Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, says the web is for everyone. Unfortunately, that isn’t always the case. Poor design decisions can present barriers for many different groups of people. In fact, research by WebAIM finds that across one million homepages, there were over 50,000,000 “distinct accessibility errors” at an average of … Continue reading Common UX Accessibility Mistakes Found on Websites
Tag: Websites
Common UX Accessibility Mistakes Found on Websites
Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, says the web is for everyone. Unfortunately, that isn’t always the case.
Poor design decisions can present barriers for many different groups of people. In fact, research by WebAIM finds that across one million homepages, there were over 50,000,000 “distinct accessibility errors” at an average of just over 50 per page.
These errors don’t just make people feel marginalized; they stop hundreds of thousands of people from interacting with your brand or buying your product.
Few webmasters want to purposefully marginalize people or limit access to their site. That’s why it’s so important to understand the most common web accessibility issues and learn how to resolve them with clean design.
Let’s get started.
Why Is UX Accessibility Important?
Because the internet has become an essential part of the day-to-day lives of more than a billion people, site owners must take steps to make sure everyone can access it equally. It’s not just a matter of human rights, however. There is an obvious financial case for making your site accessible. Given that 61 million people in the United States have some form of disability, an inaccessible site could be harming your bottom line. Make your site accessible, and you potentially open the door to thousands of more customers.
Complying with UX accessibility design trends can bolster your company’s reputation. Making an effort to cater to a particular group of disadvantaged users proves your company cares about all of its customers. This added step may encourage potential customers to do more business with your brand going forward.
There’s also the small matter of legal compliance. While there’s debate about whether the 1990 Americans with Disabilities Act includes websites as well as physical stores, that hasn’t stopped thousands of lawsuits getting filed with federal courts each year. You may not be punished for a lack of ADA website compliance, but the threat of legal action is clear.
Ultimately, designing with UX accessibility doesn’t just improve the browsing experience for users with disabilities; it improves the user experience for everyone. Even users with perfect vision benefit from a better color contrast and more labels — and your SEO certainly benefits from things like added alt text and better link descriptions.
The 7 Most Common Web Accessibility Mistakes
Making your website more accessible is as much about avoiding common issues as it is about integrating new technology. Avoid the following seven mistakes, and you’ll go a long way to making your site more accessible than your competitors.
1: Missing Alt Text on Images
Alt text is an HTML attribute that describes what an image represents. From an accessibility perspective, alt text provides information for screen readers to accurately describe images to visually-impaired users. If you don’t provide alt text or your alt text isn’t very descriptive, then you aren’t making your site’s images available to everyone.
There’s a difference between empty alt text and missing alt text. Sometimes images can be for purely decorative purposes. Where this is the case, an empty alt tag can be used, which appears as alt=””. This is ignored by screen readers and doesn’t impact usability.
Often, alt text isn’t empty but missing completely. When a screen reader comes across a missing alt attribute, it will assume that the image is important and inject the file name. For images like graphs and infographics that are fundamental to a user’s understanding of a webpage, the file name won’t be sufficient. That’s why it’s essential to create alt text for all of your images.
2: Weak Color Contrast
Have you ever tried to read a white font on a yellow background? Not easy, is it? But that could be how many users feel every time they visit your site. The truth is some people struggle to read text unless the color contrast between the font and the background is very stark. It’s why black font on a white background is such a popular choice.
The easiest way to improve color contrast is to avoid using similar colors for backgrounds and text. That means no orange font on a red background. Or green text on a blue background. Pay particular attention to design features like your website’s header or the submit button on forms, too. These features tend to incorporate brand colors and are more likely to cause contrast issues.
Alternatively, you can use a tool like the Contrast Checker from WebAIM to quantify your contrast ratio. The higher your ratio, the better the contrast and the more readable your website will be. The tool will tell you whether your colors pass or fail. As a rule, text and background colors should have a contrast ratio of at least 3:1 for large text and at least 4:1 for normal-sized text.
As you can see from the images below, dark blue text on a white background has a great contrast ratio.
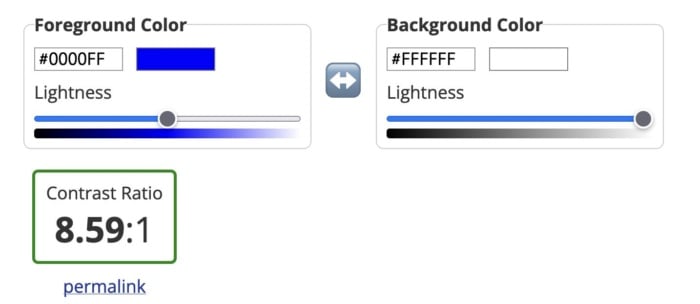
But yellow text on a white background has a terrible contrast ratio.

3: Poor Link Text
Links are a vital part of a web page, both from a user experience perspective and for SEO. But you need to accurately describe them using link text to make them effective.
While those versed in SEO might never dream of missing a chance to add a keyword in an internal link, missing link text is surprisingly common. Logos, buttons, and icons are all guilty of having no text, which means screen readers will ignore them. That’s not great if you want users to click your CTA button.
Vague or ambiguous link text is also an issue. Not only does a phrase like “click here” offer no SEO value, but it can also hamper users accessing your site via a screen reader. Including the entire http:// link without any anchor text whatsoever is even worse. Neither version contains the information these users need.
Instead, make sure the clickable text describes exactly what the user can find on the next page. In the example below, for instance, you know that by clicking the link, you’ll be directed to a page where you can get a 14-day free trial of Shopify.

Then there are navigation links. These can also create problems for screen readers if they are poorly coded. That’s because screen readers will not skip over them, meaning users will have to listen to your navigation menu every time they open a new page. Solve this by assigning ARIA roles to your navigation menus to indicate their purpose. This will help screen readers to avoid them where necessary.
4: Missing Form Labels
I’m almost certain your website has at least one form on it, even if it’s only on your contact page. But does every field have a label telling users what information they need to input? If not, your forms aren’t accessible to everyone.
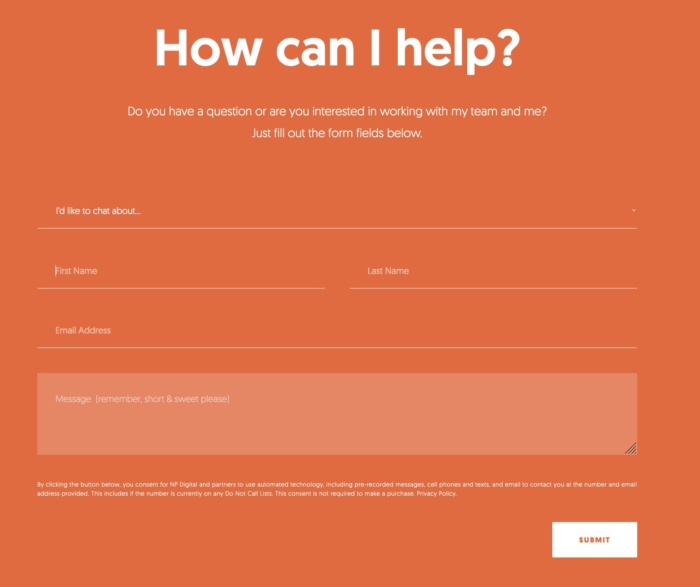
Just like with link text, form input fields need a label so screen readers and other accessibility devices can understand them and help users navigate them. A label isn’t just the placeholder text you can see in the form field, though. You also need to add a description in the form’s code. That’s because placeholder text is usually ignored by screen readers. It also doesn’t help that placeholder text usually lacks a strong color contrast.
Ideally, you’ll have a visible label inside a <label> element so everyone (users, screen readers, bots) can understand what’s meant to go in each field.
5: No Markup For Data Tables
Tables are something of a nightmare for screen readers and other accessibility devices. When screen readers come across a table, they tell the user that there is a table with a given amount of columns and rows and then proceed to list out all of the data. Unfortunately, that data may not be read in the correct order. Worse still, screen readers can’t read out tables where there is more than one set of row or column headers.
In truth, the best way to make tables accessible is to not have them at all. Of course, that’s not going to work for some websites. So, where tables are required, you need to make them as simple as possible and use the correct markup. ID, HEADERS, and SCOPE attributes should be used to correctly label each part of your table. You can also use table captions to provide additional information to users about how to best understand your table.
Another alternative is presenting your data as an image file, with appropriate alt text listing out the data. However, for complex tables, that may not be feasible.
6: Lack of Keyboard Accessibility For Screen Readers
Not everyone is going to use a mouse to navigate your website. Many visually-impaired people will use a keyboard or another accessibility device to move around your website. And that means you need to pay special attention when designing and creating the layout of your site.
