What Are Canonical Tags?
Itching to learn about canonical tags? First, let me explain why they’re relevant to your website ranking.
There’s been a longstanding belief that Google penalizes duplicate content. In case you haven’t already heard, that’s not strictly true.
As Google search advocate John Muller explains:
“…it’s not so much that there’s a negative score associated with it,”
“It’s more that if we find exactly the same information on multiple pages on the web, and someone searches specifically for that piece of information, then we’ll try to find the best matching page.”
Additionally, on its ‘how to avoid duplicate content’ page, Google states:
“Duplicate content generally refers to substantive blocks of content within or across domains that either completely match other content in the same language or are appreciably similar.”
As Google makes clear, there are times when a website owner has a genuine reason for having duplicate content, like online stores or printer-only web pages. However, these duplicate pages can cause confusion for search engines, and they don’t always know which is the original or which page you want to prioritize.
How do you get past this? You could try 301 redirects or use top-level domains, but you could also use a canonical tag URL.
If you’re wondering what canonical tags are, or you want to know how they can help you, read on to find out more.
The Basics of Canonical Tags
In the most basic terms, a canonical tag is an HTML snippet (rel=canonical). As I’ve touched on in the intro, you implement a canonical tag when you want to indicate to the search engines which is the original page. For example, you might have multiple versions of a page if you’re an e-commerce site owner or if you’ve got a mobile and desktop version of your website.
Now, if you wanted the search engines to prioritize the mobile pages, you’d add a self-referencing canonical tag to the mobile version to tell the search engine to index that page. This means that the URL attached to the rel=canonical is the page itself.
In other words, once you implement canonical tags, the search engines know which pages to dismiss and which ones to display in the SERPs.
Canonical tags are simple to add to your page by including rel=”canonical” in your header, but what does this do for your SEO?
How Do Canonical Tags Help SEO?
Canonical tags are an essential part of any SEO strategy, enabling your site to rank higher. There are several ways they do this:
First, they tell search engines which URL version is the “correct” one, preventing duplicate content from ranking lower and ensuring you get the right page indexed.
Further, a canonical tag assists your SEO efforts in other ways, like:
Syndicated content: Canonical tags allow you to better manage syndicated content. When you syndicate content from one site to another, it’s important to ensure the search engines still reference the original content. Just add the rel=”canonical” tag to your header to indicate which page you want to index.
Improved rankings: When you have multiple versions of a webpage or article, adding a canonical indicates to the search engine you want people to go to that specific page, enhancing the original ranking.
Tracking: canonical tags enable you to track traffic from different sources. For example, if you have two URL versions, say, one with www and one without. This can help you determine which version generates more traffic and optimize your site accordingly.
Regular search engine crawling: Here’s what Google has to say about crawling: “Google will choose one URL as the canonical [main] version and crawl that, and all other URLs will be considered duplicate URLs and crawled less often.” In other words, if you don’t want Google to make the choice for you, then add a canonical tag.
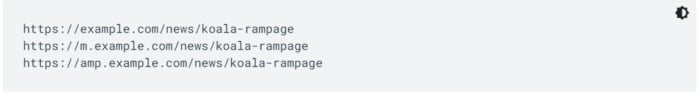
Filtering for e-commerce stores: It’s not uncommon for e-commerce stores to have large volumes of duplicate content that might look like this:
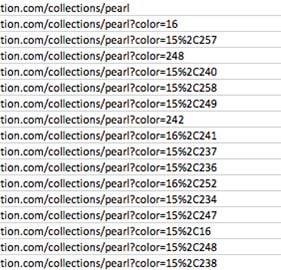
To ensure the search engines index your preferred e-commerce page, you would include a canonical tag.
What Does A Canonical Tag Do?
