Article URL: https://www.ycombinator.com/companies/evidence/jobs/Lu29GmN-analytics-intern
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=40004357
Points: 0
# Comments: 0
Article URL: https://www.ycombinator.com/companies/evidence/jobs/Lu29GmN-analytics-intern
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=40004357
Points: 0
# Comments: 0
Article URL: https://www.ycombinator.com/companies/hubble/jobs/IZ0giSa-analytics-engineering-advocate
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=39368868
Points: 0
# Comments: 0
The post Lightdash (YC S20) Is hiring an analytics engineering advocate appeared first on #1 SEO FOR SMALL BUSINESSES.
The post Lightdash (YC S20) Is hiring an analytics engineering advocate appeared first on Buy It At A Bargain – Deals And Reviews.
Article URL: https://www.ycombinator.com/companies/hubble/jobs/IZ0giSa-analytics-engineering-advocate
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=39368868
Points: 0
# Comments: 0
Article URL: https://patterns.app/
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=38602281
Points: 0
# Comments: 0
Article URL: https://www.ycombinator.com/companies/bits/jobs/cC85dw9-finance-analytics-manager Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=38527875 Points: 0 # Comments: 0
Article URL: https://onesignal.com/careers/4007708006
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=36170689
Points: 1
# Comments: 0
Article URL: https://onesignal.com/careers/bf5f67d4-f4be-44a9-9677-2bbb5686009b
Comments URL: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=33396197
Points: 1
# Comments: 0
When’s the last time you attempted to make a recipe in the dark? I’d venture to guess you’ve never done so. It’s unnecessary and reckless. Would you be surprised to learn, then, that more than 60 percent of companies have ignored marketing analytics data when making marketing campaign decisions?
Just like making a recipe in the dark is unnecessary and reckless, so too is ignoring the invaluable marketing data when making expensive and time-consuming decisions for your business.
In this post, we’ll introduce marketing analytics and its benefits. We’ll cover the types of marketing data and how to create your own report. Finally, we’ll highlight three examples of companies that used digital marketing analytics to their advantage.
Marketing analytics is the use of data to evaluate the performance of a marketing activity or collective marketing efforts.
From 2012 to 2020, the share of projects where marketing analytics were used to make a decision has ranged from 29 percent to 43.5 percent. While this number seems low, it does go to show that using marketing analytics to drive your own business’s campaigns will give you an edge against the competition.
Before we get into the nitty-gritty details, it helps to understand why marketing analytics is so important. While some companies may argue that analytics data isn’t crucial to their business, others will stake their success solely on their ability to follow the data.
Perhaps the greatest benefit to digital marketing analytics is the ability for businesses to understand big-picture marketing trends and forecast future results.
On a micro level, marketing analytics can help a business to understand the ROI of their individual programs. This can help them to determine which programs to cut and which programs to invest in. It will also teach them what they need to know for future projects.
Finally, consider that sophisticated marketers (those who utilize 5 or more analytics tools) are 39 percent more likely to see an overall performance improvement in their marketing programs. Just imagine what that growth could look like across your portfolio!
When it comes to marketing analytics data, there are three categories it can fall into. Here’s a description of each, as well as examples of the metrics used.
Descriptive analytics provide insights into the current state of your business. They answer the question, “what is happening now?”
The types of metrics you’ll see here are surface level. They provide a quick snapshot of the business as it is today but without any analysis or reasoning behind it. These metrics include page views, revenue, units sold, average unit price, and conversion rate.
Diagnostic analytics provide a root cause as to the descriptive analytics. That is, they answer the question, “why is this happening?”
When you have questions about your descriptive metrics mentioned above, you’ll dig into the diagnostic metrics. These dig deeper to find the cause of the diagnostic metrics by looking at things such as traffic sources, bounce rates, exit rates, and last touch channels.
Predictive analytics provide a look into the future of your business. They answer the question, “what’s likely to happen in the future based on past and current trends?”
As you can imagine, predictive analytics requires more sophisticated input. While you can pull descriptive and diagnostic analytics and make connections, you cannot do so easily with predictive analytics. Instead, you’ll typically need the help of a predictive modeling tool or a data analyst.
If you’ve been tasked with creating a digital marketing analytics report for your business, the steps below will help to get you started.
Where does it all begin? With the raw data.
How you pull your data will depend on the tools and platforms you use. There are many free and paid options available and you may find yourself using more than one to get a fuller picture.
Google Analytics is a free tool that provides you with in-depth website analytics. If you’re using an e-commerce platform like Shopify, you may also have access to free analytics within your account. Paid options include HubSpot, Domo, and Tableau.
There are two important questions to answer before you compile your data. They are:
To answer those questions, you’ll want to dig deeper by answering the following:
Are you pulling the data just to get a snapshot of the business, or is there something more specific in mind? Are you delivering the report to top-level executives or a direct manager? How will this data be used? How often will this data report need to be compiled?
A weekly report on the state of the business to your direct manager will look completely different than an analysis of a business unit to the CFO of the company.
You have the data and you know the purpose and audience for your report. Now it’s time to ensure you’re highlighting the right data in your report. This will come down to understanding the type of data analytics you’ll need to answer to your audience (e.g., descriptive, diagnostic, predictive).
Let’s say you’re tasked with reporting on the launch of your company’s newest product. It hit the virtual shelves two weeks ago and it’s time to evaluate its initial success. What does this look like?
