Recognizing Google Adwords Adwords is created from the expression ‘marketing keyword phrase’. Internet search engine such as Google, Yahoo, Alta Vista as well as several others make use of the ease of access of the Internet to supply firms with a tool whereby they can market to a details target audience. Google adwords provide business … Continue reading Comprehending Google Adwords
Tag: Google
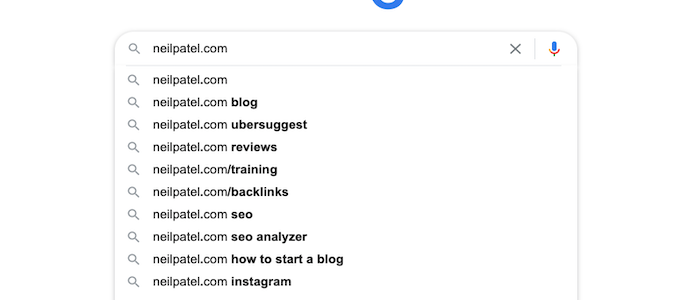
How To Use Google Autocomplete for SEO
When you type in a keyword into the search box, you know how you get a list of keyword predictions?
This is called Google Autocomplete. Its purpose is to save users time. In fact, according to Google, it lowers typing time by 25%.
There’s no doubt that this feature makes our lives easier, especially when using Google Search on mobile devices.
Google Autocomplete is often overlooked by digital marketers, so taking the time to understand it can give you an edge over your competition.
What Is Google Autocomplete?
Google Autocomplete is a Google Search feature that provides search term predictions.
For example, if you type “what is the capital of” into the search bar, you will see something like this:
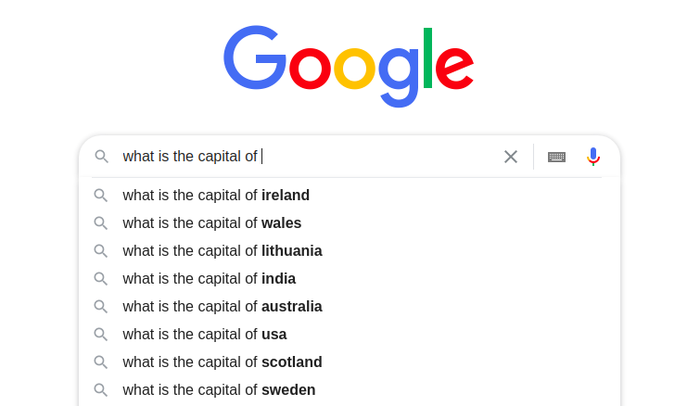
As you continue typing, predictions will adjust accordingly, until you see the search term you want to use.
You can then simply click on that option instead of typing it all out.
Google Autocomplete’s purpose is to help you save time by completing the search query that you had in mind.
Where Do Google Autocomplete Keywords Come From?
Here’s how Danny Sullivan, public liaison for Google search, explains it in his blog post on Google Autocomplete:
“How do we determine these predictions? We look at the real searches that happen on Google and show common and trending ones relevant to the characters that are entered and also related to your location and previous searches.”
Are Google Autocomplete Predictions Different in Various Countries?
Google Autocomplete predictions depend on which country you’re in.
For example, if you’re in Vilnius, Lithuania, and you type “best pizza in” into the search bar, you will see something like this:
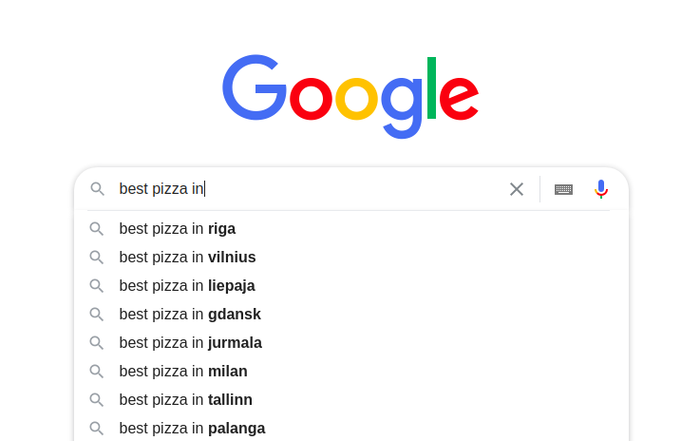
All these locations (except for Milan) are either in Lithuania or near Poland, Latvia, and Estonia.
If you change locations, Google will “follow” you, and your autocomplete options will adjust accordingly.
Are Google Autocomplete Predictions Different for Various Languages?
Google Autocomplete predictions differ based on the language(s) you’re using to enter queries into Google.
For example, if you set your default language to English, you will be shown English predictions.
However, if you add other languages that you understand, say, German and French, you’ll also be shown predictions in those languages.
Does Your Search History Affect Google Autocomplete Predictions?
When you’re logged into your Google account, Google Autocomplete considers your search history when showing predictions.
When you see a prediction that has a “Remove” option next to it (it shows up as an “X” on the far right), know that this is a prediction based on your search history—it remembers that you searched for this, but recognizes it may have been a one-time search.
What Are the Google Autocomplete Guidelines?
Not all search queries are deemed appropriate to display as predictions.
These types of predictions go against Google Autocomplete policy:
- Violence and gore
- Sexually explicit, vulgar, or profane language, though medical and scientific terms are allowed
- Anything related to hate speech or approval of hateful acts
- Sensitive information or terms about named individuals
- Dangerous predictions, meaning searches for things that could allow serious harm to people or animals to happen
Google admits that while they do their best to remove inappropriate predictions, they don’t always get it right, so they provide a way to report a prediction.
How Can You Use Google Autocomplete for SEO?
Before you start analyzing Google Autocomplete predictions for SEO, it’s essential to do these three things:
- Log out of Google or use incognito mode to make sure your search history doesn’t influence the predictions you get.
- Use a VPN if you are based in a different location than your target audience. For example, if you’re currently in Thailand, but you’re focusing on people in the United States, use a VPN to make it seem like you’re in the United States. You want to see predictions for the location where your target audience is.
- Adjust your language settings to be similar to the language settings the people in your target audience use.
These parameters will help you see the predictions similar to those shown to your target audience.
Keyword Research
Google Autocomplete can be a useful keyword research tool.
Here’s how you can make the most out of it.
Type in a Keyword, Look at the Predictions
Simply type in a keyword that is relevant to your niche and look at the predictions. This research is a great way to discover valuable long-tail keywords. (Answer The Public is another free tool that does this for you.)
Then, use an SEO tool like Ubersuggest, Ahrefs, or Moz Pro to analyze those keywords and identify ones that are worth going after.
Go Through the Alphabet
What if you don’t like any of the predictions that you got?
Brett Farmiloe, the founder and CEO of Markitors, advises to type in your keyword, then just go through every letter of the alphabet to see what predictions come up.