Specifically, users must be able to navigate your website using the space bar and tab key. Simple sites built in semantically correct HTML may make this possible without any adjustment, but more complicated websites will need to code in digital landmarks that better allow keyboard users and screen readers to move about.
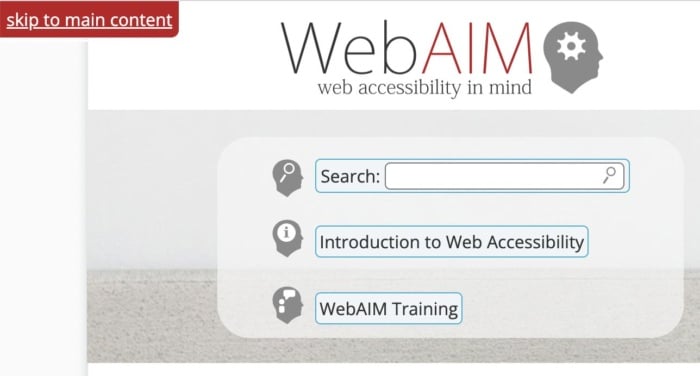
Adding skip-to-content links at the top of each page can also save your users from having to tab through every menu item every time they open a new page. These buttons, which appear when you push the tab key, allow users to navigate the site using the tab and spacebar keys to skip the navigation and head straight to the main content of the page.
7: Non-HTML Content WIthout Proper Markup</h3>
It’s easy to forget about non-HTML elements when optimizing your site for accessibility. But content like PDFs and Word documents can also be an issue. Out of the box, users cannot customize these documents to make them easier to read nor do they work well with assistive technologies. Accessibility issues are even worse when documents are produced as image-only PDFs.
One solution is to solve navigation mistakes by tagging these resources for navigation by screen readers. Another is to use Office’s built-in Accessibility Checker to improve the accessibility of these documents when you create them.
Interactive content like sliders, accordions, and drag-and-drop widgets can also affect accessibility. So, too, can dynamic content like pop-up boxes and confirmation messages. If the screen reader can’t understand when these pieces of content are loading, it won’t be able to tell users about them.
Once again, you can use ARIA attributes to resolve this issue. Tagging these interactive and dynamic elements with the correct ARIA attribute will notify screen readers that the page’s content has changed. Alternatively, you can design your site in a way that avoids the need for pop-ups and other forms of dynamic content. Static websites may not look as flashy, but they are much more accessible.
FAQs
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines are built upon the four principles of POUR: perceivable, operable, understandable and robust.
If your site is ADA-compliant, then it meets the recommendations set out in the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 and is accessible to someone with a disability.
You can make your website more accessible by improving color contrast, adding alt text, or adding keyboard accessibility for screen readers.
Allowing users to navigate your website using a keyboard instead of a mouse is an example of website accessibility. So is adding alt text to every image on your website.
Conclusion
Unfortunately, even the best designers and web entrepreneurs can create inaccessible websites. It’s why it’s so important to keep referring back to these mistakes whenever you build a website or create a new piece of content.
It’s more effort to include alt text on all images, add markup data to tables and improve the quality of your link text, but millions of users will thank you for it.
But don’t stop there. Next, learn how to create inclusive content and improve the overall user experience of your website.
What UX accessibility mistakes are you going to correct first?
Muse (YC S21) – Is Hiring, help us build 3D websites
Article URL: https://muse.place/hiring
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=30231750
Points: 1
# Comments: 0
The Ultimate Guide to SEO for E-commerce Websites
If you’re retailing products and want to reach the widest audience possible, having a well-optimized e-commerce website is an absolute must.
Why? Well, there are several benefits.
A great e-commerce website helps you understand the basics about your customers, for example, demographics like their locations, age groups, and how they found you.
By using tracking, you can then use your visitor’s information for behavior analysis to get to know them even better.
An e-commerce website does more than this, though. It can also help you understand where things are going wrong. For example, which traffic sources don’t work, which offers don’t appeal, and cart abandonment issues and their potential causes.
Of course, the more obvious reason you would want to have your site fully optimized: the growth of e-commerce worldwide. Year on year, e-commerce keeps growing, and this pattern looks like it will continue.
If you’re already online, that’s great. However, you risk remaining invisible to fresh prospects and new leads if you don’t take proactive steps to increase visibility.
How do you do that? It’s simple enough: with SEO for e-commerce.
What Is SEO for E-Commerce?
SEO for e-commerce is a strategy that helps web retailers rank higher in search engine results. A well-designed and optimized website with high-quality content will rank better in search engines such as Google, increasing your store’s visibility and driving traffic.
In other words, SEO for e-commerce concentrates on optimizing your site, which makes it easier to get leads and conversions.
However, unlike SEO for content-focused websites, SEO for e-commerce is more than just adding keywords, writing blog posts, and gaining links. You need to understand how search engines work and what they reward.
That means having a working knowledge of SEO for e-commerce, considering Google’s guidelines, analyzing buyer intent, and implementing it strategically.
E-Commerce SEO Best Practices
E-commerce for SEO is a complex field, and with millions of online retail sites in existence, it’s not always easy to make your site stand out.
While it might seem like a huge challenge to build your SEO rankings, you can make a positive start by applying some best practices. In time, this increases your chances of visibility and gaining more organic leads and customers.
For the unfamiliar, what do best practices for SEO for e-commerce look like? Well, you could start by addressing fundamentals like:
- navigation
- internal links
- avoiding clutter
- creating unique content
- including alt text for images
However, there’s far more you can do. Below, explore our list of SEO for e-commerce best practices you can implement today.
1. Perform Keyword Research the Right Way
There are many different ways to optimize your e-commerce site, and not every approach is suitable for every site or product. However, some guidelines apply to every online retailer, and one of them is performing keyword research correctly.
Yes, you want the most relevant and popular keywords in your industry, but you must also understand buyer intent.
Keyword intent is the intention behind a search query. You can identify it by looking at the specific phrases and terms people use when looking for an item online.
There are two main types of keyword intent you see most often.
Informational Keyword Intent
Informational keyword intent is used in SEO to describe the type of information the searcher is looking for.
These types of searches usually consist of:
- How tos: These are searches that contain questions such as “how do I?”
- Direct purchase: These involve searches with keywords like “buy this.”
- Factual queries: These use words such as “fact” and “information” when a searcher wants more details about a subject.
Commercial Keyword Intent
Commercial keyword intent is when people are looking for information to help them make a purchase. This means that they want to find what they need and buy it as fast as possible.
Consumers typically use commercial keyword intents when they know what they want but don’t know where to find it yet. You see this when you’re typing specific terms into Google like “buy digital camera” or “find new laptop deals.”
Commercial keyword users typically have more intent to purchase and are less likely to search for information about the product or service than just researching where to find it.
Determining Keyword Intent
Deciding consumers’ keyword intent seems challenging, but you can make it easier on yourself. For example, AgencyAnalytics breaks it down into stages.
- Analyzing SERPs: Pay special attention to paid ads, knowledge graph results, and organic listings.
- Look at Google ads for commercial intent: Seeing bid prices for keywords gives an idea of how competitive keywords are.
- Review your analytics: Look for content with high bounce rates as it may mean it doesn’t match with searcher intent.
You could also use keyword tools like Google’s keyword planner. Others you can try include:
Ubersuggest
Ubersuggest is a free online tool that can find long-tail and related words to any topic or keyword, or you can opt for the paid version.
This tool is great for content writers, bloggers, copywriters, and marketers who want to generate new content ideas or find out what users are searching for about a given topic.
Features include:
- backlink data
- rank tracking
- site audit reports
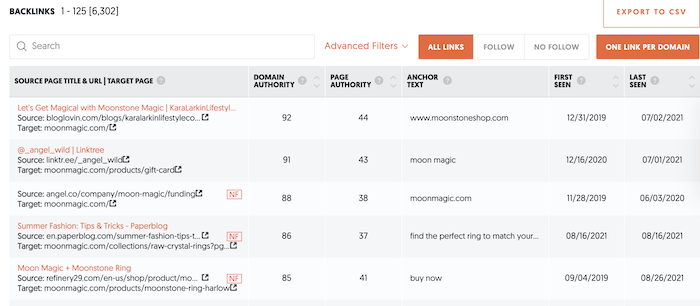
Backlink Data
To see what backlinks you are getting from other sites, go to the backlink analyzer under SEO Explorer. This can help you see who is already a fan and what related sites you can target for more linkbuilding.
