
Sic 'Transitory' Gloria Fed
The post Sic 'Transitory' Gloria Fed appeared first on Buy It At A Bargain – Deals And Reviews.
The post Sic 'Transitory' Gloria Fed appeared first on Buy It At A Bargain – Deals And Reviews.
Article URL: https://remoteOK.io/remote-jobs/105532-remote-executive-director-plumia
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=28236316
Points: 1
# Comments: 0
Google’s search engine is technically complex.
There are hundreds (maybe even thousands) of different factors taken into account so that the search engine can figure out what should go where.
It’s like a mysterious black box, and very few people know exactly what’s inside.
However, the good news is that search engines are actually pretty easy to understand.
We may not know every single factor (out of a hundred or thousand), but we also don’t need to.
I’ll bring it down to the basics with a simple method to please Google, rank higher, and bring in more website traffic.
I’ll also introduce some of the latest developments, like RankBrain, that help Google guess what you’re actually looking for (even if you don’t type it in).
First, I’m going to walk you through exactly how Google’s search engine really works so that you can see that it’s not as difficult to understand as you might think.
Google’s first job is to ‘crawl’ the web with ‘spiders.’
These are little automated programs or bots that scour the net for any and all new information.
The spiders take notes on your website, from the titles you use to the text on each page to learn more about who you are, what you do, and who might be interested in finding you.
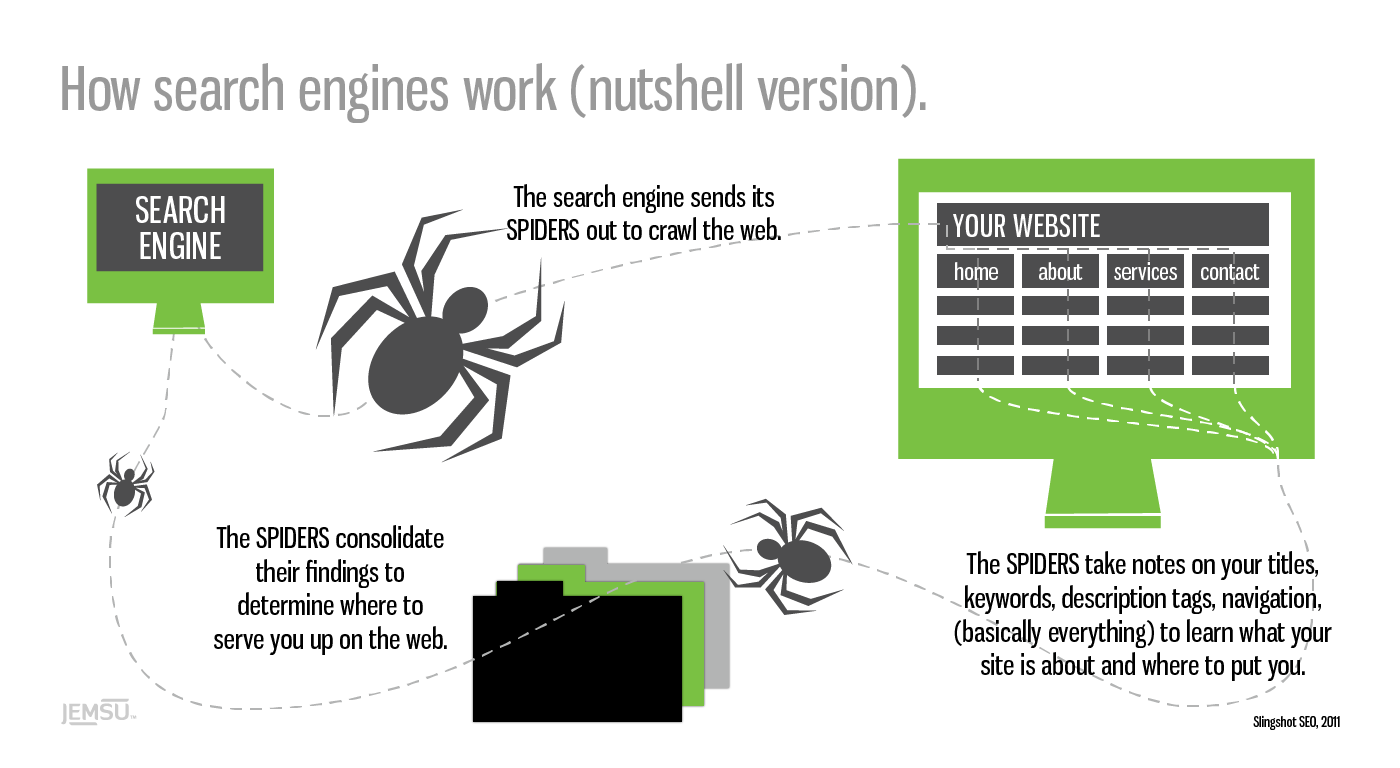
That may sound simplistic on the face of it.
Which is no small feat, considering there are more than 1.8 billion websites online today — with thousands of new sites popping up every day.
The first massive challenge is to locate new data, record what it’s about, and then store that information (with some accuracy) in a database.
Google’s next job is to figure out how to best match and display the information in its database when someone types in a search query. Scaling becomes a problem, though.
Google processes over 3.5 billion searches a day, and that number increases every year.

That means the information in its database needs to be categorized correctly, rearranged, and displayed in less than a second after someone expects it.
Time is of the essence here, because speed wins, according to Marissa Mayer back when she worked for Google over a decade ago.
She reported when they were able to speed up Google Maps’ home page (by cutting down on its size), traffic leaped 10 percent within seven days and 25 percent just a few weeks later.
Google won the search engine race because it’s able to:
One of the reasons Google is the front of the pack comes down to the accuracy of its results.
The information it displays is more likely to match what users are actually looking for.
Think about it this way.
When you type something into Google, you’re expecting something. It might be a simple answer, like the weather in your city, or maybe a little more complex, like “how does Google’s search engine really work?”
Google’s results, compared to other search engines, tend to answer those queries better. The information was the best of the best.
This breakthrough came from an initial theory Google’s co-founders actually worked on in college.
Google’s co-founders were still at Stanford in 1998 when they released a paper entitled “The PageRank Citation Ranking: Bringing Order to the Web.”
Check it out — you can read the whole thing right here!

The PageRank breakthrough was simple.
Academic papers were often ‘ranked’ by the number of citations a paper received. The more they received, the more authoritative they were considered on that topic.
