Google’s Spam Update Just Completed: Here’s What Happened
Occasionally, Google rolls out their spam update which just ensures that the results on Google aren’t filled with spam.
Because if a user clicks on a spammy result, and if this continually happens, it creates a terrible experience and people would stop using Google.
They don’t give much detail on the spam update on their website, but luckily for you, we have two things that help us determine what the changes were.
The first thing we have is we track over 900 million domains on the web, so this allows us to see patterns.
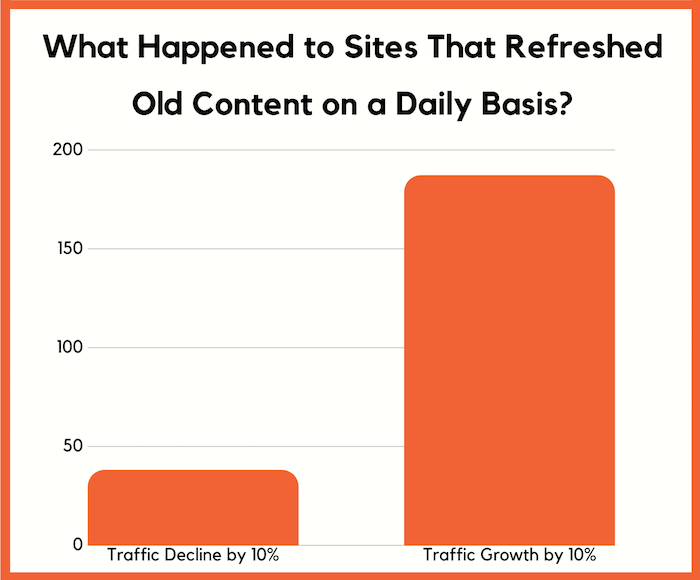
The second, which is more relevant for this update is at our agency, NP Digital, we have 100 experimental sites that use AI-written content. The purpose of those sites isn’t to “game” Google, they are more so to figure out how Google perceives AI-written content. And I will go into more detail on what happened with those sites later in this post as the results were interesting.
Purpose of the update
As in the name, Google’s main goal is to reduce spam. Now they have multiple types of spam updates, such as in July 2021 they had a link spam update.
This update didn’t specify if it was link spam-related or just overall spam.
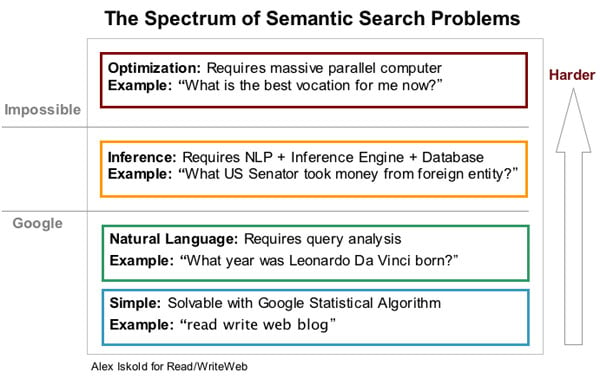
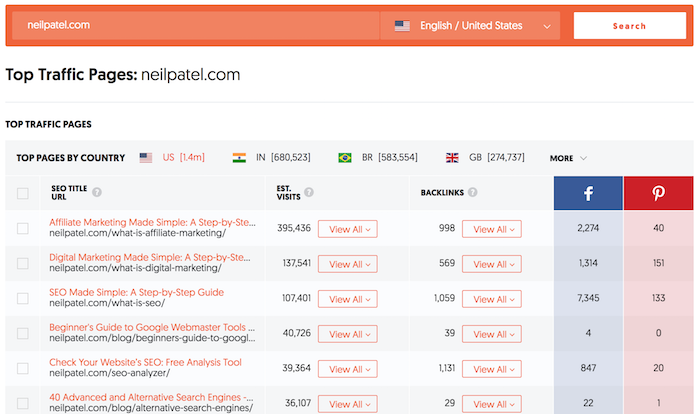
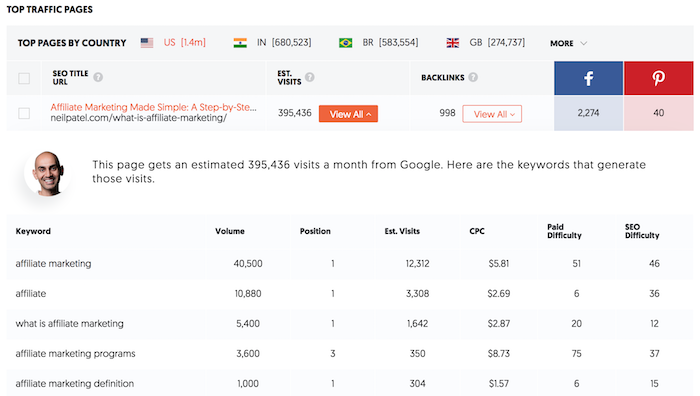
But when we look at the 900 million plus domains we track, here are the categories that got affected the most in a negative way globally.