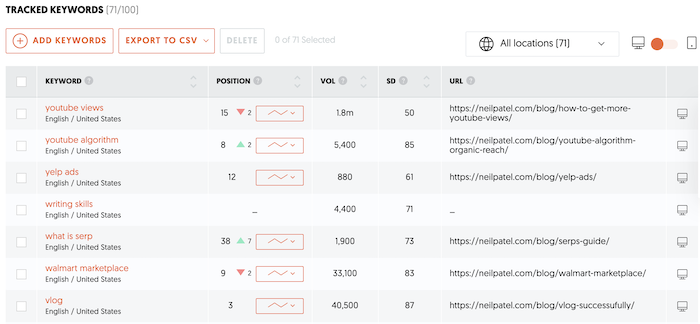
Rank Tracking
See how you rank in organic SERPs for your target keywords with Ubersuggest rank tracking. That way, you can see how you have improved over time. This is under Dashboard on the left side.
Site Audit
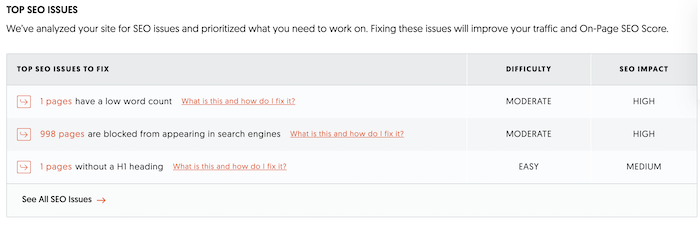
Run a site audit to track what issues need to be fixed on your site that could be affecting user experience and organic traffic. Think of the audit as a starting point, then review it regularly to make sure you’re fixing other issues. This is under the SEO Analyzer section. One the audit has run, it will tell you your top SEO issues and how to fix them.
It also has a free chrome extension to do keyword research while you’re conducting Google or YouTube searches.
Answer the Public
Answer the Public is a great tool. It lets you uncover what people all over the world are curious about and going through.
Answer the Public is intuitive, too. Just enter your keyword on the homepage to understand precisely what people are asking. It can also help you find which topics are most popular at any given time, which might be helpful as another tool for keyword research. However, if you want further guidance, there’s a set of tutorials available.
It’s free to use, but you can upgrade to pro for more features. The following example uses “multivitamins.”
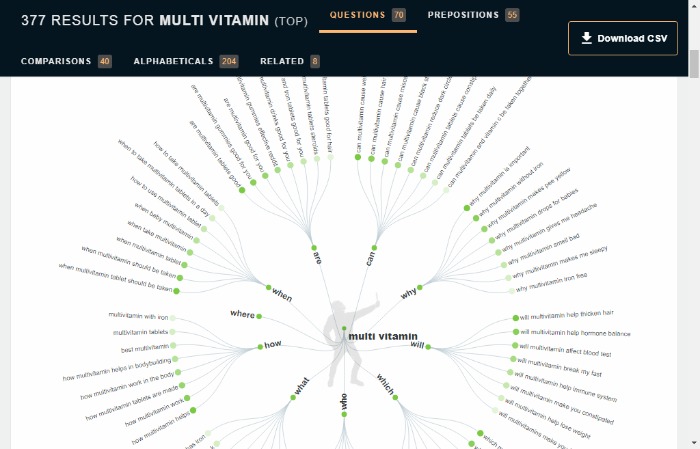
The results give a detailed picture of the kind of questions people are asking and give a better idea of intent.
2. Optimize Product Pages to Improve Ranking
If you want to attract and acquire new customers, look at your on-page user optimization. It matters because it gets your site a higher rank, meaning fresh streams of organic traffic and more conversions.
Not every area of your e-commerce site needs optimizing, so in this section, let’s focus on the ones that matter most to online retailers: product descriptions, images, and reviews.
Optimize Your Product Descriptions
A product page is interesting because it has a lot of different features that all need attention. You also want a few things to stand out from the page to gain visitors’ engagement and get them to click through.
To begin optimizing your e-commerce product pages, you need to keep in mind three key aspects:
- What are the most crucial things on the page?
- How can you maximize visibility and impact with these elements?
- How can you use this information to improve your product description’s effectiveness?
Now, start looking at what you can do to maximize the impact of your product descriptions. This could be things like.
- adding multiple, high-quality, unique images
- including keywords
- including detailed, keyword-rich descriptions
- adding calls to action (CTAs)
- including testimonials
Optimize Your Images
A sometimes neglected area of SEO for e-commerce is images. Photos are an excellent way to communicate a message and draw in an audience. However, they can also distract people from the message you are trying to convey, so be careful not to use too many images and crowd your descriptions.
Although quality images are vital to show your goods at their best, there’s more to it than that. Optimizing your images for SEO will give you higher search engine rankings and more traffic from potential customers and may gain you traffic from social media channels.
Here are some pointers for optimizing your images:
- Choose suitable images for your platform. Your host usually specifies optimal image sizes and other image guidelines.
- Provide captions with alt tags for pictures.
- Use the right keywords in file names.
Feature Reviews
Reviews provide a snippet of information that helps shoppers weigh whether to go with a particular product or store.
Reviews are vital for success in e-commerce as so many people rely on them. Additionally, they help you build trust with your potential customers and improve conversion rates.
You can encourage customers to leave reviews by sending automated messages whenever they purchase. You can also set up email campaigns to send out reminders or offers once they have left a review on your site.
Before moving on, here are more optimization tips:
- Use canonical tags to link duplicate product pages and similar group products together.
- Create a well-written page that includes the necessary information about the product, an image of the product, and a video of it in action.
- Include at least one CTA on your product page. For example, “Add To Cart” or “Check Availability.”
- Make sure you include shipping details and policies upfront so customers know what they’re paying from the start.
3. Make Sure Your Site Is User Friendly
UX stands for user experience. You can enhance UX by good design, making the aesthetics more visually appealing.
However, it’s not just about making a website look good; it’s about making it work well. UX includes everything from navigation, ease of use, and the overall “feel” of the website.
UX is also about making sure people can find what they are looking for, keeping them engaged while browsing, and giving visitors the best experience possible.
You may not think that UX affects SEO, but the interaction between the two began some years ago, and UX is also imperative for discoverability.
Additionally, recent changes mean that UX is soon to be a Google ranking factor. According to Search Engine Land, that means if Google thinks your website offers visitors a bad experience, it may rank lower. Google measures the new ranking with “Core Web Vitals” and has set out its guidelines online.
Many things can influence UX, but a few key factors are apparent:
- Ads shouldn’t interfere with the user’s view of content.
- Your site should load quickly and be mobile-friendly.
- Any website should be clutter-free and easy to navigate.
- You should include CTAs, so customers know what to do next.
Finally, use consistent styling throughout, and make it accessible.
4. Don’t Forget Long-Tail Keywords
You usually see long-tail keywords on the right side of a search engine results page (SERP).
A long-tail keyword is a term that typically has low search volume but still meets the criteria for relevancy to your business. They also tend to convert well because they’re a better match for what the searcher is looking for, and they typically give higher traffic.
For those reasons, you shouldn’t be afraid to rank for long-tail keywords because they’re a valuable source of traffic.
Long-tail keywords are great for:
- competitive niches
- increased conversion rates
- ranking new sites more easily
You can find long-tail keywords by using Google’s “People also ask” or use a free keyword tool like Ubersuggest. There are plenty of other tools available too.
The following example uses Wordtracker, where the search for “dumbells” delivered this:
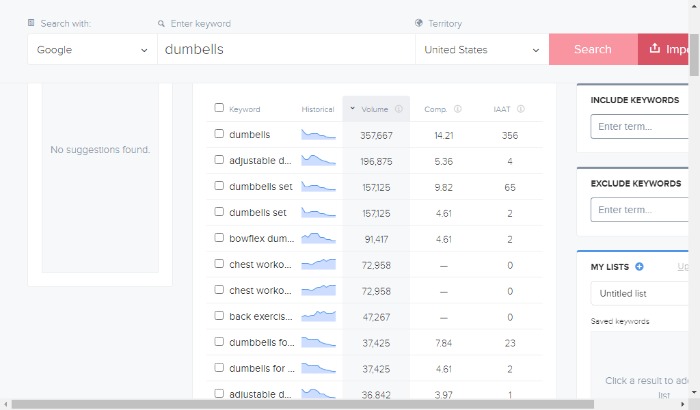
As you can see, they give you a firm idea of what your customer is looking for and of their intentions.
5. Use a Simple URL Structure
There are more detailed guides on URL structures, but this section gives you the basics.
A simple URL structure not only enhances the user experience but also improves your SEO e-commerce efforts to some extent.
