a business. It is not tied to the creditworthiness of its owner or owners. Instead, business credit scores are going to depend on how well a company can pay its bills. Hence consumer and business credit scores can vary dramatically.
There are no demands for a personal guarantee. You can quickly get business credit regardless of personal credit quality. And there is no personal credit reporting of business accounts. Business credit utilization is not going to affect your consumer FICO score. Plus the business owner is not going to be personally liable for the debt the business incurs.
Being accepted for business credit is not automatic. Building business credit requires some work. Some of the steps are intuitive, and some of them are not.
Fundability is the current ability of our business to get funding. Some factors are within your control. Others (like your time in business) are not. Your online presence and data are one area which is at or close to 100% with your control.
The better your business credit and fundability are, the more likely you will get approval for business financing. Today, let us concentrate on your Equifax report.
Keep your business looking fundable (legit) with:
If your business is over the road trucking, then it needs to be listed that way. Pro tip: when your industry can be called several different names, like long distance trucking, mention those other phrases on your website.
What distinguishes Equifax reports from reports from the other two main credit bureaus? And can you use that information to your advantage?
There are three different credit bureaus for business: Dun & Bradstreet, Experian, and Equifax. FICO SBSS and CreditSafe are also players.
In the business world Equifax and Experian are up there, but it is Dun & Bradstreet which is the major player.
Dun and Bradstreet has more than 10 times the records of the next closest reporting agency. For more information, see dnb.com/about-us/company.html. It makes sense to start with Dun and Bradstreet, even when looking at your Equifax credit report. This is because you are going to have to start the business credit building process with them anyway.
Dun and Bradstreet is the oldest and largest credit reporting agency. Go to Dun and Bradstreet’s website and look for your business, at dnb.com/duns-number. But what happens if you are unable to find it? Then get a free D-U-N-S number. You will always need a D-U-N-S number to start building business credit. Go here to get a D-U-N-S number: dnb.com/duns-number/get-a-duns.html.
A D-U-N-S number is how Dun and Bradstreet gets your company into their system. And a D-U-N-S number plus 3 payment experiences leads to a PAYDEX score. A payment experience is a record of a purchase from a business which reports to a credit reporting agency. In this case, Dun and Bradstreet. Once you are in Dun and Bradstreet’s system, search Equifax and Experian’s sites for your business. You can do so at creditsuite.com/reports.
Keep your business protected with our professional business credit monitoring.
But your Equifax credit report is going to be different. The company gets its data from:
Equifax scores answer one basic question. How likely is a business to go severely delinquent in its payments? The score is an indication of whether a company is likely to make late payments.
You can check out a sample Equifax credit report for small business at https://assets.equifax.com/assets/usis/small_business_sample_credit_report.pdf.
Here’s what’s in that report.
The first section is devoted to identifying information about your company, namely your business name and address and telephone number. This section will also include your Equifax ID. An Equifax ID is how Equifax can tell your business from similarly-named businesses.
The next section is about the Credit Risk Score. This score runs from 101 to 992. Higher numbers are better. This section also shows key factors.
Key factors are positives and negatives about your business, such as how old your oldest account is, and whether you have any charge-offs, and the size of your business.
The next section shows credit utilization. This is shown as a pie chart. It graphically shows which percent of your available credit line you are using. It also has identifying labels to show how much each percentage truly is. But it is only for your financial accounts.
The next part is your Payment Index. The score runs from 0 to 100. Higher numbers are better. It also shows Industry Median.
There is also a table explaining the numbers:
This is a line graph. It shows the average days beyond terms by date reported. It is for non-financial accounts only. Plus it shows any recent trends, so if you’ve improved your payment habits, it will show up here.
The next piece is on your Business Failure Score. This score runs from 1000 to 1880. It shows its own key factors, like recent balance information.
The next section is devoted to inquiries. It shows the date, and whether it was an inquiry on a financial or non-financial account. This is a rather short part of the report.
The bureau messages part, appears to be a free form field. It seems its purpose is to add notes to a profile. These can be notes on the number of locations, or business aliases.
The bureau summary data section contains a wealth of information. It shows:
It also shows Recent Activity, which includes:
Keep your business protected with our professional business credit monitoring.
The public records section has information on:
If there are none reported, then the date field will indicate as much.
The final section appears to contain somewhat miscellaneous information, which probably doesn’t fit in well anywhere else. such as alternate company Names and DBAs.
It also contains:
Now that you know what goes into it, you can see that some of the more important pieces of data Equifax looks into are:
Improve your Equifax score by:
Whatever improves your Equifax report is bound to improve your reports at D&B and Experian. Paying off accounts pays dividends, as does avoiding bankruptcies.
Equifax will not change your scores without proof. They are starting to accept more and more online disputes. But include proofs of payment with it. These are documents like receipts and cancelled checks.
Fixing credit report errors also means you specifically spell out any charges you challenge. Make your dispute as crystal clear as possible. If you need to snail mail anything in, then use certified mail so that you will have proof that you sent in your dispute. Correct Equifax issues at: equifax.com/small-business-faqs/#Dispute-FAQs. Be specific about the concerns with your report.
At Equifax, you would use Equifax Complete. It currently costs $19.95 per month, after an offer of 30 days for $4.95. See equifax.com/equifax-complete/Equifax.
Keep your business protected with our professional business credit monitoring.
But add together monitoring for the three biggest credit reporting agencies for a year and the cost is staggering. It costs $468 for Dun and Bradstreet, $189 for Experian, and $224.40 for Equifax (with a special). For a grand total of $881.40!
You can monitor your business credit at Dun and Bradstreet, Equifax, and Experian through Credit Suite, for considerable savings over what it would cost you at those different credit bureaus. And all in one place! Credit Suite offers monitoring through the Business Finance Suite (through Nav). See what credit issuers and lenders see so you can directly improve your scores and get the business credit and funding you need. See suitelogin.com and creditsuite.com/monitoring.