Here you’ll be pulling descriptive analytics. This includes metrics like product page views, add to carts, revenue, and conversion rate.
It doesn’t end there, though, because your audience will likely want to know whythe above metrics are what they are. Whether they’re below or above the target goals, it’s good to understand what happened to get you where you are.
This means you’ll also be pulling diagnostic metrics like last touch channel and traffic source. You can also dig into the customer demographics and behaviors.
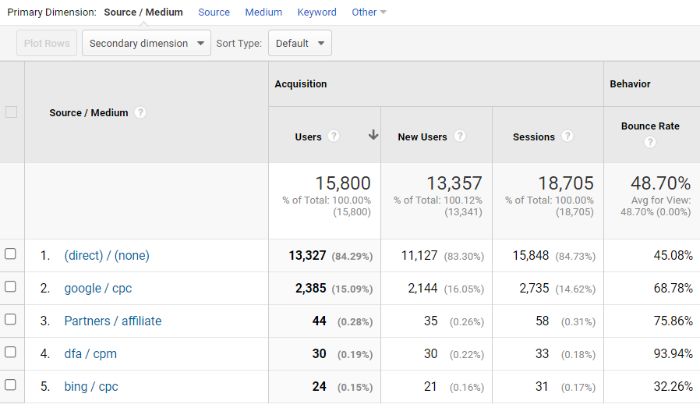
With this data, your report will begin to shape itself into more of a story than just a bunch of KPIs and graphs.
You have the data, you know your audience, and you have your story. Now it’s time to consider the best way to tell your story to make sense to your entire audience. Visuals are a crucial way of doing so.
Visuals include graphs, charts, maps, funnels, and Venn diagrams. They are a great way to help you see your data in a new light andtell your story more effectively.
The good news is most analytics tools offer a suite of visualization tools so you don’t have to find yourself reinventing the wheel. However, programs like Microsoft Excel also make it incredibly easy to turn raw data into visualizations.
It can be inspiring to see how other businesses are using marketing analytics to inform their decisions. Here are three examples for you to consider.
Averages are used frequently when evaluating marketing analytics. There is nothing inherently wrong with this approach, but as we’ll see below, it can be good to look at those outliers to determine the true efficacy of the average.
Looking beyond the average customer for Costa Rican Vacations has resulted in a 40 percent increase in website conversion.
According to Casey Halloran, the Co-Founder and CEO of Costa Rican Vacations, their team frequently looks to averages to inform their decisions: average spend, the average length of stay, and the average number of travelers.
Upon taking a deeper dive into the data, they realized the average number was so far off the actual customers’ metrics due to the extremes of the outliers. That is, the majority of their customers were on one end of the spectrum or the other with very few actually falling into the middle.
With this information, Costa Rican Vacations made a shift in its product offering. One way they did so was by adjusting the total budget slider on their homepage to go up to $20,000.
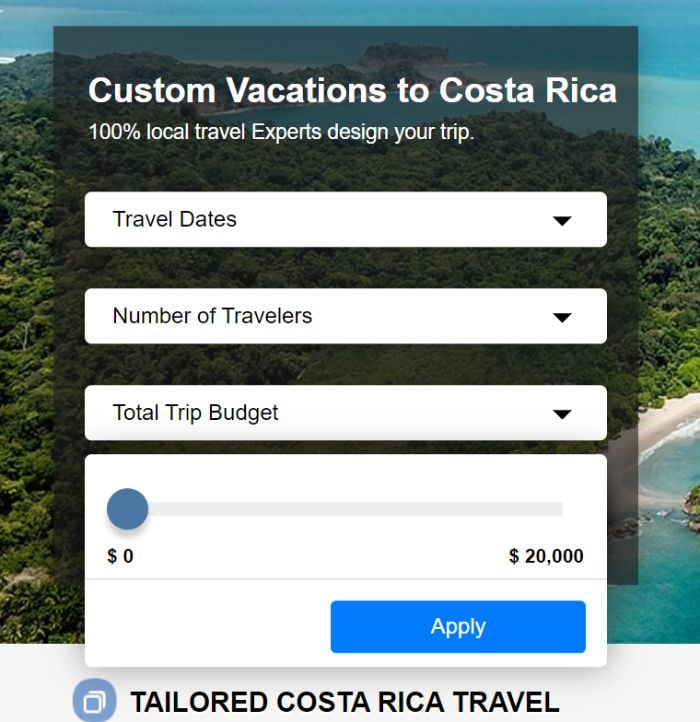
By doing so, they opened up their offering to a new, higher spending customer base and increase website conversions by 40 percent.
Other businesses, too, can benefit from this example. After all, how often do we look at averages and medians without considering the impact of our marketing decisions on the outliers? With this in mind, take time to truly understand how average your average customer really is, or whether they’re simply a product of extremes on either end.
Allrecipes is the world’s largest digital food brand. It boasts 18 websites in 23 countries and more than 85 million users. No matter how large your brand, there’s always the competition to consider. To maintain their competitive advantage, Allrecipes worked with Tableau to better understand every stage of the customer journey.
The brand had several primary objectives, including to:
Allrecipes leveraged Tableau, a business intelligence platform to visualize data all in one place. With custom dashboards and organizational collaboration, the brand was able to achieve numerous goals. In particular, let’s look at how Tableau’s device-level analytics enabled them to drive mobile engagement.