Google co-founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, wanted to apply the same ‘grading’ system to the web’s information. They used backlinks as a proxy for votes. The more links a page received, the more authoritative it was perceived on that particular topic.
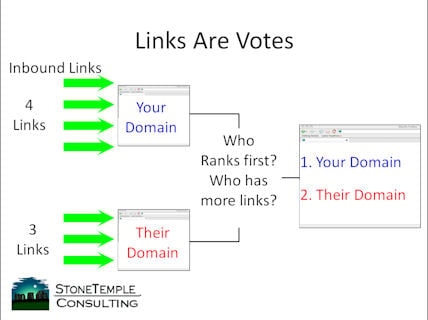
Of course, they didn’t just look at the number of links. They also factored in quality by considering who was doing the linking.
If you received two links, for example, from two different websites, the one with the more authority on a topic would be worth more.
They also considered relevance to better gauge the ‘quality’ of a link.
For example, if your website talks about “dog food,” links from other pages or sites that talk about things related to “dogs” or “dog food” would be worth more than one talking about “truck tires.”
External links (links from other sites) are also more valuable than internal links (links to different pages on your own site.)
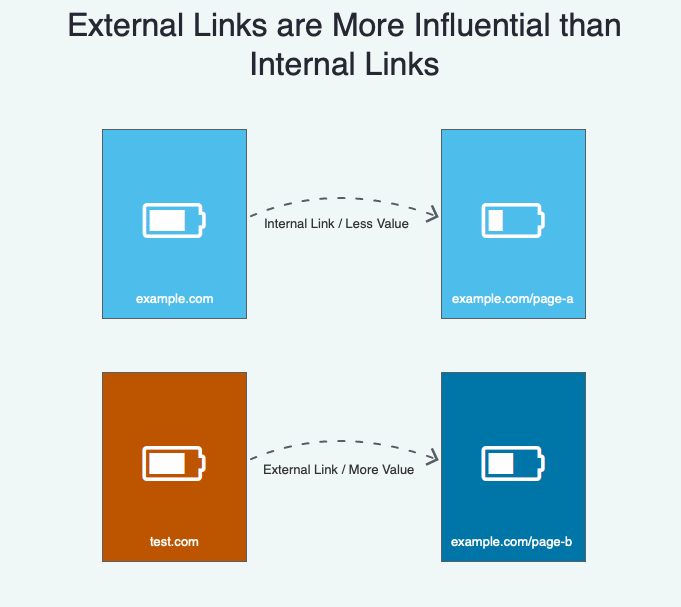
Before we go any further, please understand these concepts are over two decades all.
PageRank may have mattered years ago, but it’s evolved tremendously since then. So don’t worry about it explicitly today.
One of the reasons is because of newer algorithm developments, including RankBrain.
RankBrain was first acknowledged in 2015 by Google engineer Greg Corrado:
RankBrain has become the third-most important signal contributing to the result of a search query.
Google’s been working on this technology for years to help the search engine handle the massive increases in volume without losing accuracy.
The RankBrain secret sauce is that it uses artificial intelligence to continually learn how to improve.
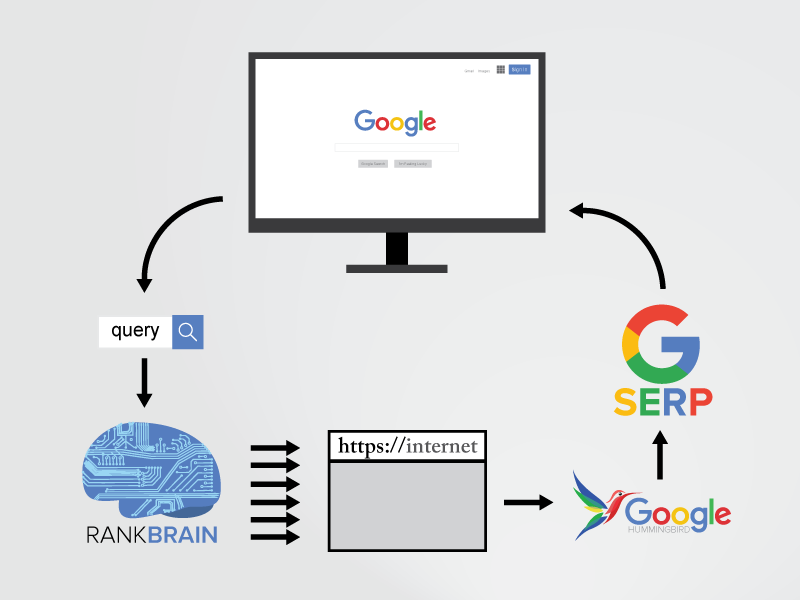
So the more it processes new information or new search queries for users, it actually gets more accurate.
For example, in 2010, Google’s algorithm “might have up to 10,000 variations or sub-signals,” according to Search Engine Land. That’s a lot!
As you can imagine, somehow managing all of those on the fly would be incredibly difficult (if not impossible).
That’s where RankBrain comes in.
Generally, the two most important ranking factors are:
Note: this changes over time, and these aren’t the only factors that matter. Speed plays a major factor in Google ranking, as do Core Web Vitals.
RankBrain, however, is still a main component. It helps analyze or understand the connections between those links and content so Google can understand the context behind what someone’s asking. This is often called semantic search.
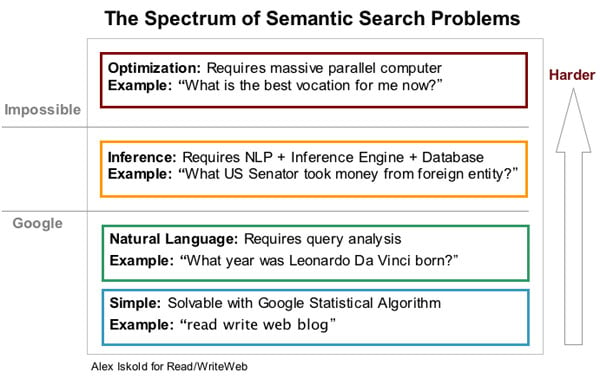
For example, let’s say you type in the word “engineer salaries.”
Now think about that for a moment. What type of engineer salaries are you looking for?
It could be “civil,” “electrical,” “mechanical,” or even “software.”
That’s why Google needs to use several different factors to figure out exactly what you’re asking for.