Equifax gets much of its data from the Small Business Financial Exchange.
Monitoring all of your business credit reports is always going to be expensive. But you can save 90% by monitoring your Dun and Bradstreet, Experian, and Equifax scores through Credit Suite.
The post Learn About Your Equifax Credit Report appeared first on Credit Suite.
Did You Want to Learn About Your Equifax Credit Report? It is time to learn about your Equifax credit report. But let us start with some definitions and background on business credit. Business Credit This is credit in the name of a business. It is not tied to the creditworthiness of its owner or owners. … Continue reading Learn About Your Equifax Credit Report
It’s time to learn about Dun & Bradstreet reports.
But let’s start with some definitions and background on business credit.
This is credit in a business’s name. It does not tie to the owner’s creditworthiness. Instead, business credit scores depend on how well a company can pay its bills. Hence consumer and business credit scores can vary dramatically.
Also, there are no demands for a personal guarantee. You can quickly get business credit regardless of personal credit quality. Also, there is no personal credit reporting of business accounts. Business credit utilization won’t affect your consumer FICO score. Plus the business owner isn’t personally liable for the debt the business incurs.
Being accepted for business credit is not automatic. Building business credit requires some work. Some of the steps are intuitive,and some of them are not.
There are three chief credit bureaus for business: Dun & Bradstreet, Experian, and Equifax.
In the business world Equifax and Experian are up there, but it’s Dun & Bradstreet which is the major player.
D&B has more than 10 times the records of the next closest reporting agency. See dnb.com/about-us/company.html.
Do you have a copy of your Dun and Bradstreet report?
They are the oldest and largest credit reporting agency. You need a D-U-N-S number to start building business credit. Go to D&B’s website and look for your business, atdnb.com/duns-number. Can’t find it? Then get a free D-U-N-S number. You will always need a D-U-N-S number to start building business credit. Go here to get a D-U-N-S number and get into their system: dnb.com/duns-number/get-a-duns.html.
The main score is PAYDEX. But a business will not get a PAYDEX score, unless it has at least 3 trade lines reporting, and a D-U-N-S number. A business needs both to get a D&B score or report.
D&B offers database-generated reports. These help their clients decide if a business is a good credit risk. Companies use the reports to make informed business credit decisions and avoid bad debt.
Usually, when D&B does not have all of the information that they need, they say so in their reports. But missing data does not necessarily mean a company is a poor credit risk. Rather, the risk is unknown.
D&B’s database contains over 350 million companies around the world. It includes millions of active firms, and over 100 million companies which are out of business. But they keep these for historical purposes. This data goes into their reports.
D&B lists over a billion trade experiences. For as accurate a report as possible, give D&B your company’s current financial statements.
To see a sample Business Information Report, go to products.dandb.com/download/2019_BIR-Snapshot-Report.pdf
D&B takes historical information to try to predict future outcomes. This is to identify the risks inherent in a future decision. They take objective and statistically derived data, rather than subjective and intuitive judgments.
Here are the sections you could currently see in a typical Dun and Bradstreet business credit profile report.
The report starts with basic company information, such as number of employees, year the business was started, net worth, and sales.
This rating helps companies quickly assess a business’s size and composite credit appraisal. Dun & Bradstreet bases this rating on information in a company’s interim or fiscal balance sheet plus an overall evaluation of the firm’s creditworthiness. The scale goes from 5A to HH. Rating Classifications show company size based on worth or equity. D&B assigns such a rating only if a company has supplied a current financial statement.
The rating contains a Financial Strength Indicator. It is calculated using the Net Worth or Issued Capital of a company. Preference is to use Net Worth. D&B will show if a business is new or if they never got this information.
This section also adds a Composition Credit Appraisal. This number runs 1 through 4. Also, it reflects D&B’s overall rating of a business’s creditworthiness.
The scores mean:
A D&B rating might look like 3A4.
Keep your business protected with our professional business credit monitoring.
This part shows two gauges. One is an up to 24 month PAYDEX. There’s also an up to 3 month PAYDEX. Hence you can see recent history and a firm’s performance over time.
Both gauges have the same scores. A 1 means greater than 120 days slow (in paying bills). A score of 50 means 30 days slow. One great score is 80, which means prompt. Also, 100 means anticipates. A 100 is the best PAYDEX score you can get.
This is Dun & Bradstreet’s dollar-weighted numerical rating of how a company has paid the bills over the past year. D&B bases this score on trade experiences which various vendors report. The Score ranges from 1 to 100. Higher scores mean a better payment performance. PAYDEX scores reflect how well a company pays its bills.
This next section shows likelihood of business failure. It also shows how frequently a business is late in paying its financial obligations. These are comparative analyses, the Financial Stress Class, and the Credit Score Class.
Overall numbers range from 1 to 5. A 1 is businesses least likely to fail. Also, a 5 is firms most likely to fail. The Financial Stress Class measures likelihood of failure.
These more granular scores range from 1,001 to 1,875. A score of 1,001 represents the highest chance of business failure. Also an 1,875 shows the lowest chance of business failure.
The Credit Score Class measures how often a company is late paying its bills. Overall numbers range from 1 to 5. A 1 is businesses least likely to be late. 5 is firms most likely to be late making payments. More granular scores run from 101 to 670. 670 is the highest risk.
It shows a spectrum of risk. Your risk category can be low, moderate, or high. Risk is assessed using D&B’s scoring methodology. It is one factor used to create the recommended limits.
This section contains:
This part repeats the D&B Rating above. It includes financial strength, the composite credit appraisal, and payment activity.
This section contains information on ownership. It also shows where a corporation is filed (i.e. which state). This includes the type of corporation, and the incorporation date.
This section gives basic information on if a company works as a contractor for the government. It also shows the kind of business a company is in. It shows what the facilities are like, including general data on its location.