According to Esmee Williams, the VP of Consumer and Brand Strategy, mobile usage had increased from 8 percent to three-fourths of all visits in recent years.
The goal was to increase mobile usage while also providing a continuous experience across devices. They performed an A/B test which showed the mobile site on all devices as a way to learn more about how users interacted with mobile site elements.
Using Tableau’s digital marketing analytics collection and visualization tools, Allrecipes used the data they collected to improve the mobile site. This included optimizing content and encouraging photo uploads with an easy-to-use interface.
While you don’t need to perform a cross-device A/B test to get these same results, your business too should evaluate mobile device engagement to understand customer behavior. Only then can you implement changes that have a measurable impact on customer engagement metrics.
Let’s end our examples with a titan of industry, Netflix.
Netflix has a customer retention rate of 90 percent which is far above Amazon Prime’s 75 percent and Hulu’s 64 percent. What is it that drives Netflix’s success? According to Netflix, its success is largely due to the collection and use of customer behavior analytics.
What kinds of data does Netflix collect and feed to their algorithm? Here are a few examples:
Of course, Netflix also looks to interactions the customer has with their shows and movies. If a user selects a show based on the 96 percent recommended rate by Netflix, does the customer finish the series? Do they rate the series well?
With more than 150 million subscribers, Netflix has a large data pool from which to gather insights. This is critical to their success considering 80 percent of viewer activity is triggered by algorithmic personalized recommendations.
Here are the answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about marketing analytics.
In addition to the three marketing analytics data types listed above (descriptive, diagnostic, and predictive), there are also said to be prescriptive analytics and cognitive analytics.
Your digital marketing analytics campaign should be scalable, sustainable, and affordable.
The needs of your business will largely inform your decision on marketing analytics tools. However, a few tools to consider are Tableau, Power BI, and Adobe Reporting.
A data analyst can certainly offer important insights for your business. For small and medium-sized businesses, though, they likely aren’t necessary.
Marketing analytics is more than just a collection of data. It provides invaluable insights that could have otherwise gone unnoticed.
After all, when you’re making big decisions regarding your business’s marketing campaigns and programs, you need to evaluate all of the data available to you. Only with a proper analysis of previous data and current trends can you ensure you’re making the best decisions for your company’s bottom line.
What percent of your business’s marketing decisions are made using analytics?
NOTE: On June 8, 2022, Christopher Coomer, VP of Data, Analytics, and Insights at NPD, will cover the essentials of GA4 in a short presentation. This will be followed by an extensive Q&A session with webinar host Will Francis of DMI. Register here. Those who attend will receive a free follow-up guide to help them transition to GA4.
Google recently announced it is sunsetting Universal Analytics in June of 2023. This means if you’ve been holding out on switching to Google Analytics 4, your time is almost up.
I’ve heard from a lot of marketers and business owners who are not excited about the switch. Change is always hard, but I really think this switch is going to be a good thing. For starters, it provides a ton more data and is more customizable—which means you can track what matters to you, not just what Google thinks might matter to you.
This guide walks you through everything you need to know to make the switch, including what you can do with Google Analytics 4, how to make the switch, and how to get started with the new platform.
What can you expect? New report functions, enhanced features, and predictive insights make this new generation of GA more powerful than ever.
Google Analytics 4 is the newest version of Google Analytics. This is a whole new generation of web analytics that will allow marketers to effectively analyze important customer usage metrics, not just track traffic.
Google Analytics 4 tracks the entire customer path across multiple platforms and leverages AI and machine learning to provide more detailed insights into how users interact with your website and app.
GA4 is also focused on customer privacy. This comes in the face of some of the latest privacy laws, such as GDPR and CCPA. With privacy-first tracking, cross-channel data measurement, and AI-driven predictive analytics, GA4 is an advanced tool that provides unparalleled insights.
The most obvious difference between Google Analytics 4 and Universal Analytics is that GA4 enables you to report on activity that occurs on both websites and applications. There are a number of other differences, including:
The first change you are likely to notice is the entirely new dashboard. It is more streamlined and many of the reports you are used to are gone or have been moved. The navigation bar to the right includes buttons for home, reports, explore, advertising, configure, and library.
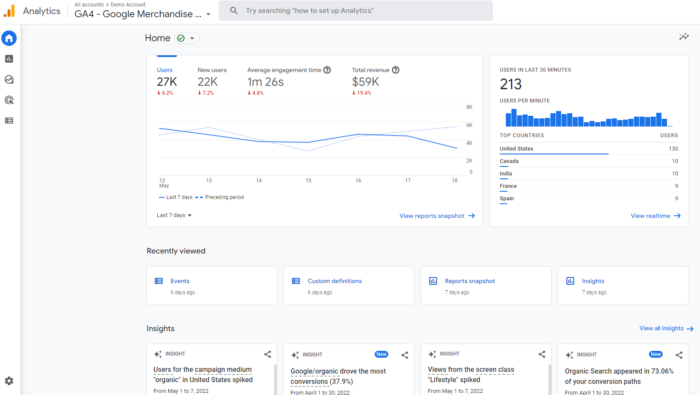
At the bottom, under Insights, you’ll see predictive insights based on Google’s AI. I’ll dig more deeply into the features and what they mean in a later section, so keep reading!