Let’s say the following events played out over the past few years:
Google’s able to piece all of these random bits of data together. It’s like a bunch of puzzle pieces suddenly coming together.
So now Google knows what type of “engineer salaries” to show you, even though you never explicitly asked for “software engineer salaries.”
That’s also how Google is now answering your questions before you even ask them.
For example, do a generic search right now for anything, like “pizza.”
Now, what do you see?
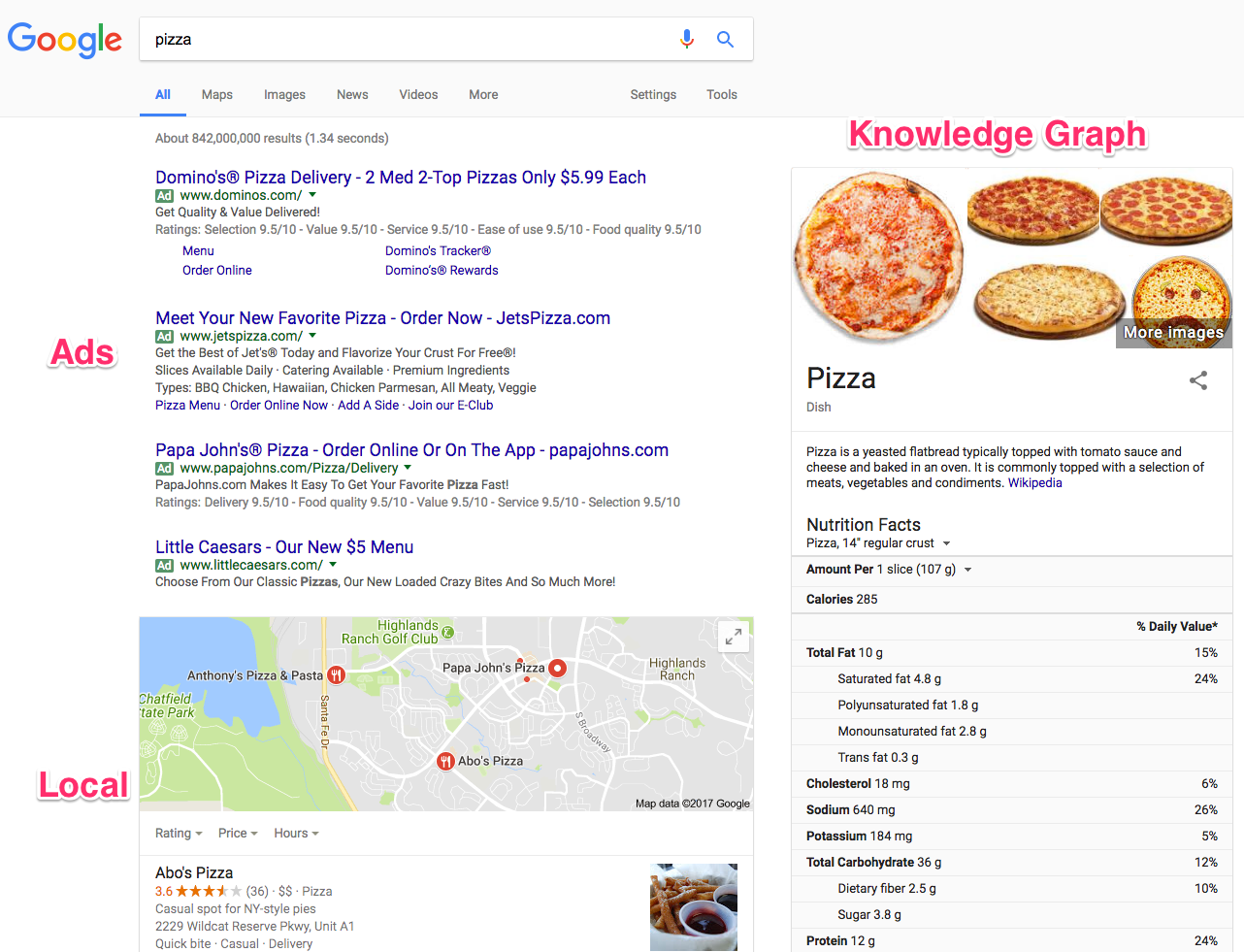
You see the typical ad spaces up at the top.
However, the local results below the ads are assuming that you’re asking “where to get pizza.”
The Knowledge Graph on the far right-hand side is serving up almost every fact and figure about pizza imaginable.
RankBrain process and filters all this data to give you answers before you even ask them.