He uses the keyword “equipment financing” as an example:
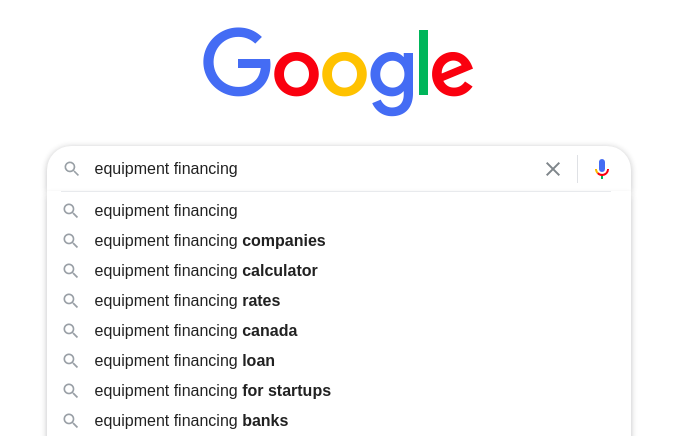
You can add the letter “a” to get a new set of predictions:
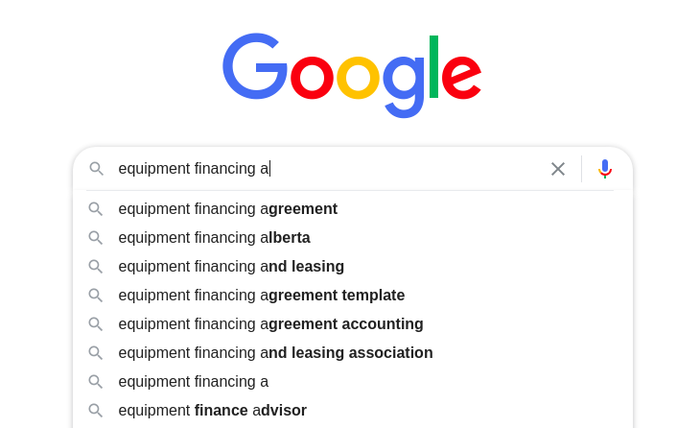
And then you can add the letter “b” to it:
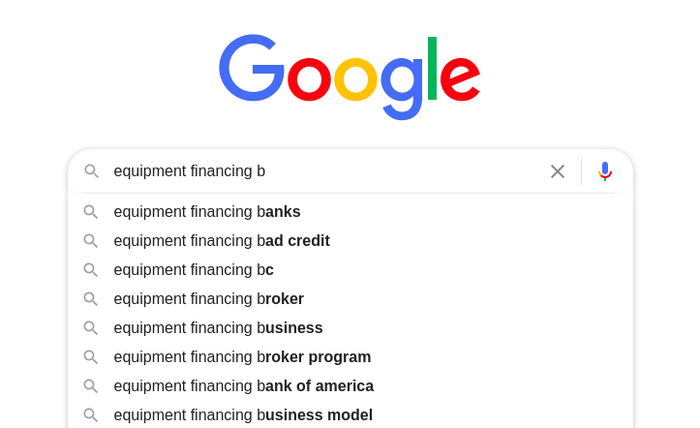
…and that’s how you go through the entire alphabet.
“This is particularly good when you are really stuck, and you are really just in need of some inspiration,” says Brett.
Let Google Fill in the Blanks
Tom Dupuis from Online Media Masters suggests using the underscore character “_” in a phrase so that Google would complete it.
He uses the keyword “chicago _ photographer” as an example:
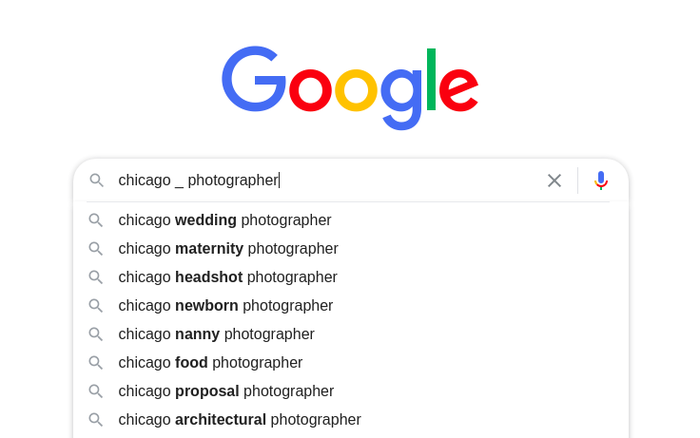
“Instead of having Google complete only the last part, this can show you a better selection of keywords depending on what type of phrase it is,” explains Tom.
Experiment With the Position of the Underscore
Dupuis also encourages people to experiment with the underscore’s position to see what new Google Autocomplete predictions show up.
For example, if you already tried “chicago _ photographer,” why not try “_ chicago photographer”?
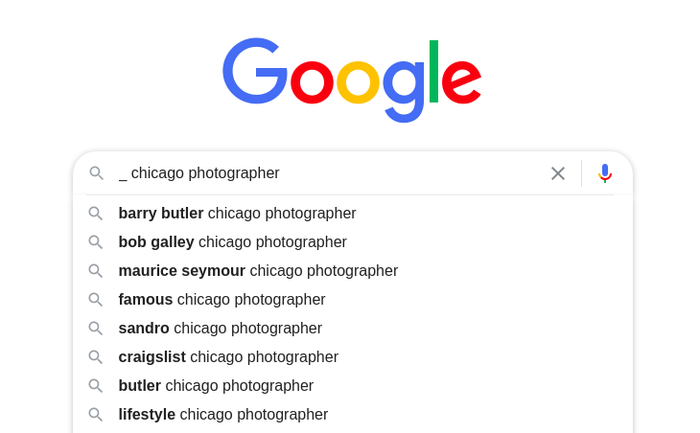
Try Both Singular and Plural Form of the Keyword
Another valuable piece of advice from Dupuis is to try both the singular and plural forms of the same keyword because this leads to different Google Autocomplete predictions.
Take one more look at the predictions for the “chicago _ photographer” keyword:

And now look at the predictions for the “chicago _ photographers” keyword:
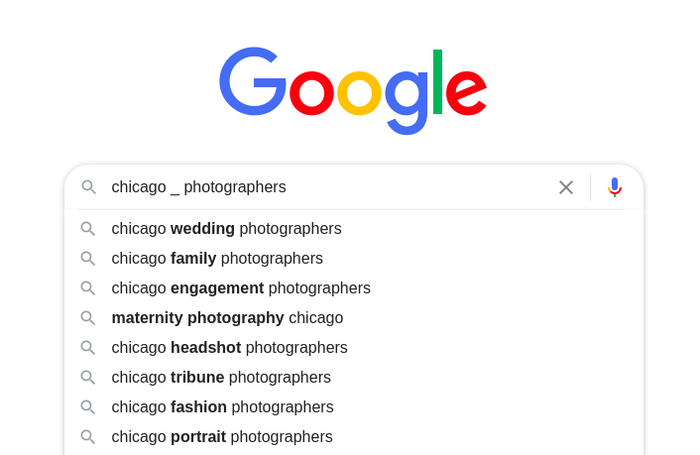
As you can see, the predictions are different, so try both forms of the same keyword.
Online Reputation Management
This tool is also useful for researching results about your branded terms, such as company, executive, or product names. Google Autocomplete can present a serious threat to your public image if an unflattering search term appears in the predictions using your brand terms
What can you do if you find yourself in that situation?
You have several options:
Address the Problem
If the unflattering prediction refers to something true, fix the problem.
The resolution won’t make the autocomplete issue go away immediately, but if the problem is solved, then over time, people will forget about it and stop searching for it. As the volume for that search term goes down, it ultimately will drop off the prediction list.
Work on Your Brand Image
Again, if the prediction is about an actual incident, you can help people forget whatever happened faster by giving them something positive to focus on.
For instance, you can feature loyal customers on your website, do a giveaway, or organize an event.
Even directly engaging with your customers on various social media platforms can go a long way towards creating a positive brand image.
Other Ways to Use Google Autocorrect Research
Google Autocorrect is a simple tool — but it can be quite powerful. From keyword research to maintaining your reputation, those suggestions can super-charge your digital marketing efforts.