The section shows the business’s SIC and NAICS codes. It also shows where the branches and subsidiaries are. This list is just the first 25 branches, subsidiaries, divisions, and affiliates, both domestic and international. D&B also offers a Global Family Linkage Link to view the full listing.
This section is for the financial statements D&B has on a business. It shows assets and liabilities, with specifics such as equipment, and even common stock offerings.
This part shows public records, like judgments, liens, lawsuits, and UCC filings.
This part also breaks down where filings are venued, like the court or the county recorder of deeds office. It shows if judgments were satisfied (paid). It also shows which equipment is subject to UCC filings.
This part shows the Credit Score Class again. It also shows a comparison of the incidence of delinquent payments. It also includes key factors to help anyone reading the report interpret these findings. Also, it explains what the numbers mean.
Here, D&B compares a company to others on the basis of region, industry, number of employees and time in business.
This section shows a Financial Stress Class and a Financial Stress Score Percentile. The Financial Stress Class runs from 1-5, with 5 being the worst score.
The Financial Stress Score Norms calculate an average score and percentile for similar firms. The norms benchmark where a business stands. This is in relation to its closest business peers.
It is a comparison to other businesses. The percentile contains a Financial Stress National Percentile. The Financial Stress National Percentile reflects the relative ranking of a company among all scorable companies in D&B’s file. It also contains a Financial Stress Score. The report shows the chance of failure with a particular score.
Keep your business protected with our professional business credit monitoring.
The idea behind this score is to predict how likely it is a business will fail over the next 12 months. The Financial Stress Class shows a firm shares some of the same business and financial characteristics of other companies with this classification. It does not mean the firm will necessarily experience financial stress. The chance of failure shows the percentage of firms in a given percentile that discontinue operations with loss to creditors.
The average chance of failure comes from businesses in D&B’s database. It is provided for comparative purposes. The Financial Stress National Percentile reflects the relative ranking of a company among all scorable companies in D&B’s file. The Financial Stress Score offers a more precise measure of the level of risk than the Financial Stress Class and Percentile. It is meant for customers using a scorecard approach to determining overall business performance.
This section repeats the 24 month and 3 month PAYDEX gauges. It also includes a repeat of the Credit Limit Recommendation. There is also a PAYDEX Yearly Trend. It shows the PAYDEX scores of a business compared to the Primary Industry from each of the last four quarters.
The PAYDEX Yearly Trend is a graph. It includes detailed payment history. with payment habits and a payment summary. This helps show if a business pays its bigger bills first or last.
Get your report from D&B at www.dnb.com/about-us/our-data.html. Update the relevant information if there are mistakes or the information is incomplete. At D&B, you can do this at: dnb.com/duns-number/view-update-company-credit-file.html.
Keep your business protected with our professional business credit monitoring.
None of the different business bureaus will change your scores without proof. They are also starting to accept more and more online disputes. Include proofs of payment with it. These are documents like receipts and also cancelled checks.
Fixing credit report errors also means you specifically spell out any charges you challenge. Make your dispute as crystal clear as possible. If you need to snail mail anything in, then use certified mail. This is so you will have proof that you sent in your dispute.
Be specific about the concerns with your report. D&B wants you to go through their Customer Service. You can also go through D&B Customer Service to add payment experiences. D&B’s Customer Service contact number can be found at dandb.com/glossary/paydex.
Business credit reports are not always perfectly correct. All of the major CRAs are committed to accuracy. But you won’t know there are errors unless you monitor your business credit reports.
For D&B only, you can monitor your reports via CreditMonitor. It currently costs $39/month. See dnb.com/products/small-business/credit-monitor.html.
You can monitor your business credit at D&B, Equifax, and Experian through Credit Suite, for considerable savings over what it would cost you at those different credit bureaus. And all in one place! Credit Suite offers monitoring through the Business Finance Suite (through Nav). See what credit issuers and lenders see. So you can directly improve your scores and get the business credit and funding you need. See suitelogin.com and also creditsuite.com/monitoring.
Dun & Bradstreet reports sport an impressive level of detail. The idea is to make it easier to decide if it’s a good idea to extend credit to another business. Also, your own company’s report can help show you where you can improve payment history. Also, you can see how your firm compares to similar businesses.
D&B is the largest business CRA. A D-U-N-S number is an absolute necessity for business credit building.
Monitoring all of your reports is expensive. But you can save 90% by monitoring your D&B, Experian, and Equifax scores through Credit Suite.
The post Learn About Dun & Bradstreet Reports appeared first on Credit Suite.
Have you ever looked at a really successful brand or person – a celebrity, say, or a big company – and wondered, “How on earth do they do it?”
Apple is one of those brands for me. Almost everything the company puts out succeeds. The company has enjoyed almost unparalleled revenue growth from 2004 to 2020 — $8 billion to $2,274 billion. That’s astounding.
But Apple’s success isn’t just a matter of making a lot of money, or selling a lot of products. How many brands that have completely changed the game in their niches the way Apple has?
Not only that, but Apple’s done it several times over, despite some strong criticism from the naysayers. The iPod, the iPhone, the iPad–all of these products pretty much revolutionized their respective market “space.” Their success is a direct result of their marketing strategies.
Apple’s marketing mix creates raving fans who stand in line for hours and hours on end, just to get the first iteration of any new product the minute it’s released throughout social media.
Apple does what it does so well that there are whole websites out there devoted to nothing but Apple products and Apple marketing. Even high-end journalistic publications like The Atlantic write endlessly about the company, dissecting what it does and how it does it.
Apple goes way beyond the “computer brand” label — they create products for their target market, loyal customers that believe make these products life better, easier, more fun, and cooler.
How on earth do they do it?
Well, design and utility are just two of the reasons behind Apple’s success and certainly give it a competitive advantage.
But, more importantly for you and me, Apple’s secrets for transforming casual purchasers into brand ambassadors can be applied to just about any business in any niche or industry.