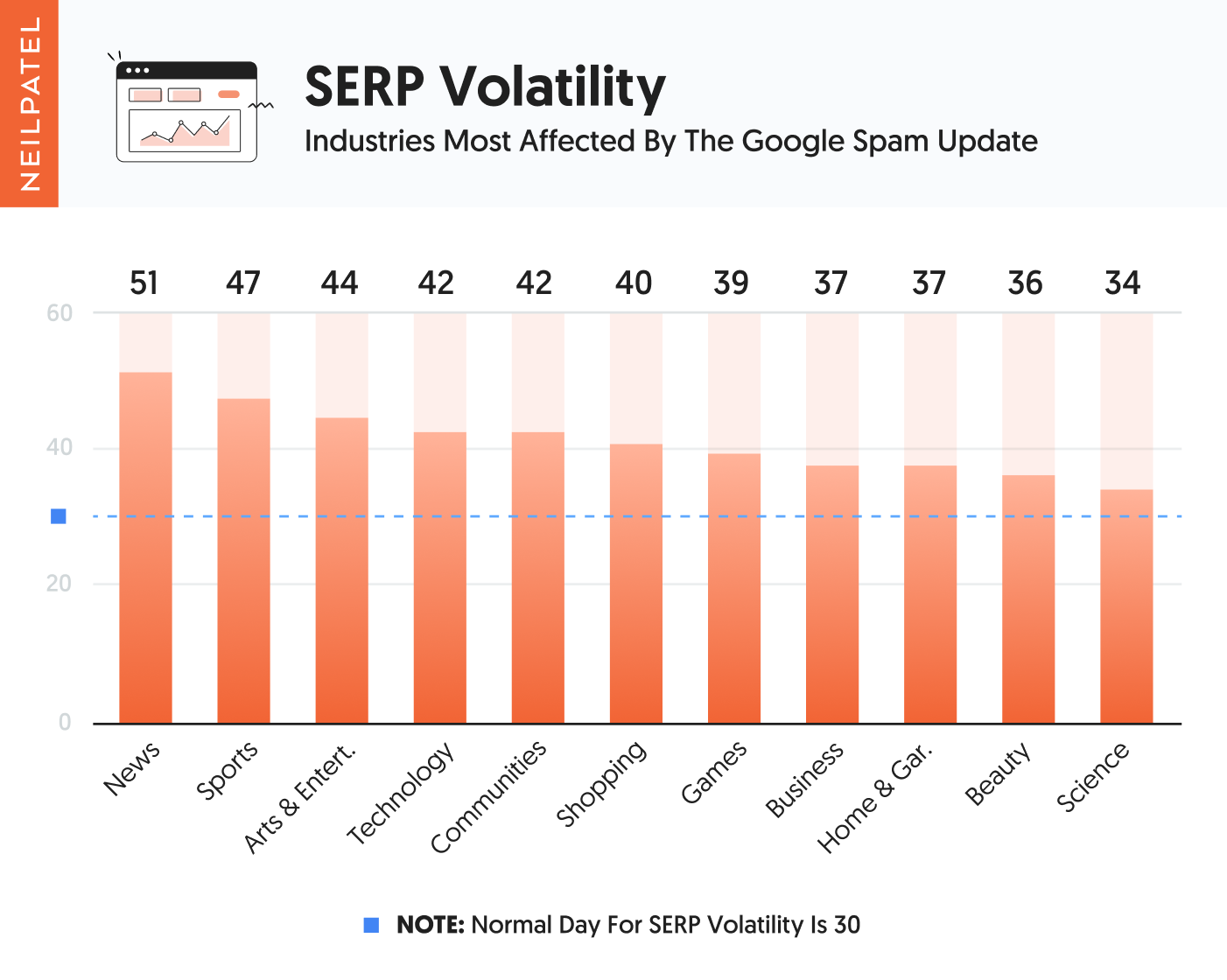
As you can see from the chart above, news and sports sites got affected the most. Followed closely by arts and entertainment and technology and community sites.