Additionally, when your e-commerce site has a simple URL structure, it’s easier to share products on social media and other websites, and it can improve SEO for e-commerce as it provides more relevant data for search engines.
For the best results, URLs should be as readable and understandable as possible.
For instance, here’s an example of what NOT to do: https://www.example.com/article-about-hiking/
It would be much better to use this URL structure: https://www.example.com/hiking-articles
Google also has some advice on improving URL structure.
Additionally, you can:
Use Keywords
Search engines scan the URL and use the keywords in the URL to determine where that page should rank in the SERPs. The keywords in the URL are called “metatags” and help tell search engines what the content or topic of that page is.
That’s why you must spend some time thinking about your keywords before deciding on a URL structure.
When people search for your business online, they often type in the precise words they’re looking for. As an example, a person may type in “online shoe store” into a search engine.
Therefore, when someone types in “online shoe store,” it’s crucial those words are somewhere in your URL structure.
Use Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs are a navigational tool. They allow website visitors to retrace previous steps and return to where they started. Breadcrumbs are not just a usability technique but also provide additional SEO benefits.
For example, if you visit a blog post from your main homepage, the breadcrumb for that post would be “Home > Blog > This Post.”
You find breadcrumbs in many web design tools, and you can add them by using markup tags or via JavaScript.
Avoid Stop Words
Common stop words are “the,” “and,” “of,” and “a.”
Stop words can decrease your content’s readability and may lower your SEO rankings.
In addition, stop words are less likely to hold a reader’s interest. By removing these words from your website, you can use those spaces for more creative and relevant copy.
6. Use Schema Markups to Help Google and Users Understand Content
Schema markups are HTML tags that provide additional information about the content on web pages. By using these markups, it can improve your SEO for e-commerce efforts.
When you use schema markup, it produces rich snippets. These are a way for search engines to show more information about specific items in the search results.
They also help people find what they are looking for faster and easier by showing different types of information.
There are many different types of rich snippets, such as:
- product markup snippets
- music snippets
- review snippets
The kinds of e-commerce schema are:
- Product schema: This is an extension for products, services, and organizations. It enables discovering new products and services in web search queries by providing rich product information such as images, price, and availability. Product schema also allows the display of product ads on the SERPs.
- Review schema: This enables online reviews. The author and title filters allow you to find specific people who have written reviews on your website or blog post and for searchers to find product reviews.
- Product availability schema: The product availability schema is a list of products that are available to purchase. It can be a single page, or it can be within an online store. Such lists typically detail the product name, description, price, images, and variants.
- Video schema: Video schema is a type of metadata used to describe the content and format. For example, video schema may include the audio language, video resolution, or age rating of the video.
- Price schema: Price schema is a technique for the pricing of products or a price range.
7. Avoid Duplicate Pages and Content
Have you ever visited a website and got the feeling you’ve read it all somewhere before? That’s all too common with production descriptions and category descriptions when online retailers use duplicate product catalogs and images.
It’s understandable why e-commerce sellers just republish the same descriptions. Usually, it’s simply because they don’t have the resources to produce fresh content themselves.
However, even if you don’t have time to rewrite everything, you can still significantly reduce the amount of duplication on your site in product descriptions and other areas.
For instance, by
- using a CMS with site-wide 301 redirects or adding canonical tags on every page that you know might have duplicates (pages with similar titles, pages that share an identical URL, etc.)
- adding a suffix to the URL
- using different product images
- adding unique keywords on other pages
8. Don’t Let Page Speed Kill Your Ranking
Website page speed loading time is the measurement of how long it takes for an internet user to open a web page. You can measure it by adding up the time to download all the non-hidden assets, such as images, scripts, and stylesheets.
Page speed is a ranking factor, and survey after survey shows consumers aren’t willing to wait around while a site loads.
Web-users say their ideal site speed is just two seconds, but the faster, the better. If you’re not sure about your current speeds, you can test it at Cloudflare or try Google’s tool.
What should you do if your site is too slow? First, you need to find the reason. It could be:
- Your site simply has too much content for your server to handle.
- Too many scripts are slowing down load times.
- Images take an excessive amount of time to load.
- There’s a problem with your web host.
While not all e-commerce site owners can guarantee a perfect 100 percent on Google’s PageSpeed Insights, you can try and fasten load times by:
- having fewer images on the pages
- compressing files
- using fewer social media widgets
- optimizing your images
- avoiding clutter and using plenty of white space
- limiting redirects and HTTP requests
- fastening your server response time
Additionally, you might want to think about changing web hosts or upgrading your hosting package to accommodate your needs better.
9. Content Does Matter for E-Commerce
E-commerce isn’t just about images and keywords. Written content should also be part of your SEO for e-commerce strategy.
Posting regular content not only attracts organic traffic. It can gain your customers’ trust, boost your website rankings, and solidify your reputation as an expert in your niche too.
There are many types of content you can focus on:
- sharing how-to pieces and answering FAQs
- new product launches and anything newsworthy
- a glossary page
- including user-generated content (UGC)
- testimonials and launches
- video demonstrations and Q and As
- webinars
For more ideas, take it a step further and get to know your audience so you understand their main concerns and problems. This allows you to write content that addresses their everyday worries and offer products that solve these.
Now you’ve got some ideas for content. However, content isn’t worthwhile without a strategy behind it. Let’s break it down:
- Get to know your customers better with buyer personas.
- Understand their preferred content. If you’re tracking your content data, you should see which content types get the most views. Additionally, you can ask customers and prospects through surveys or groups.
- Establish a content calendar and create the content.
- Publish the appropriate content for the various stages of the buying cycle.
- Use A/B testing in key areas like titles.
- Measure the results and tweak.
10. Link Building for E-Commerce
Link building is a ranking factor for SEO. Quality links tell Google that your site has credibility. Backlinks also influence how your website ranks for keywords.
Sounds great, doesn’t it? But just how do you go about creating these all-important backlinks?
A few ways to do this are:
- creating internal backlinks
- writing guest posts
- using social media ads
- sharing content on social media
- issuing press releases
- writing blog comments and sharing on forums (if allowed)
- creating infographics and sharing them online
- issuing whitepapers and case studies
These are all legitimate ways to build quality links. Although they can take time, you shouldn’t take shortcuts by buying links. Some paid links violate Google’s guidelines, and if you’re buying cheap links, the quality is usually questionable. Poor quality links lead to lower SERP rankings and reduced traffic, as well as a potential negative impact on your site’s reputation.
11. Add a Sitemap
A sitemap is a visual representation of your website or digital product. It provides visitors with a bird’s eye view of the website and explores different pages.
Your sitemap should detail all of the pages on your site, from category pages to product pages. It should also include all the subcategories, products, and other content within those sections.
You can develop a sitemap manually or use an automated tool such as Google’s Webmaster Tools to generate one. Sitemaps use both XML and HTML, although HTML sitemaps are more helpful to visitors.
Other tools for creating a sitemap are:
Lucid Sitemap Generator
The Lucid chart sitemap generator is a user-friendly tool that makes creating a sitemap for your website easy. It has many features, like adding categories and subcategories.
Powermapper
Powermapper is an easy-to-use tool for creating and updating sitemaps and allows you to generate one-click checkouts.
It’s a web-based tool with no coding expertise required. However, there is a fee.
12. Make Social Sharing Easy
Google’s Matt Cutts once said that social sharing doesn’t impact SEO, but many would disagree.
While social media sharing may not directly affect your SEO, sharing your content on social media increases brand exposure and gets people more familiar with your business.
Further, the more mentions you get on social media, the more influence this can have on your SEO by:
- driving organic traffic and increasing visibility
- improving local SEO
- expanding your content reach and enhancing brand recognition
- increasing backlinks
If you want an easy way to increase your shares on social media, consider getting a tool like Buffer or Hootsuite to automatically post content from your site across all of your social media accounts at scheduled intervals.
Frequently Asked Questions About SEO for E-Commerce
How do I Find the Right Keywords For my E-commerce Store?
There are several free resources that you can use to find keyword ideas, such as Google AdWords, Ubersuggest, and Google’s Keyword Tool. You should also look at what your competitors are using to find the best keywords for their audience.
Finally, avoid using broad keywords that generate many clicks but don’t provide much conversion value. Use long-tail keywords where you can.
How Much Does SEO for E-Commerce Cost?
The cost of SEO depends on many factors, including the number of keywords targeted, competitive landscape, and how much effort you need to optimize each page for ranking.
It’s not easy to put a price tag on SEO because it depends on how many resources you allocate and what you want to achieve. To help you budget, Search Engine Journal provides an SEO budget calculator.
What Is SEO for E-Commerce?