In addition to finding popular keywords, there are several other areas where Google’s suggestions can be useful concerning SEO.
Uncover Key Words for Local SEO
Google Autocomplete can also provide suggestions for local SEO searches you might not have considered.
Say you are looking to rank the website of a coffee shop in Denver — would you just target “coffee shop Denver”? Or do people use neighborhoods, cross streets, or even zip codes?
Google Autocomplete will tell you what terms people search when looking for a coffee shop in Denver:
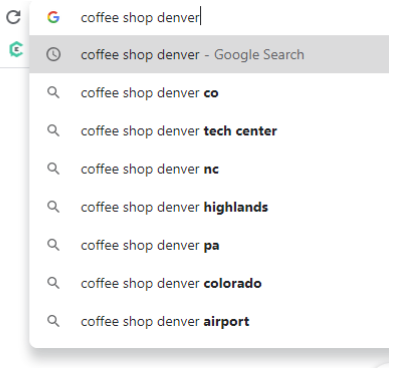
Looking at this example, what can we learn?
Denver Tech Center is a business and trading center in the southeast portion of Denver, Colorado. It’s a popular destination for business workers, so if your shop in that area, you’d want to include Denver Tech Center in your key terms list.
Denver Airport shows up on the list, so if the shop is near there, you’d want to target that term as well.
Google autocomplete shows several major landmarks (including the airport), so you will want to research if your shop is near any popular locations, such as a museum or shopping center.
There are also listings for Denver, NC, and Denver, PA, which means it’s probably a good idea to include the state.
It’s easy to assume you know what people will search — but it’s worth the few seconds it takes to check and see what inspiration Google autocomplete might offer.
Create a User-Friendly E-commerce Website
Ecommerce is big business — according to Oberlo, more than 2 billion people make online purchases annually. Despite many online shoppers, there’s also a stiff competition to get shoppers to your site.
Using autocomplete to find key terms to target is just one way to use the feature to create a better ecommerce store and create a user-friendly site.
Let’s say your e-commerce sells shoes, clothing, and accessories. Your goal is to make it as easy as possible to find what they want and make a purchase.
Google Autocomplete can help by:
- Showing which categories are most popular: For example, if you search “women’s shoes” in Google, the search engine will also suggest: “women’s shoes near me,” “women’s shoes on sale,” and “women shoes size 12.” That means people often search for shoes on sale and by size, so those are categories you’ll want to include on your website.
- Uncover popular brands: A search for “women’s tennis shoes” tells you which brands users search for most often, including Adidas and Nike. Those are brands your audience is likely to purchase.
- Get ideas for your FAQ page: Searching “are women’s shoes…” provides a list of questions people often ask, including “are women’s shoe sizes the same as men’s?” and “are women’s shoes more narrow?” Those are questions people are asking, and providing those answers could help drive more traffic to your ecommerce site.
User experiences can impact search rankings, so making a user-friendly site should be a top priority.
Get Inspiration for Content Topics
Google Autocomplete features searches that people make regularly. Targeting any of those terms or phrases is going to drive traffic. (At least it will if your content is good!)
Here are a few suggestions for getting content inspiration:
- Who, What, Where, How, Why: Use your primary key term with question words before or after (whichever makes more sense). See what Google suggests — you might uncover the bit of inspiration you need to write your next great piece of content.
- Use action verbs: This can provide creative angles for your next blog post or ebook. Searching “content marketing is…” shows a list of quirky title ideas, including “Content marketing is like a first date.” Other ideas for action verbs include: are, will, show, be, build, and replace.
- “Key Term and…”: Looking for related topics? Search your primary key term with “and” to see what associated terms searchers are looking for. For example, if you search “content marketing and…” Google suggests social media, lead generation, storytelling, and sales.
Content marketing is a critical part of SEO, so finding topics that users are searching for can improve the ranking for specific pages and a site.
Conclusion
Google Autocomplete isn’t just a neat user feature that allows you to complete a search term without typing it out.
You can also use it to discover valuable long-tail keywords that you wouldn’t have thought of yourself.
Of course, it can also wreak havoc on your life if an unflattering prediction appears next to your name or your company’s. It’s wise to keep an eye on what shows up on Google Autocomplete so that you can address a problem immediately.
Just don’t make a bad situation worse by using black hat techniques. It’s not worth it.
How do you use Google Autocomplete for SEO?
The post How To Use Google Autocomplete for SEO appeared first on Neil Patel.
How Google Local Guides Improve Visibility
As a business owner, you know reviews and fresh content are essential to your success.
Suppose you’re passionate about promoting your business. In that case, you likely spend a lot of time creating new blog articles, crafting social media posts, or developing video content to keep your audience engaged.
But there’s another, more passive promotion method that can help grow your business and boost your local search results: Google Local Guides.
Launched in 2015, Google Local Guides—also known as Google Guides—took over where Google Cities left off. If you’re unfamiliar with it, the closest comparison is the Yelp! Elite Squad.
Google Guides allows users to add reviews and other content in exchange for various perks ranging from storage space to clothing.
Since its launch, the Google Guides community has proved hugely popular. There are 120 million local guides, spanning 24,000 cities and towns.
There are several potential benefits of Google Guides for your business and its online visibility.
Let’s take a closer look at the Guides system.
What Are Google Guides?
The idea behind Google Guides is simple. It uses user-generated content (UGC) to enrich the information available on Google Maps.
Or as Google explains it, Guides are:
… a global community of explorers who write reviews, share photos, answer questions, add or edit places, and check facts on Google Maps.
Guides’ additional content can increase your business’s visibility and make it easier for consumers to get the information they need.
Becoming a Local Guide is simple. Potential Guides sign up through their Google accounts, choose their locations, and be ready to go.
Once signed up, members of the Google Guides community receive points for each action they take.
All Guides start with zero points and work their way up through 10 levels, earning various perks along the way.
Creating Lists
Once Guides reach level four, they can start to add lists. These lists may consist of favorite places, destinations the guide plans to visit, and saved locations.
As you might expect, each list a Google Guide adds must meet specific requirements. To be eligible for publication, Google state a Guide’s list must:
- have a title (i.e., a custom list, not be included in Want To Go or Favorites);
- include a minimum of four places; and
- be shared publicly.
Google Guides Perks
One aspect that makes Google Guides appealing to its members is the perks. Although these can vary from time to time, examples of the incentives include:
- early access to new Google products
- free music trials
- discounted video services
- storage space
- partner perks
- digital newspaper subscriptions
- t-shirts and socks
Other bonuses include invitations to the Google Guides convention or Connect Live events, which are open to a limited number of community members.
There’s also an active online forum that helps fuel the community feeling and allows guides to share tips, favorite images, and other information.
How Do Google Guides Points and Levels Work?
Community members start at level one and can work their way up to level 10, which offers a maximum of 100,000 points.
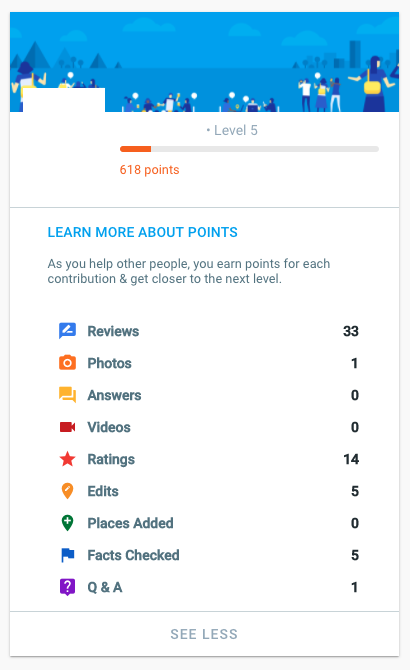
To try to ensure that Guides play by the rules, Google will close an account if a Guide violates the program’s policies.