In this article, I’m going to reveal seven pillars of Apple’s world-famous marketing mix that you can adapt for your own business.
It’s tempting to drop lots of cash on PPC ads with Google or Facebook when you want to increase your sales revenue. But, Apple knows that’s not always necessary.
In fact, Apple relies most on two completely different strategies: product placement (especially with celebrities and in popular shows) and the buzz created by positive reviews in the media.
This secret was revealed in Apple’s patent litigation with Samsung, believe it or not:

Even if you don’t have Apple’s resources and budget, you can still take advantage of this approach to increase your market share. But, you may be asking yourself “How could I possible implement this Apple marketing secret in my own business?”
Well, it may not be possible to put your product in the hands of a Kardashian, or on the set of a popular TV show.
But, you can absolutely approach insiders and influencers. If you persuade an influencer that your product or service is worthwhile and relevant to their audience, they’ll share it with their followers.
Another way to use this Apple secret is to embrace a free trial program. Offer a free trial of your service or product, in exchange for a positive testimonial.
If a free trial of your product isn’t feasible, then get in touch with your existing satisfied customers and ask for a positive testimonial or review.
Publish those testimonials on your site. This isn’t a difficult component of your marketing mix to develop.
I’ve been publishing testimonials from my satisfied clients on this site for some time now, and I can attest to the fact that they help persuade prospects to convert into clients and subscribers. You’ll see some of those testimonials on this very page.
Don’t forget to attribute each testimonial with an image or avatar, the person’s name, and a link back to their own website, if possible. This adds more social proof to the customer’s positive review of your brand and gives greater legitimacy to your target market.
You can also implement this winning Apple strategy by creating more case studies.
Nielsen research on consumer trust in marketing shows that 92% of consumers trust recommendations they get from friends and family, while 70% of shoppers trust opinions from other consumers that are published online, such as reviews.
Consider using this outline to create your case studies:

Last, but far from least, if you are going to launch a PPC ad campaign, make sure you go about it the smart way.
Choose your PPC network carefully; create a clean, well-written landing page with a clear call-to-action and make sure your ad copy and landing page are completely aligned.
If you need more help with PPC ads, the following resources will help:
Many entrepreneurs believe – falsely – that they have to compete on price. Nothing could be further from the truth.
In fact, competing on price can actually hurt your business.
Apple knows this and has never wavered on its pricing strategy.
Dropping prices and competing on price leads to a “race to the bottom.” If you’ve ever looked at job boards for freelancers, you might see some strange things. For some sites, the going rate for a blog post is $10, or even less!
This might sound like a great idea, but it’s really short-sighted when developing market share. “You get what you pay for” has never been more true than when businesses and freelancers try to underbid each other. Content marketing requires quality and it will be hard to get that for dirt cheap rates.
Your $10 post is almost certainly going to be poorly written, with no exclusive research or data to back up opinions. And, that post could simply be regurgitated from someone else’s site – or even outright copied, word for word.
Even Copyscape can’t protect you from junk content. The foundation of content marketing is quality content as the cornerstone of a marketing mix.
That’s because no freelancer could survive on $10 per piece, unless they can create each piece in bulk. But your marketing strategy won’t survive if you don’t work on smart quality.
Instead, do what Apple does.
Apple focuses on their UVP (unique value proposition), which is beautiful design that works right out of the box with ever-smaller packaging. It’s a marketing strategy that gets juice throughout social media and is very much a competitive advantage for Apple and its market share.
What about cost? Well, let’s just say Apple is absolutely not competing on price! In fact, you’ll almost certainly pay more – sometimes a lot more – for an Apple product than you would for a competitor’s version of the same product.
Take some computers, for example – let’s say, two similar laptops, like the Microsoft Surface Pro, which costs about $900. Apple’s Macbook Pro, on the other hand, costs over $1,200.
How can Apple keep its fans with a pricing strategy so much higher than the competition?
It’s because Apple doesn’t view PCs as competition. Where others focus on a single killer feature through a variety of content marketing, Apple focuses on the entire product, and it shows.
In fact, Apple routinely earns its higher prices with top-of-the-line features and specifications.
You can implement this same strategy, no matter what niche or industry you’re in and regardless what your business model may be.
Whether you’re selling products or services, the key to making this strategy work for you is to make sure that you justify that higher price to capture your market share.
For SaaS companies, that could mean creating a higher degree of personal service or a full money-back guarantee.
For coaches or consultants, the competitive advantage could mean beautifully branded deliverables, in addition to work sessions or Skype calls.
You can also follow Apple’s example by offering a variety of options for your products and services at different price points. For instance, Apple’s Macbook laptop line offers larger screens and other enhanced features, for a higher price.
Yes, Apple is like the Rolls Royce of technology products with a retail store design that look more like a show room. Their customers are more than happy to pay that premium, because they know they’ll get their money’s worth.
More isn’t always better.
Apple understands that technology consumers often get overwhelmed. That’s true of other niches and industries, as well. Overwhelm can create a confusion in a marketing mix.
Apple reduces that consumer confusion by simplifying their web and sales copy. They completely eschew jargon or industry terms. Instead, they use simple, direct words and they continually stress the benefits that consumers absolutely need and will be thrilled by. This is part of their brilliance in content marketing; high tech without high tech terms.
This approach doesn’t confuse their customers with too much information. As Leonardo da Vinci said,
Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication.
Apple keeps it simple and their customers love it giving them a loyalty with market share that is unprecedented.
Apple also follows through with this principle in the ads it does run. Remember those classic “Mac vs. PC” spots?

What Apple’s ads and marketing strategies convey isn’t specifications and features, but rather how the product can change your life and make it better.
But Apple doesn’t stop there. This is just step one in their marketing strategies.
They carry this philosophy of “simpler is better” through to their product lines, too. They don’t overwhelm prospective customers with too many choices, parameters or options. An Apple retail store is designed for test driving products not grabbing boxes.