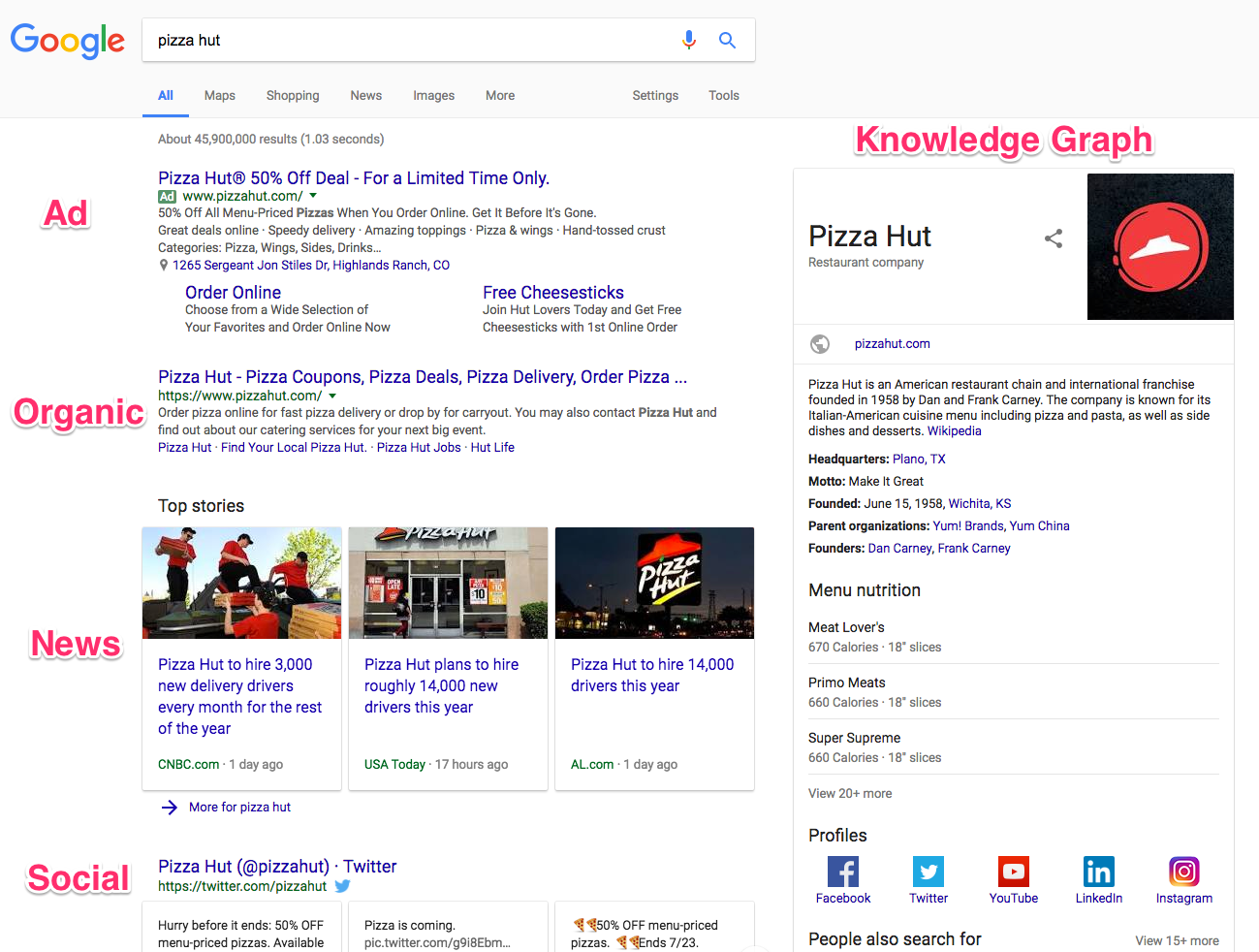
Change your search up a little (like this one for “pizza hut”) and the search engine result page (SERP) changes with new information.
Now you know how Google’s search engine really works.
While you don’t need to be an expert, understanding the basics like this can help you better figure out how to give your prospects exactly what they want (so you get better rankings and more traffic).
Here are a few of the big things to keep an eye on.
People type searches into Google to get an answer to whatever question they’re facing.
If they’re looking for an answer, it means they have a question.
If they have a question, it means they have a problem.
So your primary job is to solve someone’s problem.
In theory, it’s really that simple. If you solve someone’s problem better than anyone else, you’ll get better rankings and more traffic.
Let’s take a look at a few examples so you can see how this works in real life.
Someone comes home from a long day at work. All they’re looking forward to doing is grabbing something to eat fast and hanging out with their family or watching a new show on Netflix.
Before they’re able to throw a meal together, they try to run the kitchen sink and discover that it’s clogged.
Bummer.
It’s already getting late, though, so they don’t want to call a plumber. Instead, they head over to Google and start typing in “how to unclog drain” as their search query.
Then here’s what they see:
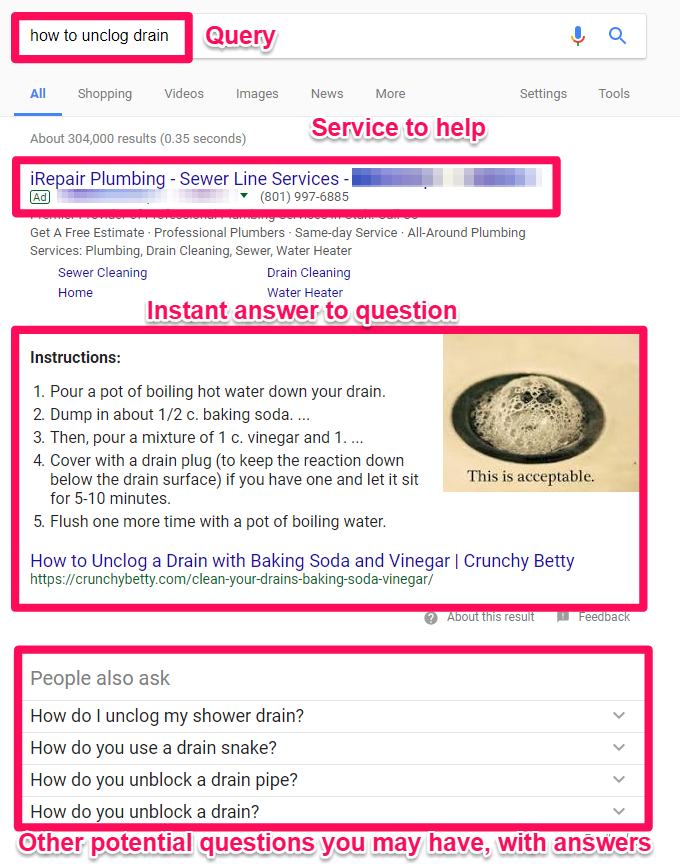
See?!
Way up at the top is an ad for a plumber (just in case you want to call in a professional).
Next up is an Instant Answer box that contains step-by-step instructions that Google believes has helped other people. So you might already be able to fix your sink without ever leaving this page!
Below that are related questions that other people commonly ask (along with their answers).
So all of this begs the question: How do you create something that can help solve a user’s problem?
I’ll answer that in one second, but here’s what you don’t do for the record:

“Keyword density” used to be an old-school tactic that was once relevant when Google’s algorithm was dumb and static. With RankBrain, Google has become a borderline genius.
So keyword stuffing like it’s 1999 will hurt you in the long run. As you can see, this is a terrible “answer” or “solution” to someone’s problem.
After saying that, there are a few places on a page that you want to pay special attention to.
For example, the Title Tag and Meta Description are used by Google to provide an official answer for what this page is about.
Those are the two elements that will also show up on a SERP when someone types in their query.
It only makes sense, then, that you should use the main topic in those areas so that everyone knows exactly what your page is discussing.

Do you want to see where that text is getting pulled from?