Some violations that may get a guide removed from the program include:
- participating as a business
- duplicating reviews
- spamming the site
- posting offensive content
- adding inaccurate information
- including unnecessary keywords
How Does Your Business Benefit From Google Guides?
Since you can’t take part as a business owner, you might be wondering how Google Local Guides can help you.
Let’s start with one of the most crucial elements for businesses today: getting found online.
Increased Visibility
With most consumers heading online to search for local businesses, and mobile search on the rise, increased visibility is more critical than ever before.
This is where the content Google Guides compile can prove invaluable to your business and potentially help your local search rankings.
A Google my Business Insights Study revealed that high-quality images are vital to your listing.
The survey revealed that profiles with more images receive increased clicks, queries, and inquiries for directions.
Let’s look at the stats. Businesses with over one hundred images received:
- 520% more calls than average
- 2,717% more direction requests
- 1,065% more website clicks
In addition, the research suggests several search benefits from image-rich Google My Business profiles.
Businesses with more than 100 images received:
- 960% more search views
- 3459% more map reviews
- 1038% more direct searches
Although Google Guides and Google My Business are different products, they’re closely correlated, with both providing information for Google Maps.
This insight means the more detailed information about your business on Google Maps, the higher the likelihood consumers will find you online—and offline.
The Ability to Keep Your Profile Updated and Accurate
As we explained at the start, Google awards points for editing listings.
Making sure your details are updated is imperative because inaccurate information such as out-of-date phone numbers or an old address reduces the likelihood a customer will find your business offline.
Besides editing listings for errors, Google Guides can correct omissions. This added detail is essential in attracting new customers.
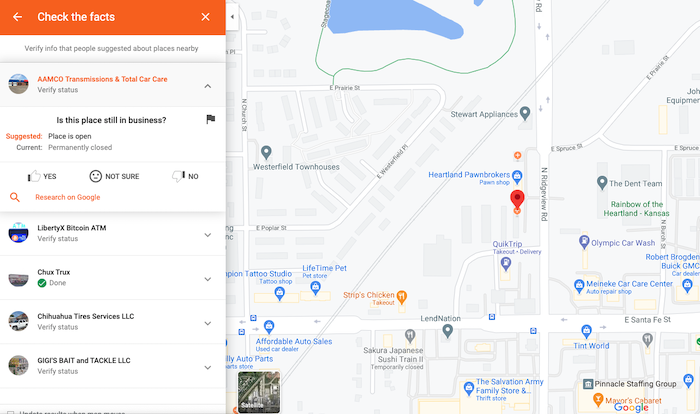
Statistics from Google show that 67% of your listing visitors would not feel the need to conduct further research if the profile includes essential information such as:
- opening hours
- locations
- images
- consumer reviews
The same study shows that 41% of users who come across an incomplete profile would continue with their research and leave the business’s profile, possibly depriving the business of an opportunity to gain a new customer.
Online Reviews
You know positive reviews inspire customer trust, but they can also help you get noticed online.
In an increasingly digital world, this online validation for your business is vital because:
- 93% of consumers say online reviews affect their buying decisions
- 91% of consumers value online reviews as much as personal recommendations
- 90% of consumers will read reviews before visiting a brick-and-mortar business
Google is the first place consumers go to read reviews these days.
The search engine leads the way in online reviews, with over 60% of would-be buyers heading to Google when considering making a purchase.
Although there has been some debate about just how critical reviews are to SEO, Google confirms they play an indispensable role in local search:
High-quality, positive reviews from your customers will improve your business’s visibility and increase the likelihood that a potential customer will visit your location.
Additionally, research from Moz confirms the importance of online reviews to SEO. Their 2018 Local Search Ranking Factors report found reviews account for 15% of local ranking factors.
Dealing With Negative Reviews
No matter how dedicated you are or how well you run your business, getting a negative review at some point is almost inevitable. It can hurt you personally, and you may be concerned that it can harm your professional reputation.
Let’s try to put this fear to rest.
Despite what you may think, your business needs negative reviews. Negative reviews allow consumers to make informed decisions. They also enable buyers to understand what could go wrong during a transaction, helping manage their expectations.
Instead of worrying about potential low reviews, your best approach is to positively and objectively respond to reviews.
Ask yourself:
- Does the reviewer have a valid point?
- Is it an issue you can address to make the experience better for the next customer?
All that said, there’s one type of negative comment that may concern you more than any other: the fake review.
Unfortunately, getting unwarranted negative feedback removed from Google Guides isn’t as easy as it could be. If the review violates Google’s terms, it will likely be removed.
But there’s no reporting option for fake reviews.
The best option may be to approach a Google Guides moderator. However, that doesn’t solve the problem of potential reputational damage over fake reviews.
Business owners can expect to, but this process is often time-consuming and frustrating for business owners who’ve experienced it.
How to Get Google Guides to Engage with You
You now know the benefits of Google Guides for your business. But how do you get them to find you and engage with you?
If you want to get more actively involved, that’s an option.
Here’s how to approach it.
Take Part in Meetups
Businesses are welcome to partner with local guides for meetups, and even offer special discounts to them. Getting to know local guides is an excellent way for your business to engage with them and build relationships.
However, you’ll want to make sure that your company and the Guide adhere to Google policies. This means:
- Local Guides mustn’t accept sponsorship in return for a positive review
- Guides can’t accept payment for hosting the meetup
- if your business sponsors the meetup or provides goods or services, Google Guides must clarify this in their meetup descriptions.
Also, Google Guides at level three and up qualify to host meetups, but they must get approval first.
Optimize Your Google My Business Page
Despite the apparent advantages of optimizing Google My Business, research has found over half of local businesses hadn’t claimed their listings.
Optimize Your Business Map’s Listing
Optimizing your map doesn’t just make it easier for locals to find you; it also makes it easier for Google Guides to discover your business.
To make your site stand out, optimize your Google map listing by:
- adding imagery
- responding to reviews
- completing your profile
- keeping your profile updated
Stress the Importance of Reviews to Your Business
There isn’t anything wrong with explaining to your customers how important reviews are to your business. However, be careful about the way you approach it.
If you need some basic guidelines on getting more reviews, Google has these suggestions:
- Begin a conversation with your shoppers about reviews.
- Make leaving feedback easy.
- Share positive reviews.
- Respond to online feedback.
Conclusion
Google Guides can help you attract new interest in your business. But you may be unaware of the potential advantages of being profiled by local guides.
Businesses with an increased amount of user-generated content (UGC) stand to benefit from increased consumer confidence in their brand, enhanced trust from Google and potentially improved local search rankings.
As a result, your business may experience an increased number of queries, enhanced visibility for your goods and services, and more visits to your offline store.
Do you have experience with Google Guides? Feel free to comment below.
The post How Google Local Guides Improve Visibility appeared first on Neil Patel.
Google Shopping Actions: How to Increase Product Visibility for Free
Did you know Google Shopping listings are free for most merchants to use? Google has also dropped commissions for its Buy on Google program. This means nearly any retailer can sign up for Google Shopping Actions and link their products without paying the 12% commission Google formerly collected on each sale. Retailers and advertisers have a unique opportunity …
The post Google Shopping Actions: How to Increase Product Visibility for Free first appeared on Online Web Store Site.