Even the products themselves are kept sleek and minimal, with simple color schemes and clean, uncluttered design. The names are short and easy to remember, including the “app store” that has made third party partners huge successes.

How can you follow Apple’s marketing strategies in your own business to capture the biggest market share?
Start by making sure your website and blog have scannable content. Research shows that only 16% of website visitors read every word on a page. The vast majority of users – 79% of web users, in fact – simply scan the page. This is imperative in understanding your content marketing and potentially using social media with smaller bits of digestible date.
To make your content scannable, use bullet points to convey benefits. Make sure that your headings and subheadings are clear, vivid and surrounded by plenty of white space. Easy to read means the target market will stay on the page and come back, increasing your market share.
Look at my homepage here, to see how I’ve done it:

You’ll notice in the above screenshot that I haven’t cluttered up the page with tons of text. There’s lots of white space surrounding the bullet points and only one image – mine – to call attention to the bullet points.
Don’t try to put every single feature of your product or service on the page.
Instead, focus on the most valuable UVP for each product. Then, stress that.
One great example of this in action is Virgin Mobile’s phones page:
Select a clean, minimalist design for your landing pages. Reduce clutter around the important sections of your page’s content, such as sidebars and widgets. Then, the user’s eye is drawn to the product or copy itself.
Finally, if you have the budget, I’d recommend hiring a professional copywriter, especially on crucial product and services sales pages. It’s not easy to give enough information to trigger a conversion or a sale while still keeping that streamlined, simplified approach.
It’s not that Apple doesn’t mention product specifications and technical details at all. In fact, every product page on the Apple website does mention those things.
But, they put it below-the-fold. Visitors to Apple’s website first have to scroll past beautiful product images and large-font simple copy telling them about the product’s benefits.
Initially, Apple customers won’t find words like megabytes or gigahertz. They find words they know and understand:
Apple knows its customers very well and has developed loyalty in their market share. And, they know how to speak to them in the language that makes them feel comfortable, not overwhelmed and confused.
The products themselves are a marketing mix that show off their relevance to the way Apple’s customers actually live their lives. For instance…
Is your website copy speaking your prospects’ language? Creating a customer profile for each of your main audience segments is the best way to find out. This helps develop the content marketing strategies specific to your audience.
Even better, the process of creating these profiles will help you to understand your audience much better. Then, you can give them what they’re looking for – and make your content even more appealing and valuable to them.
Here’s how to make sure that you’re talking to your users and customers in a way they understand and feel comfortable with.
Create customer personas for each major audience segment of your business. The more detailed these profiles are, the more useful they’ll be and beneficial to your marketing strategy.

Include factors such as age, gender, profession and other demographic information, plus psychographics – their pain points, fears, desires, etc. What motivates them to buy? What do they need before they’ll trust you? How can you fill that need?
You may have more than one profile expanding your marketing mix – e.g., older couples whose kids have already left home, singles who’ve graduated from college and haven’t married or had kids yet, etc.
Name and find a picture of a person – either from Google Images or a stock image site – that matches the profile. The idea here is to make each profile seem like an actual, living human being.
Here’s an example of a built-out customer profile, complete with name and picture, from Convince and Convert:

Speak to these people in your marketing copy, with the language they understand. Look at each page on your website and revise anything that doesn’t sound like the way you’d actually speak to these folks.
Pretend you’re actually speaking to that person and your copy will appeal strongly to similar customers.
You can also carry that same customer-centered approach throughout every aspect of the customer’s journey, including customer service. Yes customer service is a key component in marketing strategies to develop loyalty and retain your market share.
Let’s say that you’re serving an older generation. Don’t force them to use a chat-based system for customer service. Give them a phone number and a person to speak to. And, make sure that your website copy is large enough for older people to read. Giving people what they want is how you capture greater market share.
Millennials, on the other hand, prefer chat-based systems, since they’re faster and easier to use for that generation. Don’t make these customers pick up the phone, when they really prefer to type out their problem and get an instant response. Understanding this diversity of your customers helps you develop the right marketing mix.
Did you know Apple fans often create videos of themselves unwrapping their new Apple products and upload the video to YouTube?
It’s true. It’s called unboxing. Do a search on YouTube and you’ll find hundreds of Apple unboxings, each from different users across the globe.
Why does that happen?
Because Apple has created a customer experience that goes far beyond the actual purchase in a retail store. They no longer even need to be in charge of a huge part of their content marketing since their target market is doing it for them.
The “Apple experience” includes elements from every aspect of the purchasing process – comparing different product versions, trying out products in the retail store, actually buying the item, receiving it, unwrapping (sorry, unboxing) it, and setting it up.
Each of these elements doesn’t just happen by chance. They were all carefully crafted, revised and refined to appeal to the consumer’s every sense.
Take installation, for example. One of the things Apple fans truly appreciate about Apple’s computers is the ease with which you can set them up. It’s literally as simple as opening, plugging in, turning on and, voila – it all just works.
Yes, Apple spends thousands of hours on testing and designing and refining those designs. They do that so that what’s inside the box matches the box, and the box matches what’s inside.
The Apple retail store experience isn’t just a quick trip for most people. Most people who enter an Apple store end up staying in the retail store, trying the products, asking questions of the “geniuses” who work there – and many of them walk out with a new purchase. The Apple retail store inspires purchases.

The retail store is carefully designed and replicated to evoke the right “feeling” when you step inside. Warm lighting, monochromatic color schemes, and the layout of the store features all appeal to the shopper’s senses, without feeling cold and impersonal. Even the large front windows that let people outside see everyone inside having a great time are intentional.
To implement Apple’s “eye for design” secret, start by charting out your customer’s experience with your brand. Note each major step and where it takes place (i.e., on your Facebook page, a specific page on your website, etc.).
Next, analyze each piece of that “experience puzzle” and score how well it fits with your overall brand. What can you improve?