Simply right-click on a website to view the source code. For example, my homepage looks something like this:
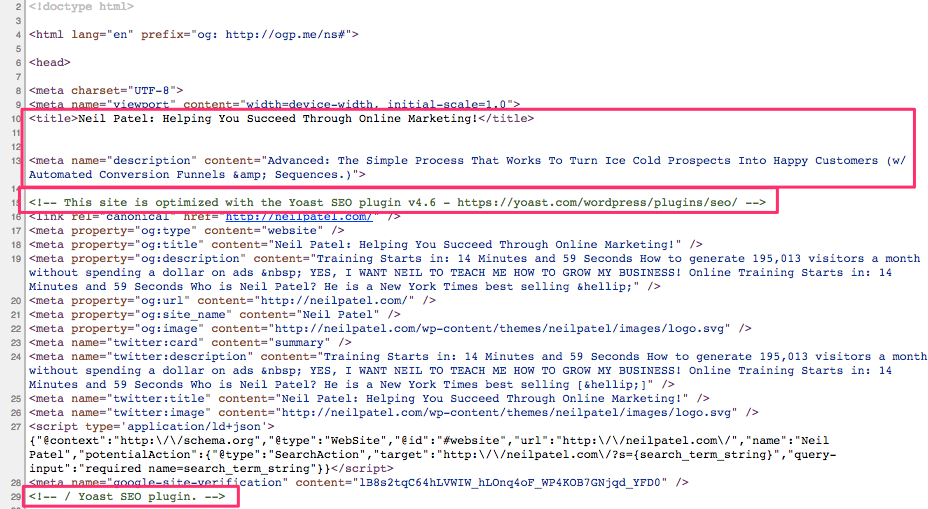
You can see the title tag and meta description at the top of the code.
I’m also using Yoast’s WordPress SEO plugin to help add these extra fields on the backside of WordPress.
That way, all you have to do is write out the specific title and description in plain text (as opposed to getting your hands dirty with code).
Otherwise, the actual page content should be written for humans (as opposed to keyword stuffing to tricks or fool the search engines).
Instead, here’s how your page content should look:

I wrote an in-depth response to help someone figure out a solution to a complex problem (keyword research).
Even though it’s a complex subject, I was trying to give them a simple, step-by-step solution so they could fix that problem ASAP.
Google even takes website usage data into account now to determine how helpful your content is.
For example, let’s say that someone clicks on your website from Google and is turned off by the poor design or hard-to-read content. So they ‘bounce back’ to Google immediately to find a different result.
That’s a bad sign! Google determines you weren’t a happy searcher. So maybe Google will try to find a few other results to swap out with that one to hopefully make everyone happy.
That’s why I also break up the paragraphs and include a lot of images. The goal is to help people quickly find what they’re looking for.
I want them to read the page faster and digest the information more easily so that they’ll stick around longer instead of bouncing away.
That’s the key to ranking well in search engines. Give the people what they want, keep them around or coming back for more, and Google will be happier as a result.
Let’s go back to our clogged drain example to see how this works in another context.
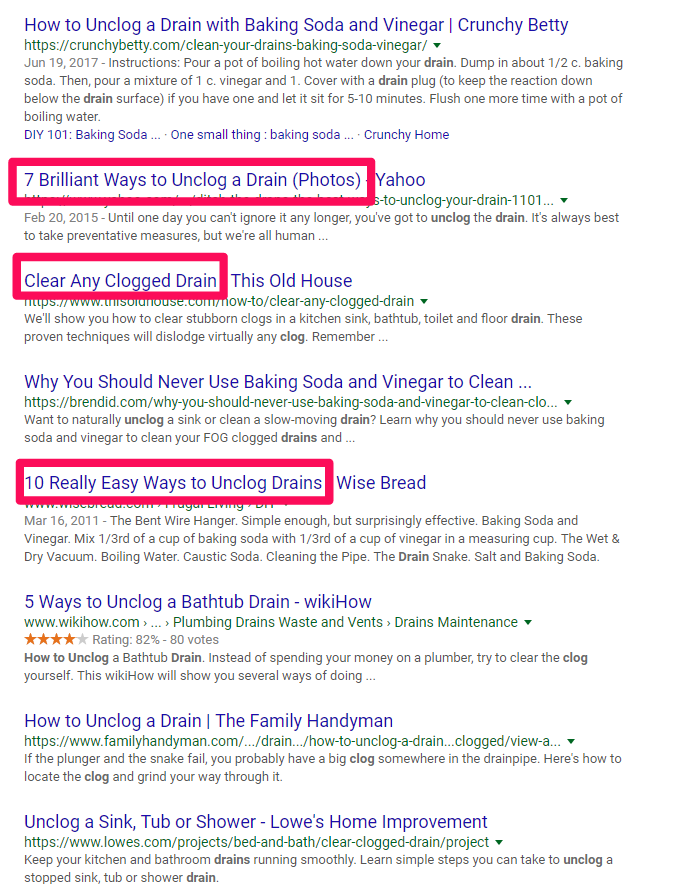
Those are all pretty good results!
In each case, the person who crafted each page provided a detailed answer to a common problem.
Let’s zero in on that second SERP result, “7 Brilliant Ways to Unclog a Drain (Photos)” from Yahoo, to discover what they’re doing so well to hit number two on a big, popular search query like that.
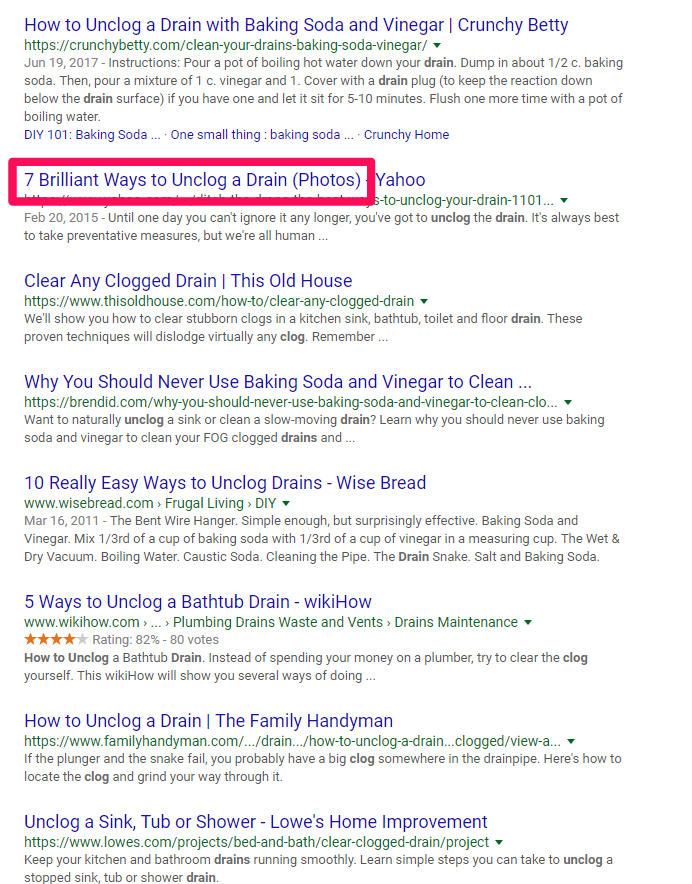
This seems like it might be a good result because it gives us multiple methods to try, along with photos so we can see exactly what’s happening.