With Universal Analytics, page views were the most important metric. With Google Analytics 4, all measurements are events. Instead of seeing generalized data, you can now gain a fuller understanding of how users interact with your app and website.
What does this mean for you? You can still view session-level reporting, but the ability to break it down by interaction means more in-depth reports and insights.
GA4 also has an array of new metrics. These include engagement metrics such as:
It also tracks a number of other dimensions, including attribution, demographics, events, and so forth.
This is a big change, but it’s actually going to make it easier to track customers throughout their journey. GA originally assumed page views were the most important metric—that is no longer true. The new parameters might have a learning curve, but you will have access to more data.
While looking at past behaviors is helpful in understanding your audience, it doesn’t help you make proactive decisions. With GA4’s powered predictive metrics, you can make data-driven decisions on a large scale.
What does this look like? For most businesses, predictive analytics can significantly impact retargeting campaigns. AI metrics include:
With the above metrics, you can create audiences based on their predicted behaviors. For example, users who are likely to purchase in the next 7 days or users that are likely to spend more than $500 in one purchase.
These audiences can then be targeted using Google Ads campaigns or even on social media.
These metrics can also improve website performance. You can create custom funnels for different audiences based on their behaviors and needs. The suggestions will continue to improve as more data is collected.
GA4 allows you to customize the dashboard, enabling you to see the reports that matter most to your business. It even works well in conjunction with Google Data Studio so you can create custom visualizations of the data collected.
You can also create custom segments based on trigger events which are essentially a subset of events that occurred on your website or application. This enables you to more accurately track customer interactions.
For example, you can create segments on all conversion events that occurred in a particular location. These capabilities make it possible to take a more granular view of your users and their behaviors.
What happens when users are active on more than one platform? With the old Google Analytics, tracking users across platforms was nearly impossible. The new Google Analytics 4 tracks both web and app data in one property (hence the beta name of Google Analytics App+Web).
Cross-platform tracking enables you to see the complete customer journey, including acquisition, engagement, monetization, and retention. You can use GA4 to track the user experience from start to finish—and from platform to platform.
This is done through unique user IDs assigned during app or website login.
With the appropriate gtag.js script, the user ID for each logged-in session will be sent from either the website or the application to Google Analytics. The ID will be reported to the GA4 property and any user metrics will be logged. When the user logs in again on an alternative platform, the reports will connect the user’s data to their unique ID and pick up where it left off.
This is incredibly useful information for any marketer, as it allows you to better understand the cross-platform experience of your users. The data can also be used to extrapolate information for a generalized demographic and build more accurate customer models
Since Google Analytics 4 can be used for your website or application (or both), there are two separate setup processes. They are outlined below.
If you currently have a Universal Analytics property for your website, then set up of a Google Analytics 4 property can be completed with the GA4 Setup Assistant.
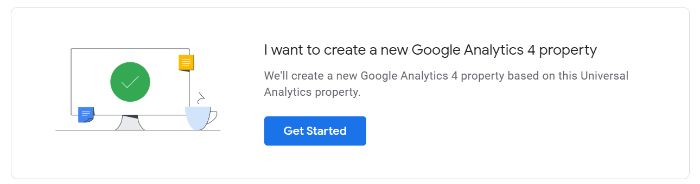
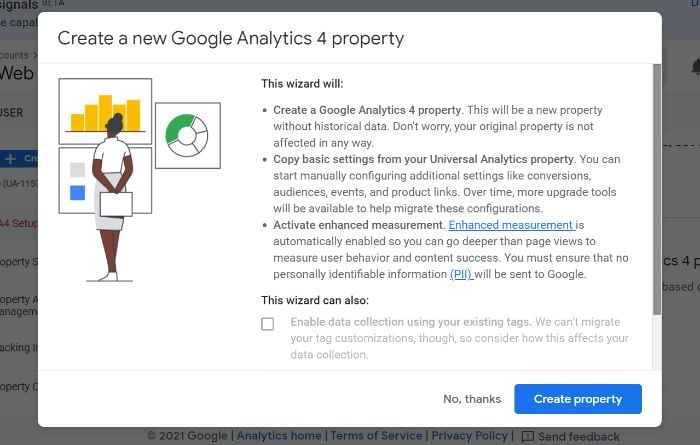
If you are unable to “Enable data collection using your existing tags,” it’s for one of three reasons:
In all three cases, you’ll need to add the tag yourself.
To upgrade your Firebase account to Google Analytics 4, follow these steps:
Once upgraded, you can find app analytics in both the Firebase console and Google Analytics.
Now that you understand the power of the new Google Analytics platform, I’ll walk you through how to use it. I will say there is a learning curve for the platform, and that can definitely be frustrating.
Start by following the steps below. This will help you understand the basics and how to navigate the new platform. If you still aren’t seeing the data you need, consider signing up for a longer-form course or reaching out to my team for more help.
The search bar in GA4 lets you access more than ever, including instant answers for specific queries (such as “how many users this month vs last year”), specific reports or insights, property configuration, or to access the help content.
Try a few queries to see what you can access, such as “how to create a report” or “top users by city.” As you learn the new dashboard, the search board will be invaluable.
Now let’s look at the new dashboard. At first glance, it might look pretty familiar. Take a look around, however, and you’ll see most of the reports you’re used to are not where they used to be.