SEO for e-commerce is the process of optimizing a website so that it can rank more highly in search engines. Several factors affect how well a website ranks on the SERPs, such as the quality and relevance of the content, the use of appropriate keywords to optimize the site, and the site’s load speed.
How Is SEO for E-Commerce Different?
When it comes to SEO for e-commerce, there are different areas you need to focus on, such as optimizing:
- product pages and descriptions
- diversifying product content and information
- images on your website
- your homepage
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “FAQPage”,
“mainEntity”: [
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “How do I Find the Right Keywords For my E-commerce Store?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
There are several free resources that you can use to find keyword ideas, such as Google AdWords, Ubersuggest, and Google’s Keyword Tool. You should also look at what your competitors are using to find the best keywords for their audience.
Finally, avoid using broad keywords that generate many clicks but don’t provide much conversion value. Use long-tail keywords where you can.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “How Much Does SEO for E-Commerce Cost?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
The cost of SEO depends on many factors, including the number of keywords targeted, competitive landscape, and how much effort you need to optimize each page for ranking.
It’s not easy to put a price tag on SEO because it depends on how many resources you allocate and what you want to achieve. To help you budget, Search Engine Journal provides an SEO budget calculator.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What Is SEO for E-Commerce?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
SEO for e-commerce is the process of optimizing a website so that it can rank more highly in search engines. Several factors affect how well a website ranks on the SERPs, such as the quality and relevance of the content, the use of appropriate keywords to optimize the site, and the site’s load speed.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “How Is SEO for E-Commerce Different?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
When it comes to SEO for e-commerce, there are different areas you need to focus on, such as optimizing:
product pages and descriptionsdiversifying product content and informationimages on your websiteyour homepage
”
}
}
]
}
SEO for E-Commerce Conclusion
SEO for e-commerce helps boost your website visibility, brings new queries and customers, and helps build your loyal audience.
It may seem like there’s a lot to think about. However, by concentrating on the main SEO best practices and optimizing the critical areas of your website, it doesn’t have to be as complicated as it sounds.
The most important thing to remember is SEO for e-commerce doesn’t happen overnight. Instead, it’s an ongoing strategy that requires updating as you go to get the optimum results.
What is your experience of SEO for e-commerce? Tell us below.
41 Factors That Influence Your Website’s Credibility
There’s one thing you’ll need to convert more website visitors: credibility.
Credibility shows customers you’re safe and trustworthy. It’s impossible to generate more leads, sell more products, or attract more visitors without it.
Almost every company struggles with website credibility. Website visitors are immediately skeptical.
If you’re an unknown, you’re unsafe.
This means website visitors will need to be persuaded before they feel comfortable enough to take a chance on your business.
Your website visitors are looking for a reason to leave.
In fact, most visitors leave web pages in 15 seconds or less. Web pages with an effective value proposition will hold visitors’ attention longer.
Scientists from Microsoft Research analyzed page-visit duration for 205,873 web pages (with more than 10,000 visits to each page).
They found visitor time-on-site follows a Weibull distribution.
Weibull is a reliability metric used to analyze and predict the time-to-failure in components.
Let’s say you replace a spare part in a random piece of equipment. A Weibull analysis predicts when you’ll have to replace that specific part again. Doesn’t sound all that helpful, does it?
Replace “component failure” with “visitors leaving web pages,” and it becomes very helpful.
Here’s what scientists learned after analyzing hundreds of thousands of web pages.
There are two kinds of Weibull distributions.
- Positive Aging: The longer a component is used, the more likely it is to fail.
- Negative Aging: The longer a component is used, the less likely it is to fail.
Scientists found that 99 percent of web pages have a negative aging effect. When website visitors hit your landing page, they’re skeptical. They’re quickly scanning the page, looking for a reason to abandon your site.
Get your website visitors past the 30-second mark, and they’ll spend a lot more time on your site.
Why? Because they feel your website is more valuable to them. What makes your website more valuable to your visitors?
Credibility.
Credibility is an essential part of an effective value proposition. Your visitors are looking for signals that show your organization is reliable, trustworthy, and knowledgeable.
How To Improve Your Website’s Credibility
The success of your website depends on your credibility.
What type of factors influence website credibility? According to BJ Fogg, a researcher at Stanford’s Persuasive Tech Lab, there are four kinds of credibility.

- Earned Credibility: Your visitors have had a positive experience with your website (e.g. helpful information, little-to-no errors, expert advice, great customer service, etc.) and found your website to be both credible and valuable.
- Reputed Credibility: A referral from a third party — like family, friends, a co-worker, or someone you know — or unbiased reviewers who have had a positive experience with your website.
- Presumed Credibility: Familiarity and assumptions — a brand they’ve heard of is more credible than an unknown (e.g., I saw your YouTube ads, I read your guest post on Forbes, I listened to your interview on the Tim Ferriss show, etc.)
- Surface Credibility: A visitor’s subjective opinion of your website (e.g., I like the design, this looks trustworthy, great content, this page is confusing, etc.) is all that matters when you’re asking them to convert.
The goal with each of these credibility factors is to stack the deck in your favor.
Building your website’s credibility is a great way to attract more of the results you want. If you want to attract more visitors, you’ll need to choose the right credibility tools at the right time.
But which website credibility factors are most important?
Here’s a list of the factors that influence your website’s credibility and how you can use them.
1. Consistency (Over Time)
As long as you’re consistent, a visitor’s trust in you will grow. By consistently doing all the things I’ve shared in this article, it creates a really good reputation with your customers.
2. No Unnecessary Requirements
When you force customers to register before they can post a comment, initiate a live chat, or purchase your product, it decreases trust.
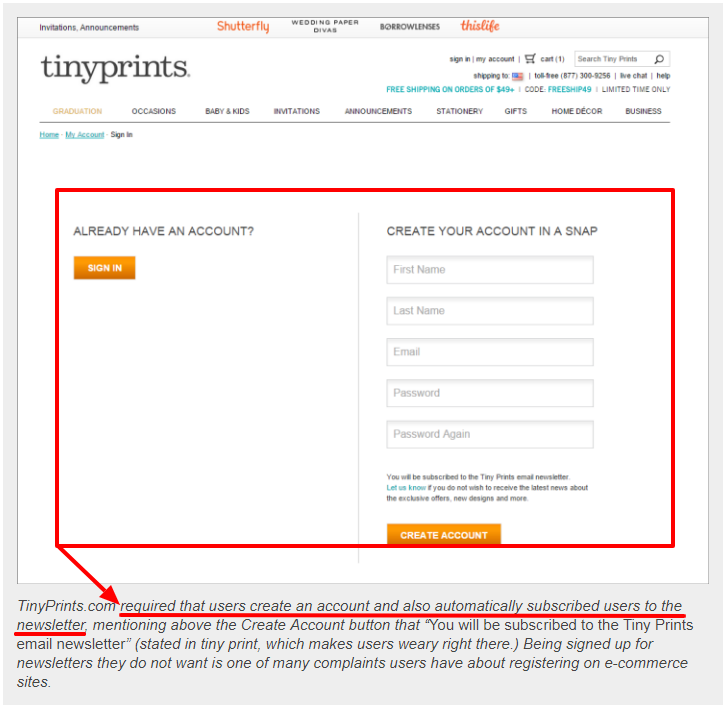
Asking for your customer’s phone number when you only need their name and email address increases resistance and decreases trust.
3. Add Helpful FAQs
Customers have questions and objections. An FAQ is a helpful way to give customers straight answers to some of their questions.
It’s common for organizations to treat their FAQs as a low-key sales page. It’s much better to be helpful, upfront, and honest with each and every one of your customers.
4. Minimize Jargon
If you’re selling to a mainstream audience, jargon isn’t a good idea. Research shows people are more likely to believe a concrete statement over an abstract one. Use specialized jargon for specialized audiences.
Sometimes jargon is a helpful way to establish credibility in a niche community, but it’s still a good idea to only use it sparingly. The more you use jargon, the more your credibility suffers.
5. An Up-to-Date Blog
Consistently creating content shows visitors your website is active and maintained. It also conditions them to check back frequently, always looking for fresh content that can help them.
6. Useful Expertise
Your website visitors are always on the lookout for expert-level content that solves their problems, moves them closer to their goals, or simply entertains them. They want expert content that’s fresh, surprising, and detailed.
7. Minimal Advertising
People hate ads. They don’t like them because they’re annoying and pushy interruptions and they’re everywhere.
It’s a good idea to minimize the advertising on your site, so it doesn’t hurt or interrupt your visitor’s experience.