Let’s click on that to see what they provide.
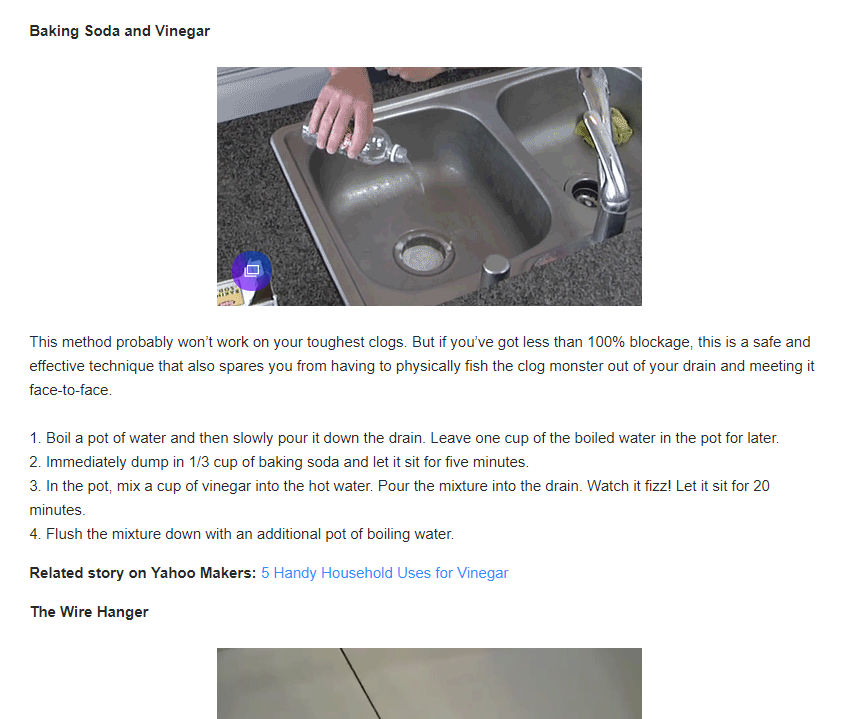
Pretty good overall!
It provides the user with good, quality content to help solve a problem. The better your content does that, the more links or ‘upvotes’ it will receive when other people find it useful, too.
Links and other citations or social signals help alert Google. They tell the search engine that your page is on the rise and to start paying attention to your website for these topics.
Your page will get better treatment, move up in the rankings, be exposed to more people, get more links or votes as a result, and continue that upward trend.
That’s where the genius of Google’s process comes into play.
It makes people happy by giving them exactly what they’re looking for. When you do it right, it gives you compounding benefits that can take off all of a sudden, expanding your website traffic as a result.
Google’s search engine is one of the most complex technologies in the world.
It crunches a mind-numbing amount of data at lightning speeds to give people exactly what they’re looking for in seconds.
When you boil it down to the basics, search engines are actually pretty easy to understand.
They want to help people find what they’re looking for.
People use Google to find answers and solutions. They have something on their minds, and they want to find an answer that helps them clear the issue to move on with their day.
How Google finds and delivers that information is the building blocks of SEO, making it crucial to growing your business online.
Now that you know how Google works, how are you going to use this information?
You came up with an idea, did your research, maybe even found some funding. You are ready to launch a business — but how do you get people to your website or store?
Pay-per-click (PPC) ads are one of the most effective ways to drive growth for your new business. Unlike brand building, content marketing, and social media, PPC ads can drive traffic today. There’s no need to wait weeks or months for your efforts to pay off.
Even if you have years of business experience behind you and are pretty well-versed in marketing, PPC ads for a new business need to be handled differently. Below, you can learn more about why PPC ads may be the way to go for your business and find tips for to make the most of them.
PPC ads can be a great way to launch a business because they allow you to reach your specific target market through keywords and target demographics.
With PPC ads, you create an ad and pay only when someone clicks on it. The ad should do something to draw the audience’s eye and make them want to click.
This type of ad is for new businesses for a variety of reasons, not the least of which is since they’re paid, you don’t have to wait to get to the top of search engine results organically. They show up at the top of the list automatically.
Some other reasons include:
PPC ads are highly targeted. When creating a PPC ad, you get to enter a ton of details about who you want to see the ad. The ad is then shown to people who fit that description. For example, you can target people based on their location, age, income, likes, family status, and even what shows they like.
While the platform requirements vary, you can set a budget limit upfront with PPC ads. You know the absolute max you’ll spend on an ad campaign when you start, then you can track the success of your PPC ad and make alterations for future ones.
This also makes it easy to scale; when you a ready for more traffic, just up your budget.
Because PPC ads are based on each click or interaction with the ad, you can follow how people respond. If an ad isn’t getting the responses you want—though remember, Rome wasn’t built in a day—you can alter the way the ad looks and see if that works better.
Being able to track the ROI of your ads directly makes it easier to pivot if things aren’t going well — or spend more money when they are.
Existing businesses have name recognition working in their favor, while new companies don’t. So, your PPC ads need to work a bit differently. While both types involve keyword research and target audiences, your research and focus on both factors need to be more intensive.
You need to use keywords specific to your brand and products in your PPC ads. Businesses that have been around for a while already know what keywords drive their traffic; you need to do a lot more digging as a new business owner.
Start with a keyword research tool. Search for words relating to your brand, determine which combinations seem to drive the most traffic for other brands, and tailor them for your needs.
Once you’ve chosen your keywords, make sure they’re in your copy so potential customers know exactly what it is you’re selling, why they should choose you, and call them to action.