Here’s an annotated version of the dashboard. I’ve labeled the navigation bar on the left as well as the different displays. For this walk-through, I’m using GA’s demo account (Which you can access here), so it may look a bit different than your version, especially if you’ve already started customizing it.
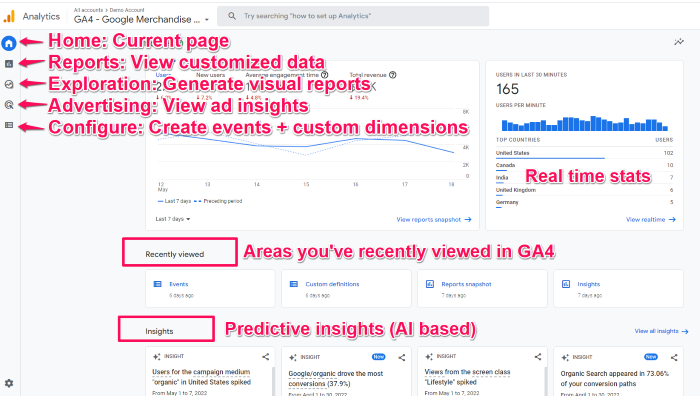
NOTE: A few of the navigation menu items including Audience and Library aren’t in this screenshot, but should be accessible in your dashboard if you have editor access.
From the dashboard, click on the second icon on the left nav bar, the one that looks like a graph: . This will take you to the reports dashboard, which shows you snapshots of different reports. Most of the reports you are used to seeing are in this tab, though they may look a bit different.
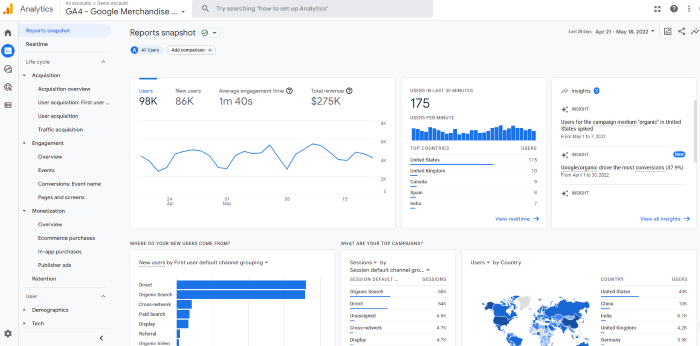
There’s a ton of data here. I won’t walk through all of it because different sites will track different metrics, so yours might look different.
But let’s say you want to see how many people viewed a specific page. In this dashboard, you’d click “engagement” and then look at the “Views by page title and screen class” chart.
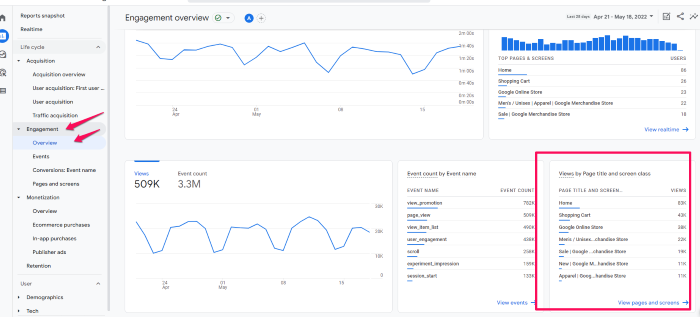
You can also view acquisition, monetization, and user demographics here. If you want to compare different metrics, select the + icon at the top (next to Engagement Overview.)
One of my favorite features is the ability to customize the reports snapshot so you can see the data that matters most to you at a glance. This will also help you get to know GA4 a bit better so you are more comfortable using it.
First, let’s create a new report.
To start, click Library at the bottom of the left navigation bar. Note, if you don’t see this option (It’s not in the demo account), it means you don’t have admin access.
Then, scroll down to the Reports table and click Create a new report. Then, select Create an Overview Report. You’ll be asked to provide the data source and GA will walk you through creating the report. (This part changes based on the type of report.)
If you want to change the layout of your overview, click the six dotsdrag indicator. This will let you drag and drop the cards. To remove cards, click the X icon. If you want to add new cards, select +Add Cards.
Events are crucial in the new Google Analytics—in fact, this is how you’ll track just about everything. You will need an editor role in GA to make these changes, so if you don’t see the options I mention, that may be the issue.
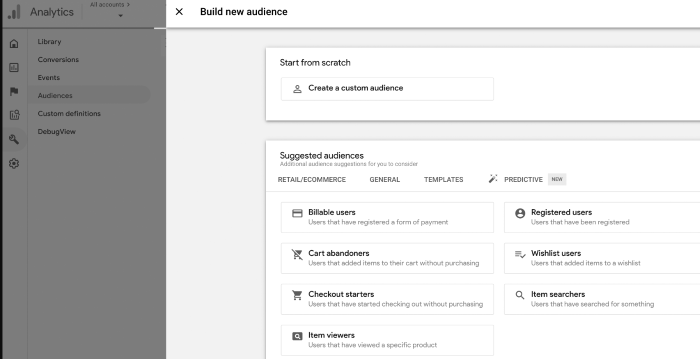
Google Analytics 4 now suggests new audiences. If you’re looking to expand your user base or break into new markets, this can be crucial information. When you create a GA4 property, you’ll tell Google about your business, including your industry category.
Google uses that information to generate new audiences that may be a good fit for your business. To view this data head to Audiences, under the Library. You’ll see suggested audiences listed under Build a New Audience.