Think about ways that you can make each point of contact with your prospect or customer cleaner, clearer and simpler. Make each part of the journey more consistent with the look, feel, visual branding elements, and personality of your brand.
Then, think about going even further. What could you do to delight your customer?
That’s the Apple way!
Think back to the first ads for the iPad, after its buzzy launch in 2010 and how simple their content marketing was.
Remember those images of people relaxing in the living room with the strange new gadget? They looked happy and comfortable.
They weren’t talking about display dimensions or processing power. They were just enjoying their iPads.
Those ads, as with all of Apple’s marketing, hit their consumers where they really live – not in the pocketbook (we’ve already seen that’s not true at all!) but in their hearts.
Emotional connections are the key to successful marketing strategies. It’s what makes certain stories, videos, and memes go viral.
Dr. Jonah Berger’s famous study showed that content that evokes high arousal emotions is more likely to go viral than content that provokes no emotional response. Examples of high arousal emotions are happiness, awe, amusement and anxiety.
Moreover, positive content is more likely to go viral than negative content. Positive emotions simply trigger a stronger reaction in users’ brains than negative ones. These are simple marketing strategies.
In his book, Descartes’ Error, author Antonio Damasio, a professor of neuroscience at the University of Southern California, states that our emotions play a crucial part in our decision-making processes, especially when we’re buying something. Marketing strategies must start with emotion.
And, neurological science tells us the same thing. Functional MRI tests prove that when consumers evaluate businesses, they primarily use the parts of their brain associated with emotions, personal feelings, and memories/experiences, not the portions associated with facts.
Above all, you’ve got to understand and publish the kind of content that your target audience wants most of all. Smart content marketing gets you the most on the web’s leading social media networks? Turns out, it’s content that evokes either awe or laughter – or both.
The testing team at BuzzSumo wanted to understand just what makes content go viral and get shared thousands of times by users. So, they teamed up with OKDork and conducted an extensive study about the marketing mix in social media.
First, the team identified the most shared content all over the web, within a specific time period. Next, they mapped each of the articles to a specific emotion, such as joy, anger, sadness, happiness, laughter, amusement, empathy, etc.
Here’s what the breakdown they created looked like:
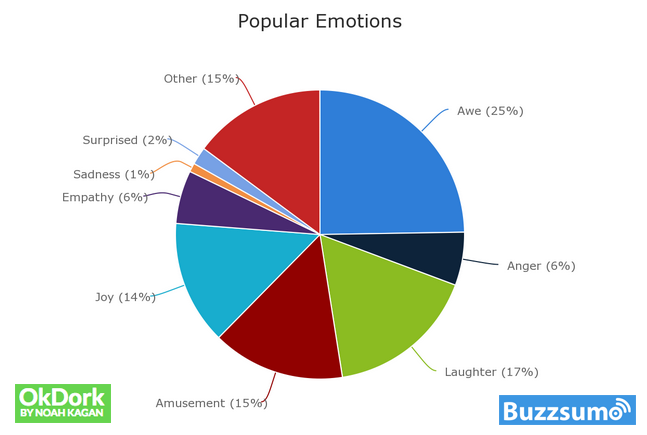
You can see from this chart that the top two emotions that the most viral content evoked in readers were awe (25%) and laughter (17%). Similar emotions, such as joy and amusement, accounted for another 29%.
What this means is that if you can quite literally make your readers happy with your content, you’ve really hit the target.
To evoke and build on your customers’ emotions the way Apple does, use emotional language in your copy where it makes sense to do so. Make sure it flows naturally. One way to do this is to use emotion-trigger words in your copy to develop smart content marketing material.
Tip: To make sure copy flows naturally, record yourself as you read it aloud. Then, play it back. If it sounds stilted or formal, revise it until it sounds more conversational.
Also, think about what emotional impact your product or service evokes in your customers. Then, look for or create images to use that evoke that same emotion.
Here’s an example: JustGiving, the world’s leading online fundraising platform, raised almost $1.5 million for its charitable partners. Look at this landing page image that the site uses:
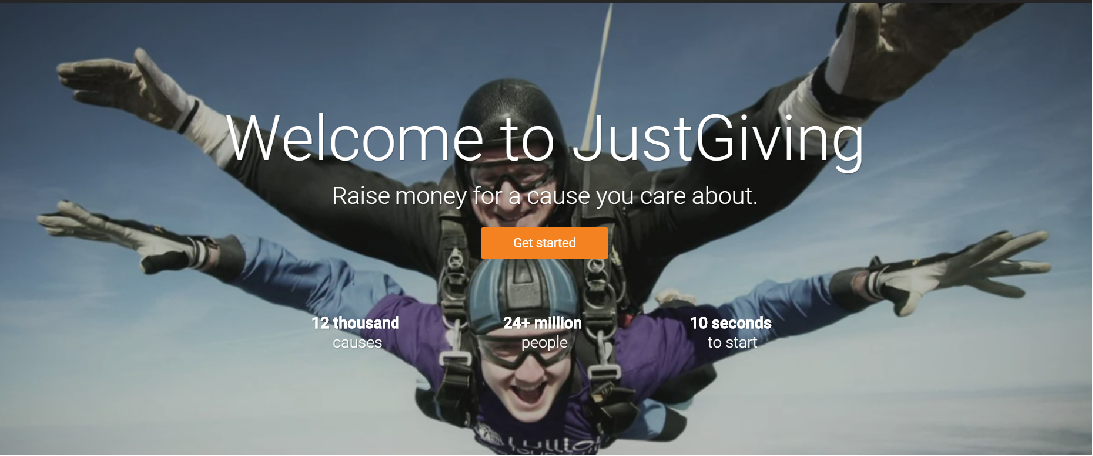
What emotions does this image evoke for you? Personally, I see joy and awe – skydiving has got to be one of the world’s most awe-inspiring activities, after all.