Here’s an example. When we search for tomato seeds, we get a selection of ads from various sellers:
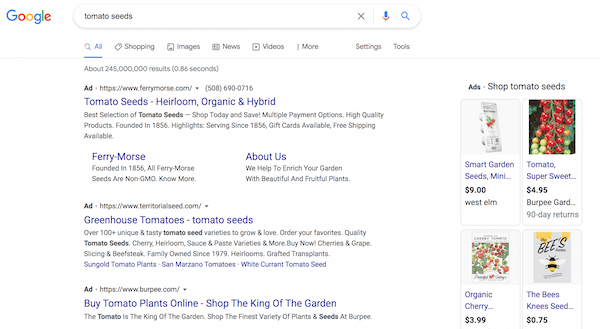
The ones that stand out showcase the tomato seeds keywords, as well as related keywords such as heirloom and organic. Unless a user searched for a specific brand, they’re likely to be drawn in by your keywords and not your brand name.
Your target audience is the group you want to see your ads. You can define them by location, age, gender, income, and more. Again, this is about being as specific as possible, figuring out who you want to buy your product via intensive research.
Your potential customers are more than just data, though. They like specific things. When you launch your first campaign, you should find out what types of ads they’re most likely to click on and create ads lining up with those details. You also need to find out where they’re most likely to click on them. Are they on Google or social media?
If they’re on social media, use strong visuals to stand out. As a bonus, you can often have a bit more copy with social media PPC ads than with search engine PPC ads. To grab their attention, use your picture and content to make it clear your new business meets your audience’s needs.
Let’s take TapRm. When you see this ad, specially targeted for those who live in NYC, you know immediately what they are all about. The various selling points, such as same-day delivery, may entice you to click and learn more.

Are you ready to dive into PPC ads to launch your business? Here are some actionable steps.
One way to ensure you’re getting the most out of your PPC ads is to zone in on exactly who you are targeting and what you want them to do right now. Don’t get distracted by possibilities down the line.
Stay focused on the market your business is best designed for and limit your reach to the most qualified buyers. These early days are the time to build buzz among your most potentially loyal customers, who will fall in love with your business.
Your audience likely found you because they searched for a resolution to a specific problem, so avoid the temptation to send them to your homepage.
Instead, think through exactly where you want them to go when they click your ad. Maybe it’s a product page, sign-up page, or landing page created just for this campaign. Since customers are likely new to your website, you want to keep the conversion journey short and straightforward.
You could create a wide range of PPC ads when you launch a business, focusing on different aspects of your business and showing up in various online spaces. But in these early days, keep it simple. Choose one of the platforms where your target audience is likely to be, either on social media or search engines, and focus on solving specific problems your customers have.
Keeping things this focused at first can help you figure out what types of ads people click on to find your site and whether or not they convert. Later, you can use this information to expand your types of PPC ads.
Once you launch your PPC campaign, keep an eye on how your ads perform. Luckily, most paid platforms track this data automatically, making it relatively easy to see how many people see the ads versus how many click.
Are people seeing the ads but not clicking? Maybe you aren’t speaking to your customers’ needs.
Are people clicking but not converting? Maybe you’re sending them to a page that doesn’t immediately solve their problem.
Keep watching the ads, figure out when and how people are converting, and change tactics accordingly.
As you continue your PPC efforts, create campaigns using campaign strategies that worked in the past, making them better each time. If you had a copy-only ad at first, you could take that copy and use it to create a PPC ad with a photo or video, for instance.
Watching your PPC campaign’s metrics can provide the feedback you need so you can create paid ads that actually convert.
The metrics you should pay attention to include:
These tell you how many people see your ads. Knowing how many people see the ad lets you know if your audience is too broad or narrow, particularly when compared to the number who click.
Click-through rates show you how well your ad design and copy are performing. If people are clicking through, you’ve made a good first step.
Once you notice those click-throughs, you’ll need to watch for conversion. Are people buying, signing up, or other actions? If not, find out why and change accordingly.
If your ads are on social media, look for interactions such as likes or shares. With your new business, these metrics may not be about conversions but to show some growth in brand awareness.
When you launch a business, you’re bound to try things that aren’t going to work. Don’t be afraid to scrap an idea and start fresh. Success in PPC ads involves trial and error until you connect with your ideal target market with a message they respond to.
You’ve launched your big idea. As a struggling startup, what’s next?
It’s time to get out there and start advertising. PPC ads can help you narrow down your focus, provide valuable feedback about how customers respond to your new business, and help you understand how to meet their needs.
What kind of PPC ads are you going to use for your next business venture?
Every Amazon seller knows how difficult it is to track and measure the impact of external advertising channels on sales. It doesn’t matter how you are driving clicks to your Amazon page; once consumers land on the website, it’s anyone’s guess what happens.
Thankfully, that’s not the case anymore. Amazon Attribution makes it possible for certain sellers to track what happens to every user they send to the platform. In this post, I’ll explain everything you need to know about Amazon Attribution, including:

Amazon Attribution is a new tool that promises to grow your Amazon business by improving experiences away from the Amazon platform.
Specifically, the tool provides analytics insight into how non-Amazon marketing channels like search, social media, display, PPC, and email marketing impact sales on Amazon. It can also track traffic sent to a different website that ultimately converts on Amazon.
Access to Amazon Attribution is available through either the platform’s self-service console or through tools that already integrate with the Amazon Advertising API.
Amazon Attribution is currently available for free, which is great news for e-commerce owners.
Amazon Attribution is currently only available to sellers enrolled in Amazon Brand Registry and Vendors in the U.S., Canada, the U.K., Germany, Spain, France, and Italy. That may change in the future, so keep your eyes peeled if you are in other locations.
Amazon Attribution lets you track a range of metrics that can impact e-commerce sales, including:
Amazon Attribution uses parameterized URLs—essentially a tracking URL. When users click on the link and go to your store, Amazon can track precisely what they do.
It’s a bit like a combination of Facebook’s Pixel and Google Analytics. Everything users do once they click on your ad is tracked, and you can see it all in an easy-to-use dashboard.
Amazon Attribution isn’t just a URL tracking tool. It has several key features marketers will want to leverage.
Amazon Attribution significantly increases the number of sales funnel data brands have access to. You’re not just limited to conversion data. Instead, Amazon lifts the curtain on how consumers interact with your product on their platform, providing metrics like clicks, detailed page views, and how many times customers add your product to their basket.
You can see campaign performance as and when it happens. Real-time reporting means marketers can optimize their marketing campaigns faster than ever before.