Frequently Asked Questions About Google Analytics 4
Google Analytics 4 is a new analytics property offered by Google. It enables users to analyze data from websites, apps, or both websites and apps. It is a complete redesign of GA, so there is a bit of a learning curve.
The main difference between Google Analytics 4 and the old GA is in what the two different property types track. Google Analytics 4 can track the analytics of both websites and applications, while the old GA can track only website analytics.
Similar to Universal Analytics, Google Analytics 4 is a free property type. There are no costs associated with using one (or more) GA4 properties on your account.
Yes, you can currently run both platforms parallel to each other. UA will stop gathering data in the summer of 2023, so make sure you’ve installed GA4 even if you aren’t ready for the switch quite yet.
GA4 is extremely customizable, which can make it hard to learn. However, once you get a hang of it, you’ll find you have access to deeper insights you can use to grow your business.
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “FAQPage”,
“mainEntity”: [
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What is Google Analytics 4?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
Google Analytics 4 is a new analytics property offered by Google. It enables users to analyze data from websites, apps, or both websites and apps. It is a complete redesign of GA, so there is a bit of a learning curve.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What is the difference between Google Analytics 4 and the old GA?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
The main difference between Google Analytics 4 and the old GA is in what the two different property types track. Google Analytics 4 can track the analytics of both websites and applications, while the old GA can track only website analytics.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “Is Google Analytics 4 free?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
Similar to Universal Analytics, Google Analytics 4 is a free property type. There are no costs associated with using one (or more) GA4 properties on your account.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “Can you run Google Analytics 4 and Universal Analytics at the same time? “,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
Yes, you can currently run both platforms parallel to each other. UA will stop gathering data in the summer of 2023, so make sure you’ve installed GA4 even if you aren’t ready for the switch quite yet.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: ” Why is Google Analytics 4 so hard to use? “,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
GA4 is extremely customizable, which can make it hard to learn. However, once you get a hang of it, you’ll find you have access to deeper insights you can use to grow your business.
”
}
}
]
}
Google Analytics 4 is a powerful analytics tool that provides invaluable insights into your audience. There are numerous benefits to GA4, including cross-platform tracking, more control over data, and AI-driven insights.
Fortunately, setting up a GA4 property on your website or app is easy. The steps outlined above should take you less than 10 minutes to complete, so there’s no excuse to put off the transition.
Have you made the switch to Google Analytics 4? I’d love to hear your thoughts in the comments.
Do you want a simple way to refine your customer experience? Then look at your CX analytics.
The data doesn’t lie. It tells you what you’re doing right and what you’re doing wrong. Once you’re armed with your customer experience analytics, you gain the necessary information to offer prospects and buyers the best possible care.
When you provide a stellar customer experience, you boost efficiency and humanize your service while enhancing loyalty and recommendations.
Yet, according to a report from PWC, 54 percent of consumers feel the customer experience at many businesses needs improvement.
However, there are more benefits to examining your CX analytics.
For example, 44.5 percent of global organizations feel that an amazing CX differentiates them from competitors, and who doesn’t want to stand out and get noticed?
Now you know the importance of customer experience analytics. In this article, I explain which ones you should measure and why they’re so crucial to your business.
Customer experience (CX) analytics uses customer data to improve customer interactions.
You can use the data to track customer behavior and preferences to better understand how customers interact with your company and its products or services. You can then use this information to improve the CX by changing designs, the way you market to customers, or how you deliver your products or services.
There are many different ways to collect customer data. Analytics tools for customer experience often use various data sources. However, some of the most common sources include website visits, purchase histories, contact centers, and social media data.
By understanding customer behavior and preferences, analytics for customer experience can help businesses deliver a better CX faster and more consistently. Additionally, CX analytics can contribute to a positive customer experience by identifying and resolving issues early.
Below are just some of the benefits of tracking your analytics.
Customer satisfaction tracking: Perhaps the most crucial benefit is that customer experience analytics can track customer satisfaction over time. This information enables companies to identify areas where they need to make changes to keep their customers happy.
Understanding customer interactions: By analyzing your data, customer experience analytics lets you understand how customers interact with your products/services. You can then use this information to enhance the customer experience and increase sales.
Lower customer churn: When you use them correctly, customer experience analytics improve the CX and lower churn rates by increasing retention. For example, if many customers are contacting customer service about a particular issue, you can address it. This aspect is vital because consumer demand for a positive CX is increasing. However, Zendesk says 54 percent of shoppers feel businesses see it as an afterthought.
Enhanced loyalty through targeting: Understanding customer behavior lets you create targeted marketing campaigns that are more likely to convert leads into customers and encourage loyalty.
Increased value and lower spending: Predictive customer experience analytics can identify high-value customers in terms of lifetime value and customer satisfaction. However, it also finds high value, dissatisfied customers. When this information is clear, it allows you to spend money strategically and save money. McKinsey cites one example of a company that shaved over 25 percent off its planned budget using this technique.
Customer experience analytics (CEA) is a growing field. With that in mind, it’s important to choose the right metrics and analytics tools for customer experience to measure customer CX to get the most accurate results.
While there are multiple metrics you could focus on, to keep it simple, we’re going to focus on six of the most valuable.
Let’s begin with the promoter score.
To arrive at your promoter score (NPS), you look at your customer feedback and customer loyalty.