As I’ve explained, canonical tags can tell search engines which version of a URL you want them to index. They’re also known as “rel canonical” or a ‘canonical link element.’ You add a canonical tag to the <head> section of your page, which looks like this:
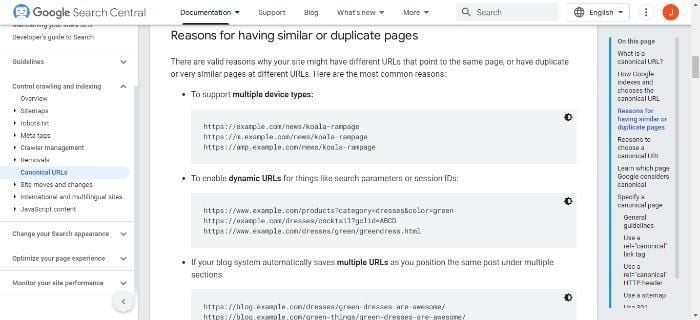
When you use a canonical tag to tell the search engine which version you prefer, it helps keep your site’s SEO consistent and can also help prevent duplicate content issues.
What Are The Issues With Duplicate Content?
First, let’s explain what duplicate content is.
We can define duplicate content as identical or similar content appearing on multiple pages of your site. Several factors can contribute to duplication, such as reprinting an article from another site, copying and pasting text from one page to another, or using multiple URLs for the same page.
Another common cause is unintentional duplication.
This can happen when two or more pages have similar titles and metadata, and it can occur when site owners syndicate their content to other websites or use software to generate pages automatically.
A further reason for duplicate content is intentional duplication. Sometimes site owners create multiple versions of a page in an attempt to manipulate search engine rankings. They may also copy and paste content from other websites to increase traffic or improve their SEO ranking – which is basically black hat SEO.
When multiple pages on a website contain the same or very similar content, it can confuse search engines and dilute the ranking power of those pages, which stresses the importance of adding a canonical tag.
How To Check for Duplicate Content
There are a few ways to identify duplicate content on your website.
The simplest is to do a Google site search; this would look like site:yourdomain.com, and see if any results show up that you didn’t expect. If you have an XML sitemap, you can also use Google’s “site:www.yoursite.com” operator to check for duplicate pages.
Other methods to check for duplicate content are:
- Checking your site’s index status in Google Search Console. Compare the number of pages indexed in Google with the number of pages you think should be indexed. The results may look something like this:
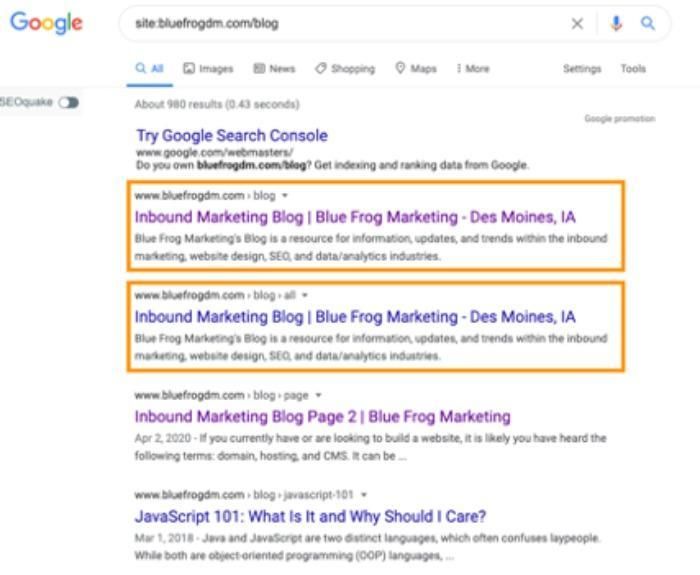
- Using the “site:example.com” search operator to find pages that are only on your site and not on other websites.
- Spotting duplicate content by using a tool like Copyscape or Siteliner. These tools will scan your website and report any instances of copied text.
- You could also use a tool like Screaming Frog to crawl your website.
How To Implement Canonical Tags
There are two ways to add canonical tags to your pages: manually or with a plugin. If you’re adding them manually, you need to add a <link> tag to the <head> section of each page that you want to canonize (make your main/original page).
If you’re using a plugin, many platforms give a simple way to add canonical tags to your pages. Below are some of the options for adding tags to various main hosting options.