8. Helpful Customer Service
Great service gives website visitors a positive experience with your site, improving earned credibility. Friendly, knowledgeable support reps show website visitors that your company is experienced and efficient. Consider adding a live chat option to make it simple for your audience.
9. Cite Your Sources
Giving sources increases your trustworthiness. As customers trust you more and more, they’ll validate your sources less and less, but only if you have a track record of citing your sources and providing them with the evidence to support any claims you make.
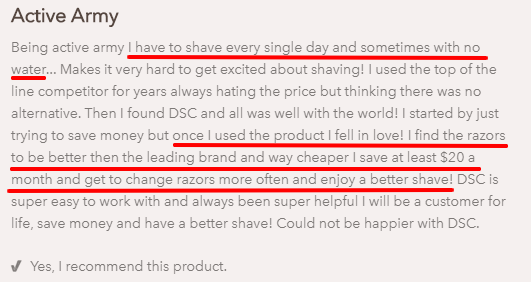
10. Customer Testimonials
Social proof in the form of testimonials gives visitors access to your customer’s mind. These testimonials show visitors what it’s like to be your customer, how you operate, and more.
The biggest downside to testimonials is that they’re one-sided, but they’re still a great way to build website credibility.
11. Include Customer Reviews
Customer reviews are similar to testimonials in the sense that customers can share their feedback. Reviews take that a step further, allowing customers, companies, and the community to have a conversation.
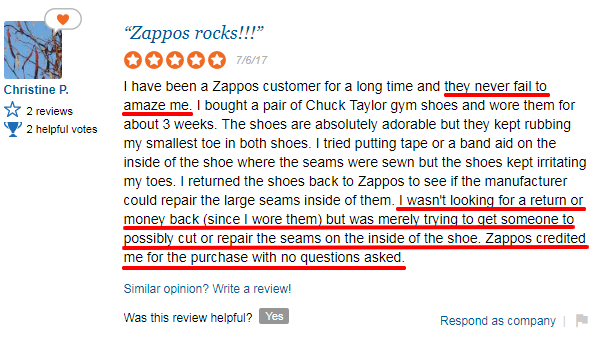
Reviews, when they’re positive, can boost credibility (and sales) dramatically. However, there is some value to negative reviews, so don’t let one bad review get you down.
12. Professional Product Reviews
These can come from influencers as large as Consumer Reports, TechCrunch, and BuzzFeed. They can also come from up-and-coming bloggers, individual reviewers with a YouTube channel, and your customers themselves.
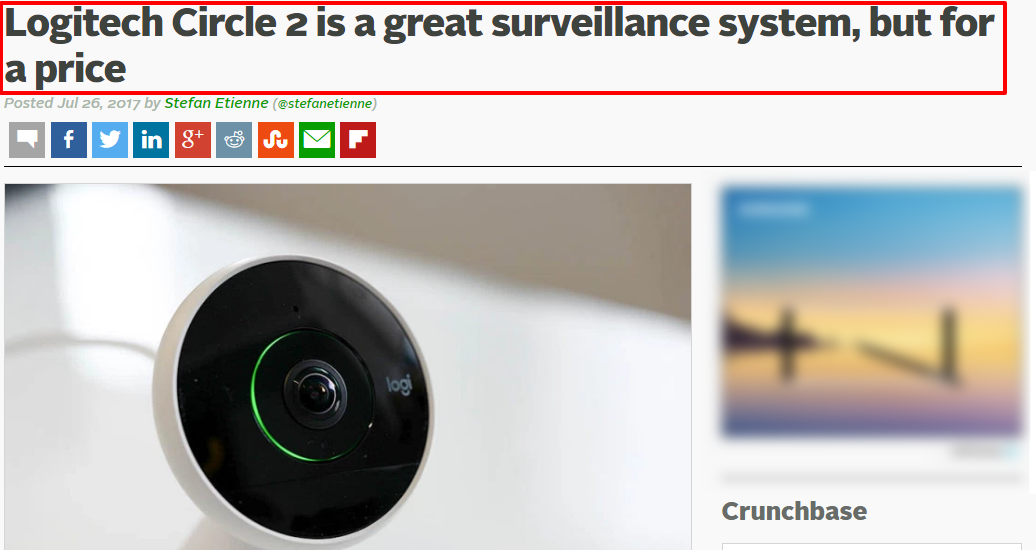
Professional reviews are often seen as more credible due to the reputation and influence of the reviewer itself. A glowing review from a powerful influencer can lead to a large increase in sales.
13. Trust Seals
Logos or seals from independent and trustworthy authorities enable you to borrow their credibility as your own. Use trust seals like Web of Trust, GoDaddy Site Seal, Norton Secured, PayPal Verified, BBB Accredited Business, and HTTPS.

14. Reviews From Influencers and Notable Customers
Big-name reviews carry a lot of power, prestige, and reach. A testimonial from a powerful influencer can boost your trust and credibility. I used this exact strategy on Quicksprout to boost my credibility dramatically.

Reviews from these influencers are easier to get when your other credibility factors are straightened out.
15. Case Studies
These are typically created in collaboration between the business and the customer. Customers share their problems and expectations going into the relationship, then their experience and the results that followed.
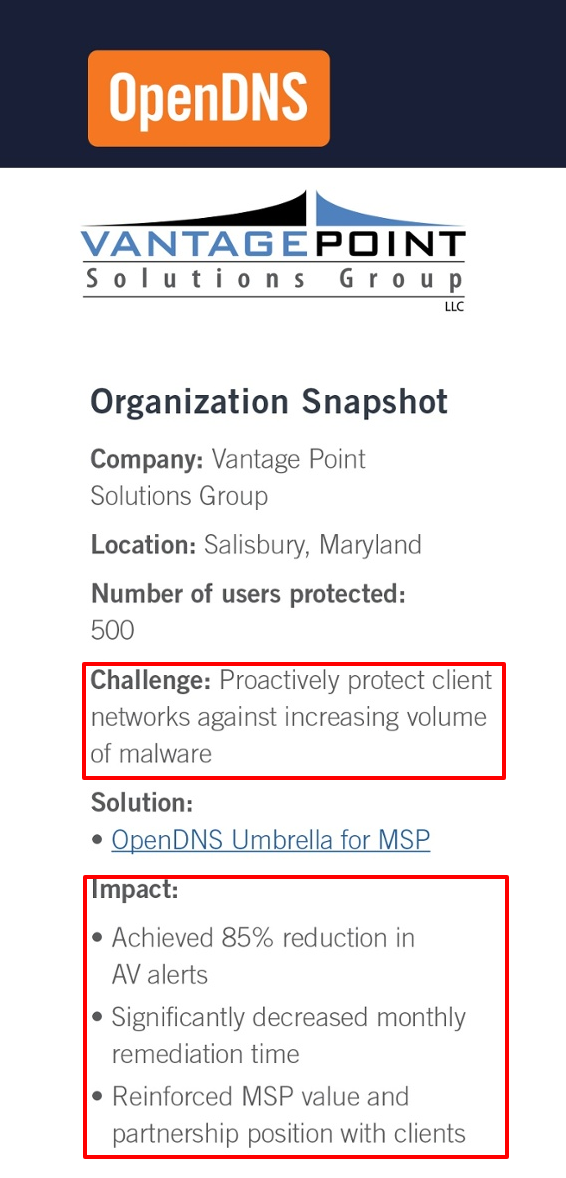
Case studies, like testimonials, tend to be one-sided. However, they boost credibility because customers are willing to share their stories.
16. Connections to Influencers
This could be as complex as a large professional network and connections to large organizations, or as simple as associating with other well-known local or minor influencers.
17. Customer Validation
Displaying your client lists, the number of clients you have, or the industries your clients are in. When customers see their competitors or other brands they trust use you, they are more likely to trust your brand.
18. Third-Party Validation
As featured in, as seen on, used by these clients — this kind of validation borrows trust from bigger, more influential sites to build trust and credibility.
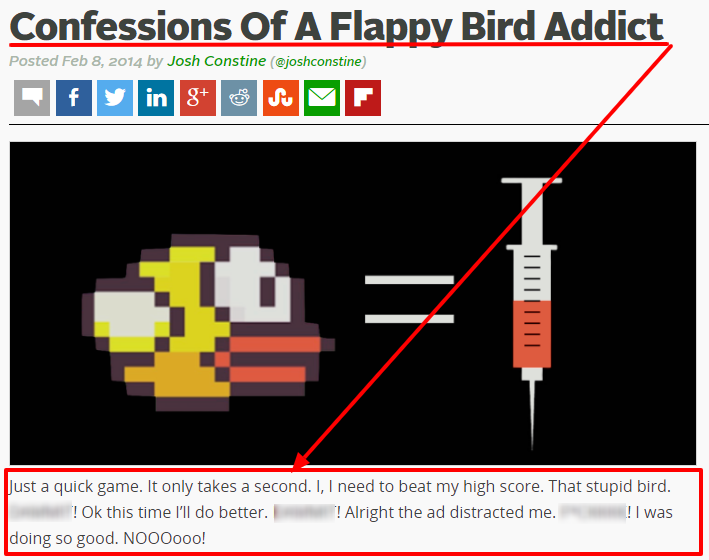
19. Press Mentions
Media exposure is a powerful credibility booster. The more prestigious the news organization, the greater the increase in credibility.