While there are many ways to calculate NPS, the most common is to use a 1-10 scale, where 1 is very dissatisfied, and 10 is very satisfied. To get an accurate reading, it’s important to ask customers how likely they are to recommend your company on this scale.
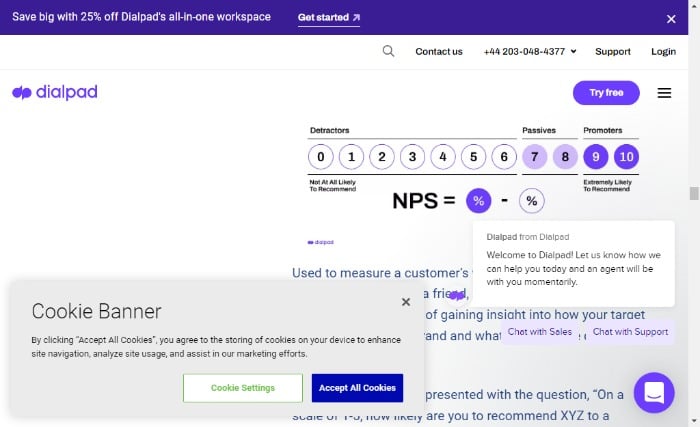
You could also use a free calculator or a tool from this list.
The higher your NPS score is, the better your customer retention, brand awareness, and customer acquisition.
An excellent example is the jewelry company, Taylor and Hart.
They consider NPS as their most important metric. By focusing on it, breaking it down, and applying the data, the company experienced a 70 percent increase in revenue.
Although you can’t guarantee the same results, you can take the same approach as Taylor and Hart by:
By tracking the NPS, the company:
CSAT is a numeric representation of satisfied customers with a given product or service.
Many companies use customer satisfaction scores (CSAT) to track their customers’ overall happiness and identify areas where they need to make improvements.
When you track your CSAT customer experience analytics, you:
However, despite CSAT being one of the most essential customer experience analytics, Gartner found that more than 70 percent of “CX leaders struggle to design projects that increase customer loyalty and achieve results.”
There are several different ways to collect CSAT data, but the most common way is to ask customers to rate their satisfaction on a scale from 1 to 10. You can do this through surveys, feedback forms, or chatbots. Alternatively, you can use a free calculator.
You should be aiming for a CSAT score of 75-85 percent. However, there are some variations between categories.
The customer effort score (CES) metric measures how much effort a customer perceives they expend when interacting with a company.
You calculate CES by averaging the responses to questions about how much effort the customer felt they exerted during their most recent interaction with your company.
By identifying areas where customers are experiencing high levels of effort, businesses can focus on making changes to reduce the amount of work customers have to do to get what they want.
But there’s more to it.
When you get your CES right, it improves customer satisfaction, and loyalty, and lowers costs associated with handling customer complaints or support requests.
In addition, according to Gartner, when CES is high:
Your CES score is also more accurate than understanding customer satisfaction rates.
Andrew Schumacher, Senior Principal, Advisory, Gartner, says:
“Customer effort is 40 percent more accurate at predicting customer loyalty as opposed to customer satisfaction,
Calculate your CES with this free calculator. There is no standardized CES score, but the higher the better.
Churn rate is an essential metric for companies to track because it provides insights into why customers leave and what you can do to retain them. Most businesses focus on this metric because a high customer churn is costly and leads to lost revenue.
There are several ways to calculate customer churn rate, but the most common is to divide the number of customers who have discontinued their relationship with you by the total number of customers at the beginning of the period. This gives you a percentage of how many customers have leftover a given period.
The average churn rate is 5-7 percent, while ten is high. However, it does depend on the industry. For instance, the average churn rate for online retail is 22 percent, while it’s 11 percent for big-box electronics.
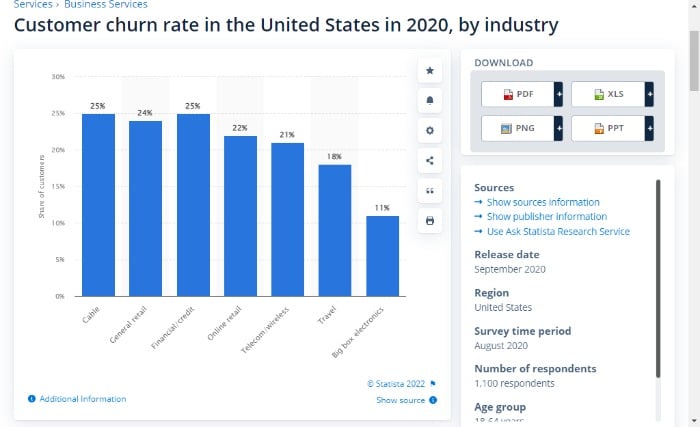
You can calculate your churn rate online. If it’s high, delve into your CX analytics and look for patterns.
Remember, several factors contribute to churn rate, and businesses can take steps to reduce it by improving customer experience by tracking their CX analytics. Another way to improve customer experience is by providing an excellent support system and giving them what they want.
From Costco to American Express to Verizon and AT&T, they’re also using customer lifetime value as a critical metric with good reason.
CLV is a CX metric that helps business owners and CX professionals understand the value of a customer over the entire span of their relationship with their company.
It considers not just the monetary value of a customer but also how long they are likely to continue doing business with them, how much business they are likely to do moving forward, and how profitable each interaction is.