There’s also the empathy and happiness that being generous and giving to worthwhile causes can create for people making charitable donations.
Finding the right images for your content can take some time and patience, but it’s so worthwhile. Images not only create visual interest on your page and break up long blocks of boring text – they can also help communicate your message and convert readers to subscribers.
In fact, I believe so strongly in the power of great images and screenshots that I routinely use as many as sixty in a single post – but I always make sure they add value, as well as depict the right emotional state in my readers. This is part of my marketing mix.
Over the years, Apple has built one of the most hardcore fan bases for any brand, anywhere in the world.
The “fanboys” (and “fangirls”) who camp out for new product launches may represent a small percentage of Apple consumers overall, but that kind of fanaticism and enthusiasm are rare.
Apple has created a brand personality and culture that’s cool, fun, and friendly — the opposite of some of its competitors. Apple’s marketing strategies include making customers want to belong to that community. Their market share shows just how successful they have been.
Do you remember Apple’s “Think Different” ad campaign? It started with voiceover narration that said “Here’s to the crazy ones. The misfits. The rebels. The troublemakers.” Haven’t we all felt like that at one time or another in our lives?
Apple smartly capitalized on the universality of that self-perception, which made its customers believe that the brand understands them and is like them.
Even small brands can build a community of devoted users and customers. You can start building a community before you even offer the first item for sale.
The first and most critical step to take in building a strong, vibrant and engaged community of users is to get crystal-clear on your brand values and personality.
You have to create a vivid and accurate picture of your brand in your own mind first — your brand’s core message, its deeply-held values, its personality and what it stands for above all else.
Then, your next step is to make sure that your pages, marketing copy and content all express those values and that personality. Every aspect of your website should be consistent with those words you chose to describe your brand, from graphics to fonts to color scheme.
Last, but not least, show your readers and users you value them, as well as their opinions. Let them know that you’re deeply interested in them with your content.
How can you do this effectively on the web? You can try any or all of the following tips to start with:
One of the fastest ways to achieve a goal is to model those who’ve successfully achieved that same goal before.
Apple, the app store, and their retail shops are role models for any smart, modern brand that wants to create a raving fan base and super-loyal customers who will refer their friends and family members.
The idea isn’t to mimic Apple. Rather, get a sense of what Apple – or any other successful business – does well, then find creative ways to do the same in your business, always keeping the marketing mix consistent with your brand.
You can learn a lot from your competition, too. Competitor analysis can tell you what they’re doing right and what you can learn from and implement in your own marketing.
What other lessons can you draw from Apple’s marketing efforts?
Article URL: https://www.workatastartup.com/events/startup-career-expo-s20
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=24699981
Points: 1
# Comments: 0
The post Meet founders from Y Combinator’s S20 class and learn about open roles appeared first on ROI Credit Builders.
Most of us grew up hearing that we could do anything we wanted. That’s the beauty of capitalism. With American business lending, anyone can start a business. We are told all we need is a great idea, and with a lot of hard work and a business loan, we can turn that idea into a … Continue reading Business Fundraising: What You Didn’t Learn in Kindergarten
Most of us grew up hearing that we could do anything we wanted. That’s the beauty of capitalism. With American business lending, anyone can start a business. We are told all we need is a great idea, and with a lot of hard work and a business loan, we can turn that idea into a thriving livelihood. The thing is, the business fundraising piece isn’t as easy as we may have thought.
I mean, the majority of us are smart enough to know that not all new businesses see success. We also know getting investors and loans is not always easy. The thing is, no one tells us what to do if business fundraising turns out to not be as easy as we thought. No one really gives any options, which means when we hit that first brick wall of a lender turning us down for a loan or an investor saying no, we don’t know what our next move should be.
Get our business credit building checklist and build business credit the fast and easy way.
For starting up a small business, the first stop on the business fundraising train is typically the bank. You go in, fill out a business plan, and hope for the best. If your personal credit is stellar, you are golden. If not, you have a problem.
That’s why traditional loans do not always work. If your personal finances cannot handle the up-front expense of starting a business, and you do not have investors, you have to find another way. This is the part that no one tells you. How on earth do you start a business if you cannot get a business loan based on your personal credit.
Okay, so, here’s the thing. You are going to have to get your business going a little at the time, on your own. Surprisingly, this strange economy created by the coronavirus is prime for this. Maybe you take on a few clients or sell to a few customers in your spare time. Who knows? You need to be in business for at least 6 months before you start applying for these types of loans. In fact, some require a year in business and a minimum revenue.
They key is, you get started, and you get started on your own. Then you figure out where you can turn for business fundraising to grow your business further. If you hit the one year in business mark, you may qualify for SBA loans.
The Small Business Administration is designed specifically to help small businesses. Whether you need working capital or a natural disaster has struck, the SBA can help.
Overall, there’s a wide range of products offered through SBA programs. Typically, the SBA does not lend funds directly. Conversely, they work through lender partners to guarantee loans. This means, they are able to leave the administration of the loans and disbursement of funds to those who regularly handle that sort of this.
This is the Small Business Administration’s most popular loan program. It offers federally funded term loans of up to $5 million. Additionally, the funds can be used for expansion, purchasing equipment, working capital and more. Banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions, in partnership with the SBA, process these loans and distribute the funds.
A credit score of 680 is necessary to qualify. In addition, there is a required down payment of at least 10% for the purchase of a business, commercial real estate, or equipment. Lastly, the minimum time in business is 2 years. Business experience equivalent to two years will do the trick for startups, so this is one you don’t have to wait for if you have experience.
These loans are available up to $5 million. Funds can buy machinery, facilities, or land. Generally however, they are for expansion. Private sector lenders or nonprofits handle these loans. They especially work well for commercial real estate purchases.
Microloans are available in smallter amounts. They go up to $50,000. Typically, they work well for starting a business, purchasing equipment, buying inventory, or for working capital. Community based non-profits administer microloan programs. Unlike the others, financing comes directly from the Small Business Administration.