20. Awards
These can raise your company’s profile and give you a nice prestige boost. The more impressive the award, the bigger the boost.
However, there’s a downside to using awards. The less credible the award, the more likely customers are to question your business, products, or services.
21. Influencer Feedback
Being visible on an influencer’s site — whether that’s in the form of a testimonial, interview, guest post, or review — introduces website visitors to you, improving your credibility before they arrive on your site.
22. Guest Posts
Writing for other well-known publications means you’re familiar. Visitors have heard of your site before hitting your landing page.
23. Advertising
When it’s used well, advertising (via platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, or YouTube Ads) creates presumed credibility in the form of branding and familiarity. If visitors have heard of you before, you’re more credible.
24. Branding
A solid brand gives you a specific place in a customer’s mind via psychological anchoring, which establishes credibility. Branding is what lasts in the long run.
25. Professional Design
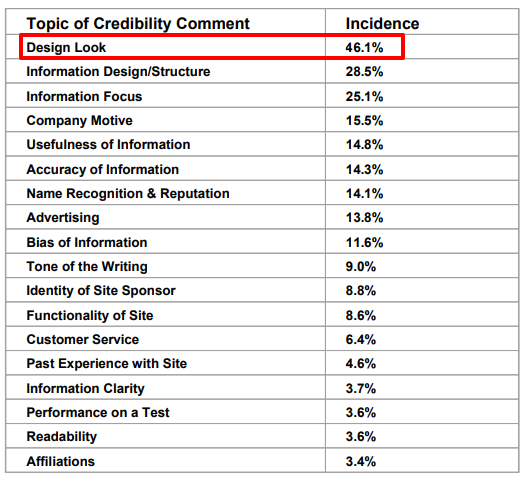
Customers form a first impression of your website in 50 milliseconds. There’s no thinking with this first impression. It’s visual, focused on aesthetics, and almost entirely emotional.
Stanford’s Persuasion Technology Lab found that almost half (46 percent) of people say a website’s design is the number one criteria for determining website credibility.
How does this happen?
Leading companies in every industry train customers, showing them what to expect. Customers take those lessons to other sites, using these leaders as a measuring stick.

26. Typography
Research shows larger fonts improve reading speeds. Website visitors comprehend more when typography is legible and clear. This seems like a no-brainer, but it can be easy to forget.
Remember, clarity trumps persuasion.
According to Flint McGlaughlin, your website visitors land on your site with a few questions:
- Where am I?
- What can I do here?
- Why should I do it?
The easier it is for website visitors to understand what you’re saying to them, the easier it is to persuade them to do what you want.
Which one is easier to understand?

Or this?

27. Simple Content
Smart marketers work to improve cognitive fluency. That’s the feeling of ease a visitor has when your content and visuals are easy to read.
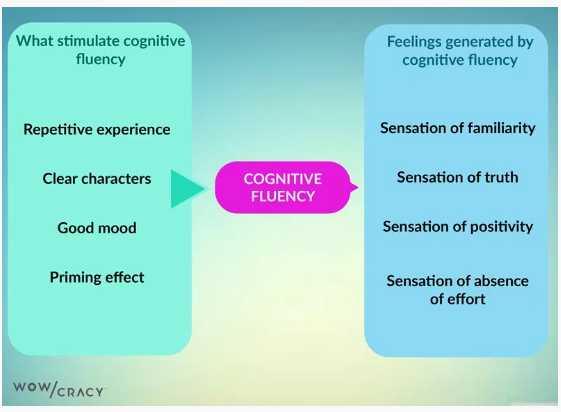
The easier your content is to understand, the more familiar it feels, thus the easier it is for visitors to decide to buy.
28. Use Good Grammar
Yeap, spelling and grammar matters because it’s part of the first impression customers form about your brand. A typo here or there won’t ruin your credibility, but a consistent pattern of bad grammar hurts your credibility. Sites like Grammarly can help keep your grammar in check.
29. Good On-Site Search
Most e-commerce visitors start the buyer’s journey in the search box. In fact, a visitor that uses site search is 1.8X more likely to convert.
Website visitors often have a hard time with search. The keywords they use don’t always lead them to what they’re looking for. So, it’s often a good idea to redirect searches to navigation whenever possible.
30. Website Navigation
Your website navigation communicates trustworthiness to visitors. They expect your navigation to be organized and to use appropriate imagery and colors.
The easier it is for customers to find what they’re looking for, to solve their problems, the more trustworthy your website/business appears to be.
31. Ease of Use
Usability experts trust PURE Scores to rate website ease-of-use, focusing specifically on tasks.
- Can website tasks be accomplished easily?
- Do website tasks require a large degree of cognitive load or physical effort?
- Are website tasks difficult for target visitors?

Website visitors are drawn to websites that are attractive and easy to use. Ease of use can also impact Google ranking.
32. No technical problems
Broken links, missing pages, slow web pages, development bugs — these technical glitches decrease visitor confidence in your business and their willingness to convert.
33. Contact Information
Posting your phone number, address, email, live chat links, social media profiles, and hours of operation show you’re a real business and not a fly-by-night operator. Visitors feel confident knowing they can contact you whenever they run into trouble.
More importantly, your visitors know how to contact you.
34. Staff Photos and Bios
Customers want to see real people run your business. They want to hear your story, verify your background, and see who they’re giving their money to.
Sharing staff photos increase conversions. Hiding staff photos sends the message that you’re untrustworthy or hiding something.
35. High-Quality Images and Visuals
Website visitors expect your images and visuals to add context and meaning. Most websites use images (e.g., stock photos) as decoration, which according to Jakob Nielsen, are completely ignored.
Poor quality images will actually hurt your credibility and conversion rate.
Whenever possible, use real people in your photos, photos that display product details, and give visitors large, hi-res photos when they ask for it.
36. Clear Policies
Website visitors want to know what happens to their information. What’s your return, warranty, and privacy policy? Will you share their data with 3rd parties?
Customers look for this info when they’re close to conversion.

37. Clear Link Text
The anchor text in your links should describe the destination or outcome. It’s always a good idea to tell your visitors where you’re taking them.
38. Order/Product Information
How long will it take for customers to receive their order? How much does shipping cost? What comes with their order? Is the warranty included? How long does it last?
Website visitors want to see order, product, and fulfillment information upfront.
39. Convenience
The more convenient and compelling it is for your website visitors to buy, the more likely they are to spend. Look for ways to reduce user friction.
40. Displaying Prices
As far as a credibility factor goes, this one is tricky. If you’re selling to enterprise customers and you display your prices, it could be a turn-off. B2C and B2B (small to medium) businesses want to see the price.
As a general rule, people want to know how much your product or service costs.
For most customers, the value of what they’re getting and their perception of your price is just as, if not more, important than the price itself.
41. Share Guarantees and Warranties
These create clear standards you’ll have to follow. Customers get peace of mind knowing you’re willing to stand behind your products and services.
You get more business because customers feel more confident about doing business with you.

Website Credibility Factors Conclusion
If these credibility factors are important to your target visitors (and they are), they should be important to you. f
Credibility factors don’t apply equally in every industry. Some industries may prefer specific ones over others.
What’s important is that you use the credibility factors that matter to your customers.
There’s a simple solution if you’re not sure: just test it. Then keep testing until you find the solution that works best for you.
If you’re still unsure, ask your visitors. Many of them are willing to tell you what they think if you’ll take the time to ask them.
What types of strategies do you use to improve your website credibility?
10 No Code Creation Tools to Build Websites, Apps, and More
While you once had to be fluent in code to successfully build a website or an app, those days are now far behind us.
How?
Thanks to no-code creation tools.
These revolutionary interfaces allow users without classic programming backgrounds to build websites and apps through a graphical interface rather than using code.
The utility doesn’t stop there: No-code tools can help entrepreneurs and marketers achieve feats that in the past were reserved exclusively for programmers.
These tools also support automated processes, allowing organizations and individuals to save time by automating time-consuming tasks.