This information allows you to make strategic decisions about what types of customers to invest in acquiring and retaining, what kinds of experiences to offer them, and when it might make sense to let them go.
There is an easy-to-use online CLV calculator. For guidance, with your CLV, you are looking to make three to five times your acquisition cost.
Once you have your number, you can apply it. As a Bain & Co explain, you can use CLV to:
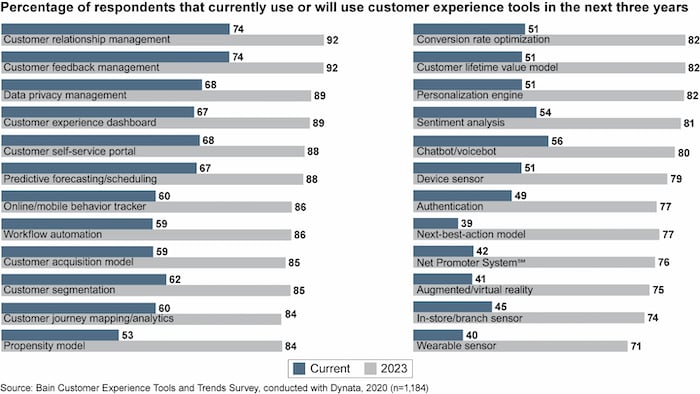
However, with your tracking, you might want to use a range of CX analytics tools, rather than focusing on one or two; research from Bain and Co shows that companies are most satisfied with results when they use a combination of tools. Further, by 2023, 92 percent expect to be using CX experience analytics tools for customer relationship management.
Engagement metrics track how people interact with your brand on social media. There are many different types of engagement metrics, but some of the most common ones include clicks, likes, shares, and comments.
I can’t overemphasize the importance of tracking social media analytics. If you post something and no one clicks on it, shares it, or comments on it, you know that you need to rethink your content strategy.
The potential of social media is best explained by looking at the runaway success of TikTok. According to its stats, 44 percent of visitors visit the site every month to find something new.
TikTok also impacts every stage of the customer journey, including:
Then, post-purchase, buyers head back to the site to create reviews, unboxing, tutorials, and how-tos.
The above should be enough to persuade you of the power of social media. If you’re already on sites like TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook, make sure you’re paying attention to your tracking with tools like Google Analytics, SproutSocial. and HootSuite.
CX analytics come in various forms, including CES, CLV, and social media engagement. They come in a mix of categories, including marketing analytics software, and customer service analytics software, which measures the effectiveness and quality of customer service interactions. Then there are social media and web and behavioral analytics.
There are several free tools businesses can use to track their cx analytics. One such tool is Google Analytics. Google Analytics allows companies to track website visits, engagement, conversions, and goal completions. Another free tool is Survey Monkey. Survey Monkey allows businesses to create surveys and collect customer feedback to measure customer satisfaction and loyalty. Finally, another free tool you can use for CX analytics is Simply Measured, for social listening and analytics.
Data analytics can improve customer experience by helping businesses better understand their customers’ needs and preferences. Data analytics can also help companies to identify and respond to problems quickly. For example, if lots of people are complaining about a particular issue, data analytics can help businesses identify the cause of the problem and take corrective action.
Customer experience is one of the most critical factors for businesses today. In a world where consumers have endless choices, it’s essential to provide an exceptional customer experience to stand out from the competition. Finally, studies show that improving customer experience can increase sales and revenue.
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “FAQPage”,
“mainEntity”: [
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What are the types of customer experience analytics?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
CX analytics come in various forms, including CES, CLV, and social media engagement. They come in a mix of categories, including marketing analytics software, and customer service analytics software, which measures the effectiveness and quality of customer service interactions. Then there are social media and web and behavioral analytics.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “Can I track my customer experience metrics with free tools?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
There are several free tools businesses can use to track their cx analytics. One such tool is Google Analytics. Google Analytics allows companies to track website visits, engagement, conversions, and goal completions. Another free tool is Survey Monkey. Survey Monkey allows businesses to create surveys and collect customer feedback to measure customer satisfaction and loyalty. Finally, another free tool you can use for CX analytics is Simply Measured, for social listening and analytics.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “How does data analytics improve customer experience?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
Data analytics can improve customer experience by helping businesses better understand their customers’ needs and preferences. Data analytics can also help companies to identify and respond to problems quickly. For example, if lots of people are complaining about a particular issue, data analytics can help businesses identify the cause of the problem and take corrective action.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “Why should marketers care about customer experience analytics?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
Customer experience is one of the most critical factors for businesses today. In a world where consumers have endless choices, it’s essential to provide an exceptional customer experience to stand out from the competition. Finally, studies show that improving customer experience can increase sales and revenue.
”
}
}
]
}
Customer experience analytics is a valuable tool for businesses. Businesses can improve customer service and make strategic decisions about their products and services by tracking customer interactions and analyzing the data.
With the right tools and data, businesses can improve their customer service and boost their bottom line.
However, you need to be measuring the correct data. Although there are several metrics you could focus on, don’t get overwhelmed.
The six metrics featured in the post are enough to get you started and give you a clearer picture of what’s going on in your business.
To further optimize your results, you can adopt a range of automation tools to enhance the overall CX experience.
Do you use customer experience analytics in your business? Which ones work best for you?