Become a Google Partner and Join the Google Ads Inner Circle
Does your company manage Google Ads for third parties, and do you maintain some success with the pay-per-click (PPC) platform? If so, you may want to become a Google Partner, the search giant’s members-only club.
Joining the Google Partners program can provide you with immense benefits, such as specialized training, invitations to exciting events, and focused instruction to help you boost your Google Ads performance.
You already know Google Ads work. They convert 50% better than organic traffic, and most businesses earn double their ad spend, making advertising on Google highly effective and a no brainer.
Almost anyone can use Google’s PPC system to advertise on Google and grow their business (with the right budget and know-how).
Only a select few applicants become Google Partners and earn the world’s most popular search engine’s endorsement and other significant benefits.
Here’s what to know about becoming a Google partner.
Google Partner Members Get to Display a Google Badge
The definition of prestige on the search engine’s paid advertising platform is a Google Partner badge. Displaying the badge on your site shows that you’ve passed Google Ads product certification exams. It also tells customers you possess in-depth product knowledge, making you a Google PPC superstar.
Find the Google Partner Specialties That Interest You
As a Google Partner, you have the option of specializing in one or more Google Ads product areas. These include Search Advertising; Video Advertising, Display Advertising, and Shopping Advertising.
Let’s run through them one by one.
- Search: By passing this certification course, you highlight your ability to create and optimize ads that perform well on Google search. That means they’re prominently displayed and receive clicks with buyer intent. And if you need to, you’re able to advise others on keyword strategy and budget planning because you’re a search engine master.
- Video: This certification indicates your expertise in implementing and optimizing YouTube ad campaigns.
- Display: This certification area gives you the means to create compelling visual ads that snag the attention of customers on two million sites and 650,000 apps in Google’s combined networks.
- Shopping: As a Shopping Advertising Google Partner, you know how to place products on Google Search and set up your Merchant Center inventory. You also know how to create winning Google Shopping campaigns. Keep in mind: this certification is not available in all languages. See the Google Ads Help Center to learn more.
How Do You Join the Google Partners Program?
Applying to become a Google Partner is free, and anyone can try to join the program. Google gives you all the information you need to pass the exams and flourish in your chosen certification area. Whether or not you pass the certification exams is up to you.
What Are the Benefits of Becoming a Google Partner?

Google wants you to pass the exams and be successful in your Google Ads endeavors. To help you out, Google gives you access to a range of essential benefits, including education, support, expanded reach, and other rewards.
Education to Succeed
Google has pulled out all the stops to ensure you get the best Google Ad education possible. Skillshop learning courses help you develop and hone your skills, while certifications are provided to prove your knowledge. Google also makes available a host of valuable case studies, access to like-minded professionals, and much more on Think with Google and Google Trends.
Valuable Support
Google’s product support is available to help you by giving you access to relevant advice and a range of resources, including Google Ads Recommendations and Google Ads Help Center.
Expanded Reach
With Google Connect, you can display your thought leadership and host co-branded events. You can even onboard new clients or pitch potential ones with Google Ads promotional offers.
Business Acceleration
Google’s Acceleration program is a specialized online education system designed to help you boost your skills and business growth.
Bonus Rewards
By taking part in the Google Partners Rewards program, you get a chance to expand your knowledge by engaging in a series of quarterly challenges designed to help you gain new clients, optimize campaigns, or obtain certification. You even get access to seasonal insights, pitch decks, product advice, and a suite of other exciting rewards. You also have a chance to win prizes.
How Do You Qualify to Become a Google Partner?
The first thing you’ll need to do is pass the required Google Ads certification courses for your specialty areas. You must also meet the spend requirement across your managed accounts.
Finally, you must demonstrate performance by consistently delivering strong client and company growth. In other words, you must become an active and exemplary Google Ads user.
What Are the Partner Badge Requirements?
Once you’ve become a Google Partner and have demonstrated your expertise in Google Ads, you can be considered for a Partner Badge. You’ll need to meet a few additional requirements to apply.
Growth
You must consistently show advancing ad revenue and growth, as well as an expanding customer base.
Ad Spend
You must meet a 90-day ad spend requirement of $10,000 across your managed accounts. This sends a message to Partners that your company has a healthy level of activity. Google Partners will evaluate your account based on your manager account during an 18-month period.
Certification
Your company needs one user certified in Google Ads who has admin or standard access to the Google Ads manager account. It can also be any account linked to your manager account.
Google Badge Requirement Changes
Be prepared for a new set of rules to qualify for a Partner Badge. Many of the basic rules will still apply, but you won’t be required to adopt all the recommendations or achieve a 100% optimization score to earn a badge.
Going forward, you must achieve a 70% optimization score to qualify. Google introduced this optimization score to help users understand what was working and what wasn’t, and how to fix elements that weren’t performing.
Pay close attention to any suggestions Google gives you, as advertisers who increase their optimization scores by 10 points see a 10% conversion boost, on average.
New Ad Spend Requirements
To qualify for a Google Badge in 2020, your Google Ad spend must be at least $10,000 in 90 days. In 2021, this requirement will change to a $20,000 ad spend over 90 days, across your managed accounts, to prove your company maintains healthy advertising activity.
Certification
This year, In 2020, your company needs a user to certify in Google Ads or have standard access to the Google Ads manager account. In 2021, half of your eligible users will have to obtain certifications from Skillshop. As a partner, you’ll need to demonstrate your proficiency consistently.
Premier Badge Requirements
To meet the requirements for a Premier Partner Badge, you must deliver strong Google Ads revenue and growth, meet a higher ad spend across your managed accounts, and have two or more users in your company who are certified in Google Ads (or who have admin or standard status on your organization’s Google Ads manager account).
In 2021, once your company has succeeded in earning a Google Partners Badge, you have an opportunity to be chosen for Premier status. The program will grant Premier status to the top 3% of participating companies each calendar year. The companies are selected based on annual ad spend, client growth, client retention, and other information. The evaluation process is conducted annually and may exclude some markets.
Get Listed as a Google Partner on the Marketing Platform Directory
When you become certified as a Google Ads Partner, you’ll be listed in the Marketing Platform Directory. Your listing will include your business name, a short description of your organization, partner type, and the product certifications you possess.
There are two types of marketing platform partners: Certified Companies and Sales Partners.
Certified Company
This descriptor means you’re educated about Google Marketing Platform products. You’re able to use your expertise to offer quality services to your customers, whether you’re consulting, training, implementing Google products, or offering technical support.
Sales Partner
Certified Companies that help Google sell products are known as Sales Partners. Becoming one gives you access to special perks such as customer management tools, sales opportunities, and co-marketing opportunities.
How to Obtain Company Certification
Know the Rules
Familiarize yourself with Google’s Partners Terms and Conditions. It is essential to read the document when you get time. You have a lot invested in Google Ads. The better you know the rules of the game, the more successful you can be at it.
Initial Requirements
Google will ask for your company’s size and structure, the services you provide, and pricing practices. You’ll be judged on your track record of client satisfaction and your consistent Google Ad investments’ success.
The reason for this level of scrutiny is that Google wants to work with forward-driven companies that maintain a healthy ad budget and use it wisely.
Google vets you for Partner certification by scouring the web for clear documentation that proves client engagement, planning processes, frameworks, and templates. Google wants to know your clients can rely on you for complex solutions and receive pleasing results.
Lastly, your website should be populated with useful content that clearly describes your offerings.