Most of these sites are heavy content-based and not product oriented.
When we looked at the sites affected here’s what we found:
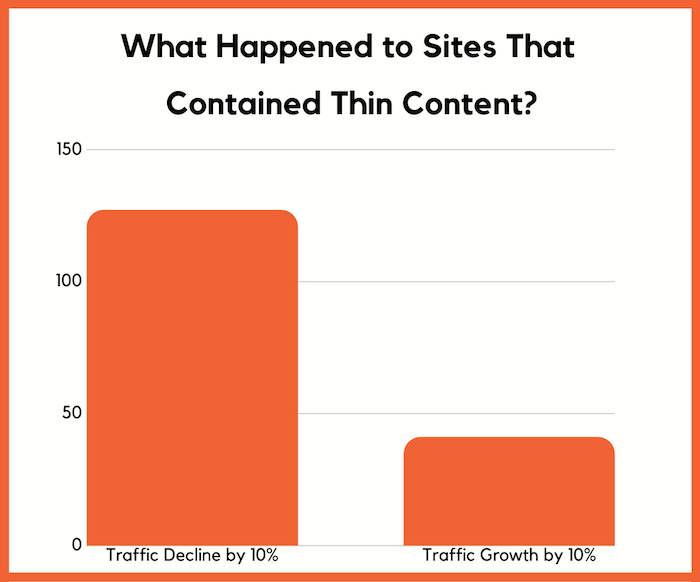
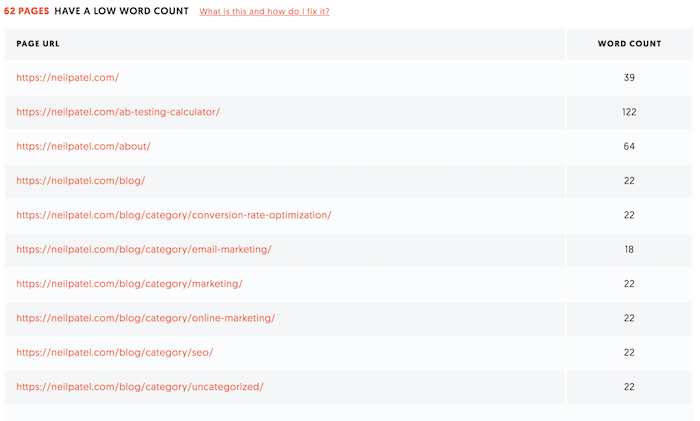
- Thin content – most of them didn’t have amazing content… a lot of them had thin content. And to clarify that, by thin content, I don’t mean low word count, I mean content that really didn’t provide much value. In essence, the content was surface level and once you finished reading it you didn’t get many insights or any actionable points or value.
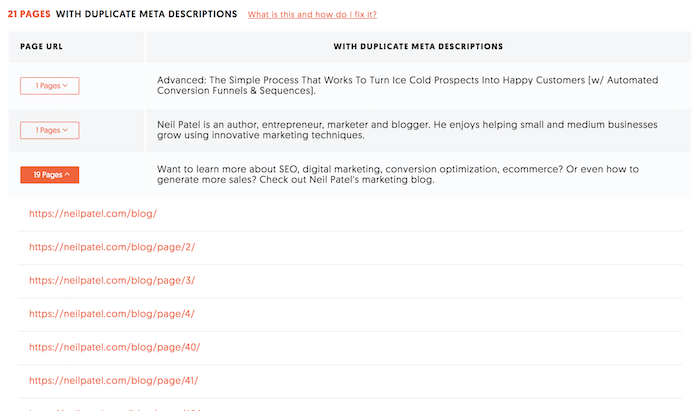
- Poorly created meta tags – a lot of the websites affected had pages with duplicate meta tags or ones that were obviously written for search engines and not humans.
- Keyword stuffing – shocking people are still keyword stuffing. Of the affected sites most of them didn’t keyword stuff, but roughly 3.89% of them did. Whether it was in their content on meta tags, they were using keywords in an excessive way that made the reading experience not ideal.
As you know there are many other factors in SEO. We just couldn’t find any other major patterns. From a surface level, some of the things they looked at seem kind of similar to the helpful content update.
We also looked at the backlinks of the sites that lost the most traffic we couldn’t find any patterns. Now, this doesn’t mean Google did or didn’t look at links as a factor of spam in this update, more so we just didn’t see any patterns.
Now here is where it gets interesting…
AI-generated content
Remember how I mentioned that we have 100 AI-generated websites? They are in a variety of industries, and they all have over 60 pages of content if not more that are all AI-generated, and of course, we manually built links (didn’t buy them, and you shouldn’t ever buy links) so that it would help the sites rank.