What’s better than time saved?
Money saved.
By eliminating programming fees and reducing billable hours spent on tedious processes, you can drastically reduce your costs.
Want to learn more?
In this post, we’ll unpack the 10 best no-code creation tools and what they can do for you.
Who Should Use No-Code Creation Tools?
The short answer: everyone.
If you don’t have a background in writing code or app development, don’t fret.
No-code tools provide users with visual interfaces that eliminate the need for a seasoned code writer.
Perhaps you want to launch a new personal website but are intimidated by the process behind the layout. There’s a no-code tool for that.
By using these tools, you can take website or app creation into your own hands, whether you’re familiar with code or not.
Even if you are familiar with code, these tools can help you automate tedious processes that bog down your daily workflow.
Benefits of No-Code Creation Tools
While we’ve already covered the obvious benefits of code-free creation tools, there are several other benefits to these tools that can have an impact on your business.
Increased Focus on Pain Point Solution
Rather than spending excessive amounts of time trying to find and hire the right programmer, you can focus on honing in on the true value of your app for your customer by identifying and speaking toward their pain point.
Reduce Development Cost
When you opt to use a no-code creation tool, you can plan to save a substantial amount of your budget previously dedicated to development needs. With low or no price points, these tools can make a significant difference in your bottom line.
Speed of Release
Not only will you save money when you use a code-free creation tool, you’ll also save time. Developing custom websites and apps is hard and time-consuming; using a tool with prebuilt templates is easy and saves countless hours.
Secure Environment
Regardless of what you’re building, a secure environment should be of the utmost importance. When you use no-code creation tools, safety nets are prebuilt into the platforms, allowing you peace of mind.
10 No-Code Creation Tools You Need to Try
There are a lot of no-code creation tools out there, all with different functions for different user groups. We picked out our top 10 favorites that help solve specific needs without having to write a line of code.
Bubble
When you use Bubble, you gain the ability to craft interactive apps for both desktop and mobile browsers.
With Bubble, you get design freedom without having to wrangle the intricacies of code.
While traditional web applications require a manual deployment process, Bubble manages deployment and hosting. The platform also offers limitless users, traffic volume, and data storage.
In short, this is your go-to for building production-ready apps.
Zapier
We’re fans of any tool that enhances connection and automation, which is why Zapier is on this list. With this tool, you can connect the apps you use daily.
Through “Zaps,” users sync Gmail with Dropbox, Dropbox with Slack and so on.
If you don’t use the above apps, don’t worry. Zapier connects thousands of apps.
By building these connections, workflow is simplified, saving you time and eliminating unnecessary processes.
Stacker
This one is pretty cool. Stacker allows users to turn spreadsheets into apps, enabling you to securely share data with customers.
This lets you turn manual processes into automatic ones, streamlining onboarding and applications, enabling real-time collaboration, and ensuring secure file upload.
In essence, Stacker supports automation and collaboration through an easy-to-use, app-like interface that does all the coding for you.
Voiceflow
In need of a voice or chatbot? Voiceflow should be your go-to no-code creation platform. Regardless of what channel you’re using to reach your audience, Voiceflow designs, prototypes, and launches conversations for any channel.
With Voiceflow’s unique functionality, you can build engaging, contextually-layered conversation and voice apps to create an always-on interaction for your customers.
Additionally, you can standardize approach across sites, projects, and channels with the tools’ simple duplicative ability.
BugHerd
BugHerd helps you aggregate and implement website feedback.
This easy-to-use tracking tool enables users to instantly identify bugs through a visual component similar to a sticky note.
Comments will be pinned to the buggy element, allowing you to address issues directly from your website.
This tool also allows users to track given feedback on a list of bugs, ensuring you resolve issues as they arise.
Functionality includes adding comments, ranking bug severity, bug assignment, and report generation.
Perfect for the coder and non-coder alike, this tool makes bug removal a breeze.
SquareSpace
This easy-to-use website builder provides users with countless aesthetic templates to build the site of their dreams.
Whether you’re setting up a third-party extension or starting an e-commerce store, SquareSpace provides users with access to designer fonts and color palettes to allow for endless customization.
Equipped with an intuitive dashboard, SquareSpace also allows users to track visitors’ behavior and origin, allowing for a better understanding of the audience.
Once you’ve identified that audience, the platform comes equipped with social tools and email campaign builders to help you stand out among the crowd.
MemberSpace
This tool allows you to segment your website for different member groups.
Offering paid courses or video tutorials? Restrict access to payment groups with easy-to-use MemberSpace.
With MemberSpace, site owners control all member experiences, since members never move to an external site. They can login, manage access, and interact with content all from the safety of your site.
MemberSpace works across the content management system (CMS) tool continuum, so if you change platforms, you don’t have to change functionality.
Additionally, and perhaps predictably, given the tool’s purpose, users gain access to a private community that hosts conversations centered on the tool and membership topics.
Airtable
This online database allows collaborators to edit, store, and share information, whatever the term information means for the particular user group.
With similar functionality to an editable, online spreadsheet, users are invited to interact with Airtable.
While this tool may sound like other online spreadsheets, it has two distinct differences.
First, it’s easy-to-use nature instills in novices and experts alike feelings of proficiency.
Second, Airable allows users to manage databases, not sheets. Given the complexity of databases, the ability to handle them through simple, streamlined workflows is a boon to collaborative teams.
What’s more, the tool Airtable grows in tandem with teams, allowing increasing levels of sophistication as team needs evolve.
Parabola
Is your workflow bogged down by time-consuming manual processes?
If you answered yes, Parabola might be your new best friend.
This handy tool automates any task you can do in a spreadsheet.
Save time, reduce errors, and boost efficacy through automation. By using the tool’s drag-and-drop builder, routine reports and complicated tasks are all automated, allowing you to focus on what really matters: growing your business.
Payhere
Wading into the world of e-commerce? Payhere can help you get paid anytime, anywhere.
This no-code creation tool enables you to send a simple link across any medium (think video call, social media, email) and get paid.
The tool also features both one-time and recurring payments, making it easy for consumers to set up their payment schedules.
In addition to the overall payment functionality, Payhere allows users to create a simple, one-page storefront where all your payment links can be displayed. You can link to this storefront from your social platforms or in your email signature.
This simple tool is a must for you sellers out there.
No-Code Creation Tool Trends
It makes sense that the demand for low- and no-code tools will continue to grow since usage doesn’t demand extensive background.
In fact, Research and Markets reports the low-code market could be worth upward of $187 billion by 2030.
As the market for these platforms continues to skyrocket, here are the top three trends users of these tools should anticipate in the coming months and years:
1. Increased Adoption
As more and more consumers move away from traditional programming, you can anticipate increased availability and adoption of both no- and low-code platform models.
2. Rise of Automation
With the profusion of no-code tools with functionality to automate cumbersome, manual processes, expect to see a much more streamlined workforce.
3. Fusion Developer Teams
While developer teams have historically been made up solely of programmers, the rise of code-free creation tools is driving a more blended development team. By combining traditional coding with tools, organizations can build custom websites and apps that are created with a variety of different expertise.
Want to build an app, website, or other digital asset but don’t know how to code? Here are 10 tools to try.
- Bubble
Your go-to tool for building apps for desktop and mobile.
- Zapier
Connect apps, tools, and other programs to streamline your workflows.
- Stacker
Turn spreadsheets into apps and automate processes like onboarding and apps.
- Voiceflow
No-code chat bot or voice bot creator.
- BugHerd
Better understand web feedback with this easy-to-use tracking tool.
- SquareSpace
Build and launch your website in minutes with no coding experience.
- MemberSpace
Control the membership experience by integrating with your CMS>
- Airtable
Online data base that makes storing, editing, and managing information easier.
- Parabola
A handy tool to automate tasks from a spreadsheet to reduce errors and boost efficiency.
- Payhere
Get paid fast with a one-page storefront.
Conclusion
Regardless of where you work or what you do, it is inarguable that some function of your life can benefit from the offerings of the above 10 tools.
You no longer need a background in programming to accomplish your digital goals. As you start your next digital marketing campaign, ask yourself: Which processes can I automate to reduce manual workload and increase focus on overall success?
By answering this question, you’ll be able to isolate areas for improvement, optimizing your strategies and reducing manual processes.
What’s your favorite no- or low-code creation tool to use?
For Your SEO – Single vs Multiple Websites [Infograph]
Single Vs Multiple Websites Which is better for SEO in 2020? Single or multiple websites? I used to work for a company that deals with organizing events and exhibitions. They have about 3 major events annually and their events are quite well-known. But the thing is since each of the events has its own separate …