Product Expertise Requirements
Certification rules stipulate you must have at least five local, full-time experts working with Google Marketing Platform products. Each must have passed an associated certification exam.
Google considers your team’s size, expertise, and rate of certification. The company notes that it does make exceptions for smaller companies who have difficulty meeting this particular requirement.
You’ll also need to submit a comprehensive review of each product you offer. The review is meant to represent advanced work that shows strategic planning and optimization toward your organization’s goals.
The review will also display your ability to go beyond basic or standard implementations and use and demonstrate your client’s goal through statistics and testimonials.
Google essentially wants a case study that proves you can walk the walk.
How Do You Check Your Partner Status?
You applied for the Partners Program, and you’ve been waiting, but haven’t received a response. Take action and check the status of your certification. If you don’t receive certification, keep trying and using the resources Google gives you. Do that, and you’re sure to become a Google Partner before long.
Conclusion
Being vouched for by Google and having a Google Badge to show for it are just two of the benefits of becoming a Google Partner.
Being a Google partner also gives you access to easily consumable courses. Google gives you everything you need to maintain a Google Ads campaign and keep it growing far into the future.
And when customers see your Google Badge, watch out. That may be all they need to choose you for the successful future of their Google Ad campaigns.
Have you tried joining the Google Partners Program? What was your experience?
The post Become a Google Partner and Join the Google Ads Inner Circle appeared first on Neil Patel.
How to Use Events to Optimize Your Facebook And Google Ads
Your website is bustling with activity. Visitors are constantly interacting with it.
But are you taking full advantage of everything that’s happening on your website for your paid marketing?
Every interaction a visitor has with your website… a pageview, a click… can be used to better understand your audience.
And when you understand your audience you can target them in a smarter way, and get more bang for your buck from your paid campaigns on Facebook and Google.
Both Facebook and Google refer to these user interactions as Events. They allow you to track them using a tracking code installed on your website.
What Are Events?
Events are user interactions that don’t involve loading another page on your website.
In e-commerce, the prime example of an event is Add to Cart.
Another event can be filling out a field in a form, as opposed to a form completion that usually triggers loading a “thank you” page. Filling out one or more fields without submission (also known form abandonment) can also be recorded as an event.
In essence, you can record any action a user makes as an event, such as watching a video, clicking on a link, or even downloading a PDF.
Why Events Are Important
Events are important because they indicate the intent of your website visitors and which ones are more likely to become a customer or a lead.
If a visitor watched a video on your website, it demonstrates an interest in your offering.
In e-commerce, even if a visitor did not complete a purchase, an abandoned cart shows a high purchase intent. Sure, something has prevented the visitor from completing the purchase, but any visitor who got that far is worth your attention.
By tracking events you’ll be able to make a more focused offer to these users in your paid campaigns.
How you may ask?
By injecting the events tracking data into your paid campaigns and using this data for more precise targeting and an optimized offering.
Think about it, if you can group together all the visitors who watched a certain video and set up a customized campaign for them that referenced what they saw in the video, wouldn’t that make for a far more effective campaign than a generic awareness message?
It sure will.
Let’s discuss how you can use event tracking to get more out of your ad campaigns on Facebook and Google.
How to Set Up Events on Your Website
With both Facebook and Google, you’ll need to use code for setting up events on your website.
So lets go over how you do that…
Setting Up Events Using Facebook’s Pixel
Standard events on Facebook include:
- View content
- Search
- Add to cart
- Add to wishlist
- Initiate checkout
- Add payment info
- Make purchase
- Lead
- Complete registration
Here is the official Facebook guide for setting up events.
First, you need to verify that you already have the Facebook Pixel code embedded in the header code of every page of your website, between the <head> and </head> tags. If you don’t, first go ahead and insert the base Pixel code.
Next, select the event that you wish to track for a specific page from Facebook’s list of events. Let’s say Add to Cart event, which looks like this:
fbq(‘track’, ‘AddToCart’);
Paste the Add to Cart event code above the </script> tag.
Here’s how it should look:
Here’s what each number in the image stands for:
- Your header code
- Your base Facebook Pixel code (the ID number is unique to every website)
- The specific event code
You’ll need to repeat this on every page you want to track one or multiple events. Each page needs its relevant event code.
Event Tracking Setup Using Google Analytics
You can also track events in Google Analytics for even more insight. For event tracking in Google Analytics, you’ll need to create custom code snippets for every event.
Here is the official Google Analytics guide for setting up events.
The code is then added to the link code of the item or action you want to track so when the item is clicked, it will be displayed as an event in Google Analytics.
The event code is made of four elements – two required elements and two optional elements:
- Category (required) – defines a group of actions you want to track
- Action (required) – the type of action you want to track
- Label (optional) – for your monitoring convenience, stating what’s the event is about
- Value (optional) – assigning a numeric value to the event; can be monetary value, or just a scale
The basic structure of an event code looks like this:
onclick=”ga(‘send’, ‘event’, ‘Category’, ‘Action’, ‘Label’, ‘Value’);”
The code should be added within the href link code, before the link text:
<a href=”www.examplewebsite.co.uk/pdf/company_brochure.pdf” onclick=”ga(‘send’, ‘event’, ‘PDF’, ‘Download’, ‘Company Brochure – PDF Download’);“>Download Our Brochure</a>
In the example above, no Value was assigned to this event.
There Must Be a Better Way
All this event data needs to be injected into your paid campaigns in order to optimize them but before we get into that, let’s talk about the elephant in the room.
Code!
Dealing with code isn’t ideal for marketers. It’s just not our forte.
It holds us back since constant optimization is one of the core principles of online marketing.
And when you need your development team for every act of optimization, well, it’s not ideal.
Is there a better way to track events on your website? Yes. There’s a tool called Oribi that offers exactly that – no code event tracking.
Oribi tracks every interaction on your website, page views, and button clicks, automatically. It collects all this data and makes it all available to you. Even when you make changes to your website, like adding a page or changing buttons, events are updated dynamically. As said, all of this is done without any code business on your behalf.
Here’s how event tracking looks in Oribi:
The value here is apparent. You don’t need to decide which events to track, and you don’t need your development team to track it for you. Everything is tracked for you. You just need to follow the data.
Using Event Data to Optimize Your Paid Campaigns
Now you can use all this event data that you collected so diligently to better segment and optimize your paid campaigns and get more return on your ad spend.
There are two main objectives for tracking event data:
- Internal – being able to analyze how visitors are interacting with your website and from that optimizing the UX (user experience)
- External – exporting the data to your paid campaigns to better segment them – group together audiences according to their place in the funnel and specific interests in order to deliver more relevant messages
Let’s look again at the Add to Cart event. As mentioned, adding an item to a cart shows a high purchase intent. These visitors, even if didn’t complete the purchase, declared their interest in your product.
They are ‘worth your efforts’ to continue and court them in the hope they will complete a purchase in the future.
But they are all different, and you can better understand them based on the item, or items, they chose.
If you could, for example, group together all those visitors who added a shirt and then group together those who added a pair of shoes – wouldn’t your customized paid campaigns for these two distinct groups be so much more valuable?
You’ll be able to deliver a highly relevant message, or offering, in your ads.
This is just the tip of the iceberg as far as segmentation and optimization of your paid campaigns that can be achieved with event tracking.
Two Main Use Cases for Ad Campaign Optimization Based on Event Tracking
Both Facebook and Google offer very strong optimization capabilities for their ad campaigns.