Because of the wealth of metrics Amazon Attributes provides, marketers can understand how the users they send to their store behave once they get there. Do they add the product to their basket as soon as they land on a page? Do they find a different product they prefer? Do they not buy anything at all? Amazon Attribution lets you answer all those questions and more.
Amazon Attribution lets marketers create different tags for every marketing channel. Facebook Ads, Google AdWords, blog posts, social media posts, it doesn’t matter. You can make hundreds of tags so you always get granular detail on the performance of every channel.
It’s not an overstatement to say Amazon Attribution could be a transformational tool for sellers and vendors. Before the tool was created, tracking off-Amazon marketing campaigns was an absolute nightmare.
There was simply no way to differentiate traffic from separate marketing channels. It was all dumped together.
Let’s say you made 500 sales, and you know that your own Amazon ads generated 100 of them. That leaves 400 sales that could have come from any marketing channel or even through an organic Amazon listing.
Do you see what a problem that is for marketers trying to find the best channel? There’s no way they can tell.
Amazon Attribution changes everything completely. Now marketers and brands will be able to see precisely where each sale comes from, and that comes with a bunch of benefits.
“Why use Amazon Attribution in the first place?” I hear some of you ask. There are several reasons eligible brands should start using Amazon Attribution immediately. Here’s my top three.
It’s not always easy to calculate the ROI of your non-Amazon marketing efforts, especially if you use multiple channels. Amazon Attribution allows sellers to see exactly which advertising efforts drive the most sales and provide the highest ROI. With a clear picture of what’s working and what’s not, store owners can focus on their most profitable channels.
Amazon Attribution lets you understand how users interact with your store and the broader Amazon ecosystem. If traffic from one demographic converts better than others, you can optimize your existing campaigns to drive more users that do convert and fewer of those that don’t.
Some sellers may find the concept of sending external traffic to Amazon strange, but it’s becoming increasingly important. Amazon is becoming increasingly dominant in e-commerce. At the same time, the price of sponsored ads on the platform continues to rise.
When you understand which marketing channels are most effective and how consumers interact with your products on Amazon, you can start to make real, data-backed decisions. The kind of decisions that will help you sell more on Amazon For some that could be investing more in a specific marketing channel. For others, it could be adjusting the price of their products.
What’s more, new sellers are signing up to Amazon every day. Oberlo recently reported that a million new sellers are joining Amazon every year. With so much competition, external traffic can be a vital lifeline to help sellers survive.
External traffic helps you sidestep the competition for listings on Amazon and drive traffic directly to your storefront. There’s no need to pay for sponsored ads on Amazon when you drive traffic directly to your products.
External traffic can seriously increase the number of sales your store makes. This can have a huge impact on your overall sales. Sales velocity is one of the ranking factors Amazon uses in its A9 algorithm, so the more sales you’re making, the higher your products will rank in the future.
The insights from Amazon Attribution can help you learn more about your customers than ever before. You may find that one product doesn’t convert as well as you thought it did, for instance. Or that customers prefer one product over another.
You won’t just be improving your Amazon store’s performance, either. These kinds of insights can improve your business outside of the Amazon platform, too.
The first step to getting started with Amazon Attribution is filling out a signup form and logging in to your account.
Once your account has been approved and set up, you can start matching products to the campaigns you’re tracking:
Amazon Attribution is an incredible tool, but unfortunately, it’s not available to everyone who sells on the platform. Luckily, there are several alternatives you can use instead.
Amazon Associates tracking links were the most popular way to track external traffic to the store platform before Amazon Attribution. With Associates tracking links, you get paid a commission every time a customer converts.
Unfortunately, this tracking solution is nowhere near as in-depth as Amazon Attribution. You’ll only be able to see which items users bought, not their behavior on the site before conversion. Plus, Amazon Associates only get one tag. That means it can be hard to differentiate between traffic sources.

Pixelfy.me is a URL shortener and tracker built specifically for Amazon sellers. You can create and track every kind of Amazon link, including Supreme, Brand, Canonical, Store Front, Add-to-Cart URLs, and many more.
Pixelfy.me can track almost everything apart from conversions. While that’s not as comprehensive as Amazon Attribution, Pixelfy.me does let you pixel users to retarget them in the future.

The Amazon Super URL Tool is part of the AMZ Tracker suite of tools. It does not offer sellers more insight into the way users shop their store, but it can significantly improve the quality of inbound traffic and boost sales as a result.
The platform’s special URL shortener makes Amazon believe visitors have searched for specific keywords on Amazon instead of going directly to the listing. Amazon should rank your products higher for these keywords, as a result, which can lead to more sales.
Amazon Attribution is the best way to track how off-site traffic performs on the Amazon platform. If you run external marketing campaigns for your Amazon store and are serious about optimizing your Amazon store, then Amazon Attribution is a must.
Not only can you optimize your marketing campaigns, but you can also increase conversions, too.
Creating Attribution tags is easy. Just follow my advice above or contact my team if you want an Amazon marketing agency to do the work for you.
How many external marketing campaigns are you currently running to Amazon?
Article URL: https://www.dover.com/open-roles/growth-product-engineer Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=26640412 Points: 1 # Comments: 0 The post Dover (YC S19) is hiring our first Growth Product Engineer appeared first on ROI Credit Builders.
The post Dover (YC S19) is hiring our first Growth Product Engineer first appeared on Online Web Store Site.
The post Dover (YC S19) is hiring our first Growth Product Engineer appeared first on ROI Credit Builders.
Shares in HSBC slumped after news articles detailed “suspicious activity reports” filed by it and other major banks to U.S. authorities, putting fresh pressure on a stock that has already dropped sharply this year.
The post HSBC Stock Hits 25-Year Low first appeared on Online Web Store Site.
Inc-Query | Operations (not-dev) | Full-time | REMOTE (US/APAC) | https://inc-query.com Small, profitable, rapidly growing, fully remote tech company. We program surveys insanely fast for private equity and management consulting clients. If you enjoy dealing with very smart clients in a somewhat technical and fast-paced environment, this role may be for you. The Survey Director …
The post New comment by fovc in “Ask HN: Who is hiring? (September 2020)” first appeared on Online Web Store Site.
Article URL: https://jobs.impraise.com/o/frontend-developer-3
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=23721615
Points: 1
# Comments: 0
Article URL: https://apply.workable.com/jerry/j/630F7C6695/ Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=22255992 Points: 1 # Comments: 0