Even though SBA loans have less stringent requirements, sometimes they still won’t do the trick. What then?
If you see that you do not qualify for SBA Loans, private loans could be an option. They should be the second option for business fundraising, after SBA loans. Here’s why. They typically have higher interest rates and less favorable terms than traditional and SBA loans. That’s the downside. The upside is that their eligibility requirements are even easier to meet than SBA loans, making them a viable option if you do not qualify for other types of financing.
There are lots of private lenders out there, but be careful. Do your research, check the Better Business Bureau, and read reviews so that you know what you are getting into. Some of them are fine, but there are a lot of bad seeds in this category as well. Proceed with caution. Here’s a list of lenders to get you started.
Fundation offers an automated process that is super-fast. Originally, they only had invoice financing. Then they added the line of credit service. Repayments are automatic, meaning they draft them electronically. This happens on a weekly basis. One thing to remember is that you could have a repayment as high as 5 to 7% of the amount you have drawn, as the repayment period is comparatively short.
You can get loans for as little as $100 and as high as up to $100,000, but the max original draw is $50,000. They do have some products that go up to $500,000. There is no minimum credit score requirement, but they require at least 3 months in business. Also, $50,000 or more in annual revenue and a business checking account with a minimum balance of $500 are necessary.
Fundation reports to Dun & Bradstreet, Equifax, SBFE, PayNet, and Experian, making them a great option if you are looking to build or improve business credit.
The minimum amount available from BlueVine is $5,000 and loans go up to $100,000. You must have annual revenue of $120,000 or more. In addition, the borrower must be in business for at least 6 months. The personal credit score minimum is 600. It is also important to know that BlueVine does not offer a line of credit in all states.
They report to Experian. They are one of the few invoice factoring companies that will report to any business credit bureau.
Get our business credit building checklist and build business credit the fast and easy way.
With OnDeck, applying for financing is fast and simple. You apply online, and you will receive your decision once the application processing is done. Loan funds go directly to your bank account. The minimum loan amount is $5,000 and the maximum is $500,000.
The personal credit score requirement is 600 or more. Also, you must be in business for at least one year. The annual revenue requirement is at least $100,000. In addition, there can be no bankruptcy on file in the past 2 years and no unresolved liens or judgements.
OnDeck reports to the standard business credit bureaus.
Okay so, that’s how to make it work in the beginning. Still, wouldn’t it be great to not have to worry about it? How would it feel to know that, if you needed a business loan, you would have no trouble getting one? How does that even happen?
While there are no guarantees in life, the best chance you have at making this happen is to build strong business fundability. That is your ability to get funding for your business based on the merits of your business and not completely on your own personal finances. To do this, you have to understand exactly what it is that makes your business fundable. There are a lot more working pieces than you may imagine.
The first step in building fundability has to do with how you set up your business. Regardless of whether you are just getting started or if you have been operating for ages, if these things are not done, do them now. The sooner the better. You cannot build business fundability if you do not establish your business as an entity separate from yourself, and that doesn’t just happen. You have to make it happen.
Make sure your business has its own phone number, fax number, and address. That doesn’t mean you have to get a separate phone line, or even a separate location. You can still run your business from your home or on your computer. There are options for virtual business addresses and internet based phone numbers that will serve these purposes nicely.
Next, get an EIN for your business. This is an identifying number for your business that works in a way similar to how your SSN works for you personally. It’s free from the IRS.
You have to incorporate your business as an LLC, S-corp, or corporation. Which option you choose doesn’t really make a difference for fundability. However, it can make a difference for your budget and needs for liability protection. Talk to your attorney or a tax professional about which one will work best for your business.
You are going to lose any time in business that you already have. When you incorporate, you become a new entity. You basically have to start over. You’ll also lose any positive payment history. This is why you have to incorporate as soon as possible.
Separate Bank Accounts
Open a separate, dedicated business bank account. There are a lot of reasons for this, but the first one is that it creates the separation you need to start building business credit, which is necessary to fundability.
Licenses
A legitimate business should have all of the licenses it needs to run. If it doesn’t, red flags are going to go up all over. Research what you need to do to ensure you have all of the licenses necessary to legitimately run your business at all levels.
Website
Spend the time and money necessary to make sure your website is professionally designed and that it works. Also, splurge and pay for hosting. Don’t use a free hosting service. Along these same lines, your business needs a dedicated business email address. Make sure it has the same URL as your Website. Don’t use a free service such as Yahoo or Gmail.
While setting up your business in this way is vital, there are a host of other things that affect fundability. Here’s a brief rundown.
This is a cornerstone of fundability.
Two examples of this are LexisNexis and The Small Business Finance Exchange.
Specifically a D-U-N-S number. Get one on the D&B website. You cannot have a business credit file with Dun & Bradstreet without one. Since they are the largest and most commonly used business credit agency, you have to get this number.
This includes how many accounts you have, what types of accounts, and whether or not you pay on time.
Not only do you have to have separate contact information for yourself and your business, you need to be consistent with when and where you use it. For example, if a business account has your personal address on it, it could cause problems. Be sure to keep everything up to date.
One example is ChexSystems, which keeps track of bad check information.
This is everything to do with the application from when you apply to which lending products you choose to apply for.
Get our business credit building checklist and build business credit the fast and easy way.

If you hit a brick wall with traditional loans, don’t despair. Don’t let problems with business fundraising stop you. Just fix the problem. There are other options. In addition to these financing options and finding investors, you can explore grants and crowdfunding. While the fierce competition with each can make it hard, they are still viable options. However, you have to start working on fundability now, wherever you are in the life of your business. If you do, one day you will not have to worry about business fundraising. You will be able to access all you need.
The post Business Fundraising: What You Didn’t Learn in Kindergarten appeared first on Credit Suite.