There are two objectives for this:
- Ability to segment your audience in order to deliver a highly relevant message (the more segmented the audience is, the more relevant your message can be)
- Ability to reach new audiences that are also relevant to your offering
Let’s look at how these objectives are achieved through specific features in Facebook and Google ad campaigns.
Facebook’s Retargeting and Google’s Remarketing
The simplest way to explain the Remarketing feature is this:
When you visit a website, a tracking cookie is installed on your browser (yes, that’s the famous cookies message you now see everywhere). After you leave the website, you begin to see display ads from that website.
This is the remarketing feature: it allows advertisers to show you ads of the website you visited on other websites.
The ads can be general, just a reminder of the brand, but they also can be more personalized. The more directly related the ad is to the content you viewed, the impact it will make, thus increasing the likelihood of a purchase or return visit.
Let’s say you browsed a vacation apartments website. You looked at apartments in Lisbon, but didn’t make a reservation. A couple of days later, while scrolling down your Facebook feed, you all of a sudden see an ad that says “Still thinking about Lisbon?”
Now that’s powerful. It will stop your scrolling. It will make you think about Lisbon again. If you clicked the ad, it would take you back straight to the Lisbon section of that vacation apartments’ website.
So by tracking events – in this case browsing a specific page – you are able to deliver highly targeted, super relevant, and hopefully mighty engaging ads to audience that already demonstrated interest in your offering.
Facebook’s Lookalike Audience and Google’s Similar Audience
The simplest way to explain the Lookalike (Similar Audience) feature is this:
Based on your audience attributes, Facebook and Google are able to target similar people and show them your ads.
Behind this simple explanation, there is a highly complex algorithm able to locate people with similar interests, demographics, location, and professional background.
Facebook and Google are able to do this thanks to the vast amounts of data they have on their users.
Let’s say you track a video as an event. The video is a top-of-the-funnel content that explains the benefits of using the app you are offering. Website visitors who watched the video are “recorded.”
You can define the visitors who watched the video as a specific “audience” in Facebook or Google Analytics.
Then, the algorithm finds similarities between the visitors who watched the video and based on this data, can show your ads to other people who never watched the video but share the same similarities with your audience.
This is an incredible tool to expand your potential audience and reach people that are likely to be interested in your offering. This gets you more value on your ad spend.
Connecting the Dots: Events, Audience, and Targeting
So, now you know how Facebook and Google can help you refine and optimize ad campaigns, but what is the process to set it all up?
The first part of the chain is identifying the events and inserting the proper codes for all pages and types of events. We’ve already covered how to set them up, both on Facebook and Google Analytics.
How you define an event is crucial for the success of the campaign and determines which strategy you’ll use either remarketing or a lookalike (similar) audience.
Once you have the events set up, it’s time to connect them to your ad campaign. In this context, “connect” means enabling Facebook and Google to use the data collected from the event tracking to optimize the ad campaign.
Facebook Event Tracking Ad Optimization
Let’s start with the easier of the two.
Once you inserted the event tracking code to the various pages of your website, the events data is available for you on your Ads Manager.
As opposed to Google, where you need to first import the event data from Google Analytics to Google Ads (we’ll get to how to do it in a sec), on Facebook this action is taken care of for you.
Still, you’ll need to locate this data. Here’s how:
First, log in to Ads Manager and click the Pixels tab…
Then, on the left, choose “data sources”, it will take you to your pixel…
Now you’ll see a general breakdown of your events…
And to give you an overview of this report, a few things you should know:
- Events received is the total number of events recorded by the pixel
- Top events list the highest-performing events
- Activity shows the number of events recorded per day for the past week
Now, I want you to click on the “details button”.
Here you can see the actual breakdown of events, by volume and date. You can segment the visitors based on their actions, as we discussed before, or use the different segmentation for Lookalike audience creation.
Since you are already in Facebook Ads Manager, all the information is available for campaign targeting and optimization.
Google Analytics and AdSense Event Tracking Optimization
It’s a two-step process. First, you need to define the events in Google Analytics, and then import them into Google Ads.
Step #1: Define the event in Google Analytics
In your Analytics account, click the “Admin” tab in the bottom left corner. Then click the “Goals” tab.
Select “+New Goal”…
Choose the “Custom” option…
Name your goal…
Select “Event” option…
Now you’ll need to refer to the four elements you defined in the event code you had inserted for the specific event. This:
onclick=”ga(‘send’, ‘event’, ‘Category’, ‘Action’, ‘Label’, ‘Value’);”
The Goal you’re creating will have a specific box for each value. It looks like this:
The text you are entering here must be identical to the text in the code. If it won’t, the event won’t be recorded.
You’ll need to repeat the process above with every event you’re tracking.
Step #2: Import the event into Google Ads
In your Google Ads account, click the “Tools” tab at the top navigation bar. Select “Conversions” from the dropdown menu.
On the left side of the page, click “Google Analytics”…
You’ll see a list of all the goals you defined in Analytics…
Select the ones you want to import. Then click “Import”.
And you’re done. The events you track on your website are finally available for segmenting your remarketing campaigns and creating similar audiences.
If you don’t want to this yourself, Oribi can also do it for you.
Conclusion
Event tracking provides you with valuable data on your website visitors, such as level of intent, specific interests, and place in the funnel.
This provides better optimization of your paid ad campaigns on Facebook and Google.
You should use event data to deliver highly relevant and effective remarketing ads to segmented audiences who have already visited your website.
You should also use event data as the base for creating lookalike or similar audiences for ad campaigns targeting potential audiences who have not yet visited your website.
By optimizing your paid ad campaigns with event data you’ll be able to better engage users, increase your conversion rate, and get more of your ad spend which results in less money for more clicks.
Have you tried event tracking to help optimize your Facebook of Google ad campaigns?
The post How to Use Events to Optimize Your Facebook And Google Ads appeared first on Neil Patel.
How to Use Events to Optimize Your Facebook And Google Ads
Your website is bustling with activity. Visitors are constantly interacting with it. But are you taking full advantage of everything that’s happening on your website for your paid marketing? Every interaction a visitor has with your website… a pageview, a click… can be used to better understand your audience. And when you understand your audience … Continue reading How to Use Events to Optimize Your Facebook And Google Ads
How to Build Links Using Google Alerts
Link building is hard. But did you know that Google makes it easier for you?
Seriously… they do make it easier because they provide you with free tools.
No, I’m not talking about the ones you already use like Google Search Console and Google Analytics…
They actually have tons of other tools. Some you may have heard of, but I bet you don’t use them.
And today I am going to show you how you can build links using Google Alerts.
What is Google Alerts?
As the saying goes, if it isn’t on Google, it doesn’t exist.
Google is the most popular search engine in the world. Their database contains hundreds of billions of web pages and is over 100,000,000 gigabytes in size.
Because of their massive size, they are able to crawl web pages more frequently than any SEO tool including my own, Ubersuggest. This is precisely why you want to start using Google Alerts to build links.
So, what is Google Alerts?
As I mentioned above, they have a bigger database of web pages than any other link building or SEO tool. So, you’ll want to use their database to find easy link opportunities and ideally without wasting time digging through billions or even thousands of web pages.
Google Alerts allows you to create notifications on any subject, topic, or keyword.
So, when a new web page talks about anything that could be an easy link opportunity, you’ll get notified in an email.
Just like this one…
So, let’s set it all up step by step so you can get some backlinks.
How to set up Google Alerts
First, I want you to go here.
You’ll see a screen that looks like this (make sure you sign in at the top right).
I want you to type in your domain name without the www or the https part.