And in reality, we actually have over 681 AI-generated sites, but most of them don’t get enough SEO traffic. For example, when a site only gets 1,000 visitors a month from Google it is too hard to see patterns as visitor counts drastically change from day to day.
But 100 of the AI-driven sites generate at least 3,000 visitors a month from Google.
None of the sites sell anything or collect leads, they are just informational sites in different industries.
Now of the 100 AI content-generated sites, 53 have their content created purely through AI. And they also have their meta tags and even the headings within the article all created by AI.
Those pages don’t link out to other sites or even internal pages as AI content generation tools don’t really add links.
One thing to note is that most of the AI tools don’t really create content over 500 words unless you start adjusting the content or have the AI writer create content a paragraph at a time.
But for the first batch of AI sites (53 of them), we didn’t have humans modify or change up any of the content. We purely used the content that was created by AI in the form it was created including the meta tags the AI writer created.
Now in the second batch, we had 47 sites, on these sites we used AI to create the content, but then we had a human modify the content to ensure it was better and provided more value. Humans also added internal and external links, they modified the meta tags to be more user-friendly, and they added images and embed videos within the article when it made sense.
The one thing we didn’t do was increase the length much. Because from what we see from our Ubersuggest AI Writer most people just use AI-written content and don’t modify it much. When they do modify it, it tends to be slightly, and people really aren’t adding much in word count.
With our sites, we wanted to replicate what most marketers are doing with AI to get a sense of what Google is trying to solve.
Can you guess what happened to those sites?
The first group of AI-written content, which had no human intervention when it comes to modifying the content didn’t perform as well as the ones that had human intervention.
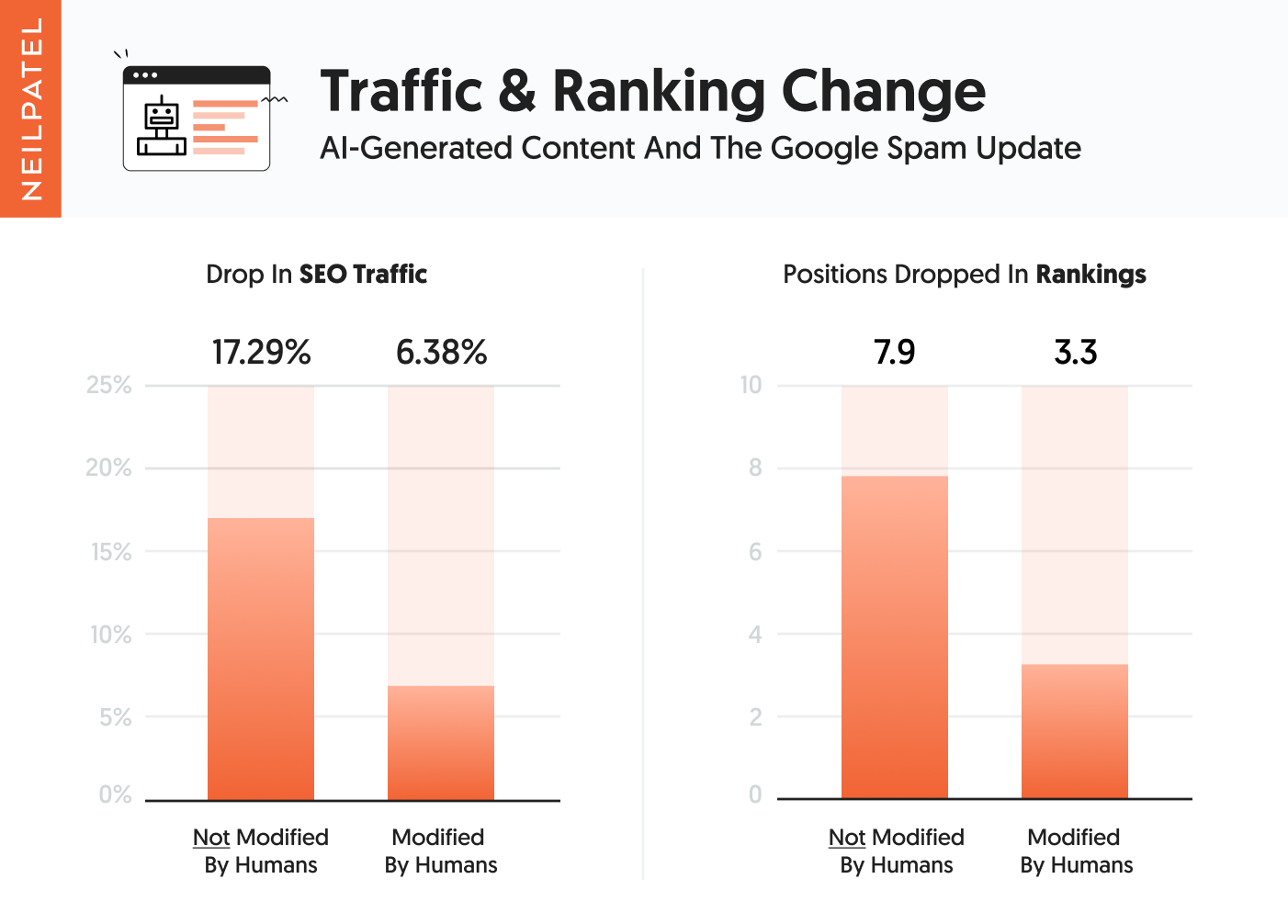
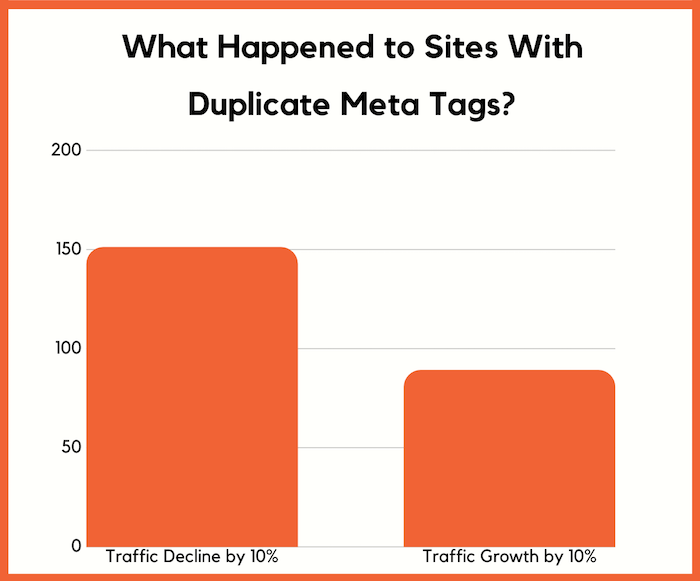
In essence, they saw on average a 17.29% drop in traffic and their keyword rankings dropped on average by 7.9 positions. Keep in mind that may seem like a lot but none of them really had number 1 rankings for any popular term.