Implementing Canonical Tags in WordPress
If you’re using WordPress, the easiest way to add a canonical tag is with a plugin. WordPress users can install it by:
- Going to the installation page on WordPress and selecting ‘Add new’
- Look for the Yoast SEO plugin
- Activate Yoast
- Then go to the ‘after activation’ option
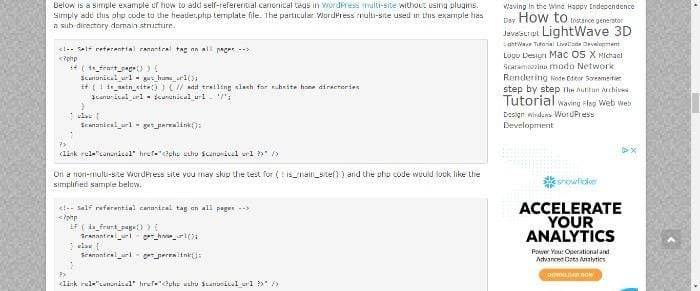
You can also install canonical tags manually by adding some PHP code to the header, which looks like this:
Implementing Canonical Tags in Shopify
Shopify has a guide explaining how to add a canonical tag url.
Or to add canonical tags manually, just:
- Go to your admin panel
- Find the ‘sales channels’ option, go to ‘online store’ and click ‘themes’
- Select the theme to edit, select ‘actions’ then ‘edit code’
- Go to layout and choose theme.liquid
- Insert code into closing ‘head’ tag
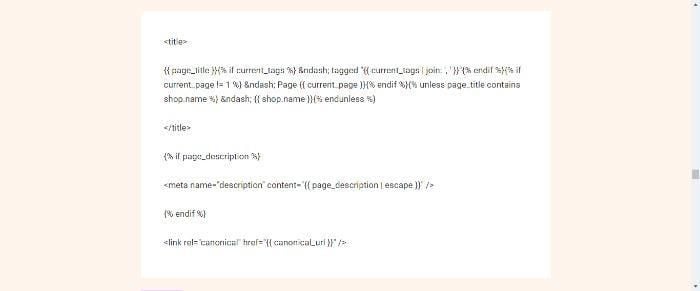
- Enter the code, which looks like this:
Implementing Canonical Tags in Squarespace
Fortunately, canonical tags are easy to implement on Squarespace websites. In the Squarespace editor, all you need to do is:
- Go to ‘Pages’
- Choose the gears option
- Select ‘advanced’ from the menu
- Follow the directions from there.
Best Practices For Implementing Canonical Tags
With canonical tags, there are a few best practices to keep in mind. First, always use a canonical tag when you have multiple page versions.
Second, make sure the canonical tag points to the correct page. If you accidentally point to the wrong page, it can result in lower rankings for that page. :
Also:
- Use canonical tags on all duplicate pages; this ensures that the search engines only index one version of each page.
- Implement absolute URLs when specifying the canonical tag to enable search engines to index pages correctly.
- Only specify one rel=”canonical” tag per page.
One good idea is to make sure that you audit your canonical tags to help identify any potential implementation issues and correct them. SiteChecker offers a free trial of a canonical URL checker.
Finally, only use canonical tags when necessary; too many canonicals can hurt your site’s ranking potential.
FAQs
A canonical tag looks like this: example.com?dress=1234 and example.com/dresses/1234 (Source: Google).
Some people argue that canonical tags are unnecessary, as Google has stated that they do not use them as a ranking factor. However, if you want to avoid duplication issues and have a preferred page you want to direct traffic to, then a canonical tag may be the way to go.
Conclusion
A canonical tag is important for helping search engines understand the relationship between pages on a website. Canonical tags can prevent duplicate content issues and enhance your SEO efforts, allowing your preferred pages to get indexed by search engines.
There are significant benefits to adding canonical tags, such as improved web page performance, more regular crawling, and easier tracking. They’re also highly beneficial for e-commerce site owners who often have multiple pages of duplicate content.
Although there are other methods you could use, a canonical tag is quick to implement, and major platforms like WordPress and Shopify have options to add plugins to simplify the task.
Do you use canonical tags? How have they helped you?