The second group saw a 6.38% drop in traffic and on average a drop in ranking position by 3.3 positions.
But then when we dug deeper because I was curious to see the results for each site, we noticed that not all the sites were hit by the update.
Of the first group of 53 sites, in which the content was NOT adjusted by humans, 14 of them were hit by the update and saw traffic dips between 31.44% and 73.18%. On average the 14 sites lost 51.65% of their traffic.
From the second group, which had humans slightly modify the content, 8 sites were hit. They lost between 29.52% and 81.43% of their traffic. On average those 8 sites saw a 42.17% drop in traffic.
Now what’s funny is some of the other sites in both buckets saw smaller traffic drops such as a few percentage points and a few even saw slight traffic increase from SEO traffic by up to 4% when you compare pre-update and post-update traffic as it took 48 hours for the update to roll out.
But here is where it gets interesting, in the first group of the 14 sites that were affected, 13 of them also saw traffic drops from the helpful content update. And from the second group, all 8 of the sites were hit by the helpful content update.
One thing to note is that there weren’t tons of days of data post update from when Google finished rolling things out to when I released this blog post. And I didn’t want to compare Sunday traffic with Wednesday traffic. As you need to look at Sunday versus last Sunday to remove biasedness. Nonetheless, the above stats are what we saw and the ranking drops also confirm that these sites were hit by the update.
Conclusion
From what we are seeing, the majority of this update focused on content, meta tags, and keyword stuffing. It doesn’t mean Google didn’t look at other factors such as links or duplicative content, but we saw the biggest patterns related to the factors I mentioned above and AI-generated content.
If you want to do well in the long run focus on the user, it really is the way to win. In the short run, you may not come ahead but in the long run, you will.
Just ask yourself questions like is this piece of content going to be helpful to users? Is using the same meta tags on all pages helpful? Is my website providing enough value that people will want to link to me?
In essence, you are just spot-checking yourself and doing what’s best for users.
What did you see from the Google spam update?