In my case, I would type in: neilpatel.com
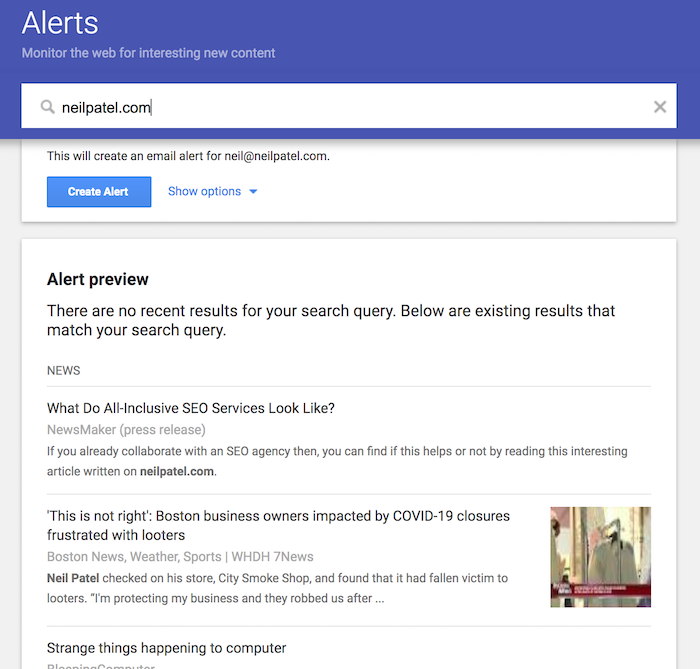
You may see an alert preview like the one above, but if you have a newer site you probably won’t see any results, which is fine.
Then I want you to click on the “Show Options” link next to the “Create Alert” button.
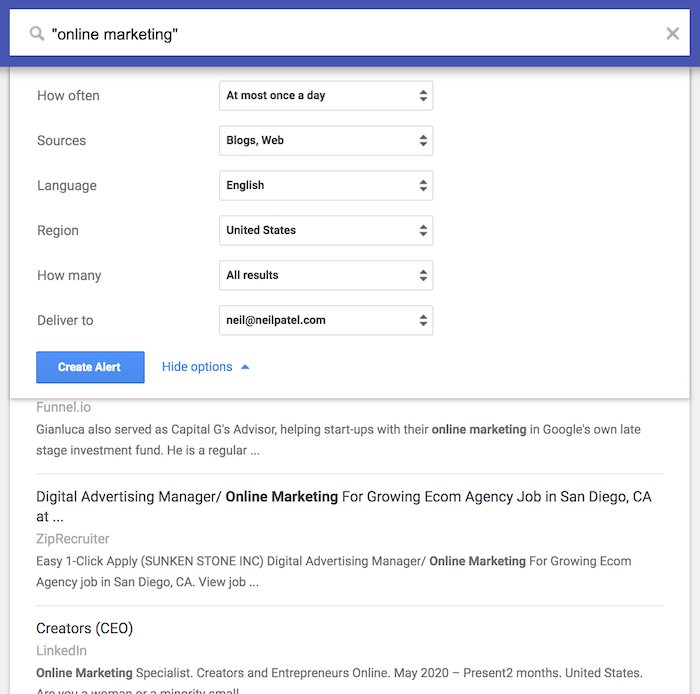
Your settings should match mine:
- How often – at most once a day
- Sources – Blogs, Web (select those 2 options, you don’t want news as an option as it tends to create more irrelevant results and we’ve found that it is harder to get news sites to link back to you)
- Language – English (or the language you are targeting)
- Region – any region (or you can select the country you are targeting although I recommend picking “any region”)
- How many – all results
- Deliver to – should be your email.
And then click “Create Alert.”
Up to once a day, you’ll get an email with a list of pages that mentions your website or domain.
I want you to repeat the process and create an alert for the following items:
- Your domain – you should have just done this.
- Brand name – in my case I would create an alert for “Neil Patel.”
- Product names – if you are selling any services or products you can create an alert around that. In my case, I would create an alert for “Ubersuggest.”
- Industry terms – create alerts for anything related to your industry. When people are talking about your space, it is an easy link opportunity. In my case, I would create alerts for the terms: digital marketing, online marketing, and SEO.
- Your email address – create an alert anytime someone gives out your email. Again, another easy link opportunity.
Here’s what mine looks like:
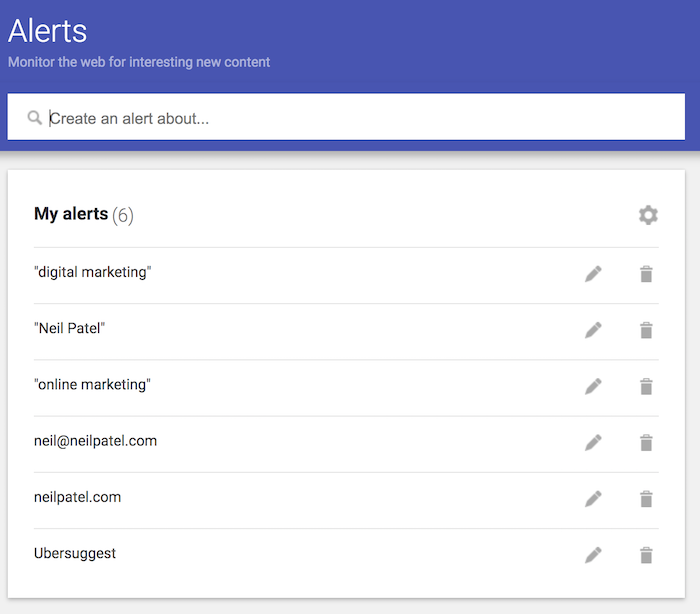
You’ll also notice for all of my two-word phrases I have quotation marks around them.
For example, I would not create an alert for: Neil Patel
But, I would create an alert for: “Neil Patel”
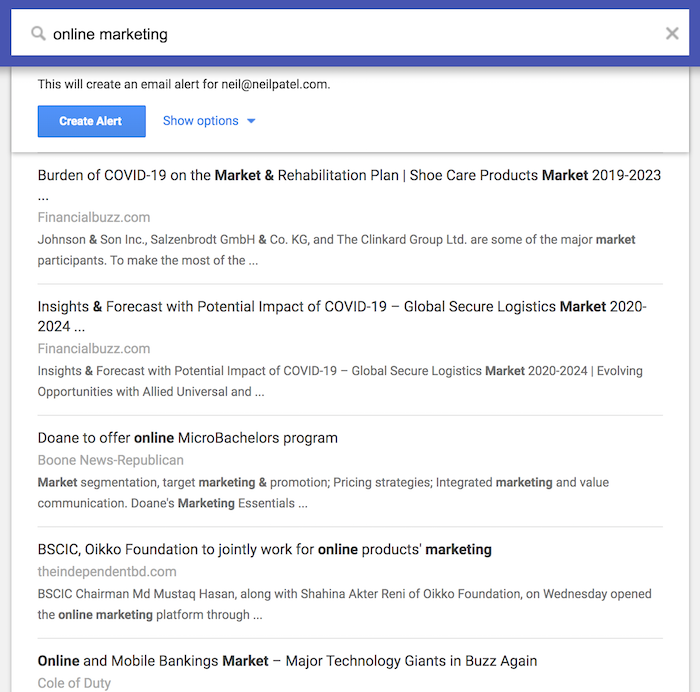
The reason being is that alerts for two-word phrases without quotes aren’t as relevant. For example, here are some alerts from the term: online marketing.
When I use quotes, here are the results.
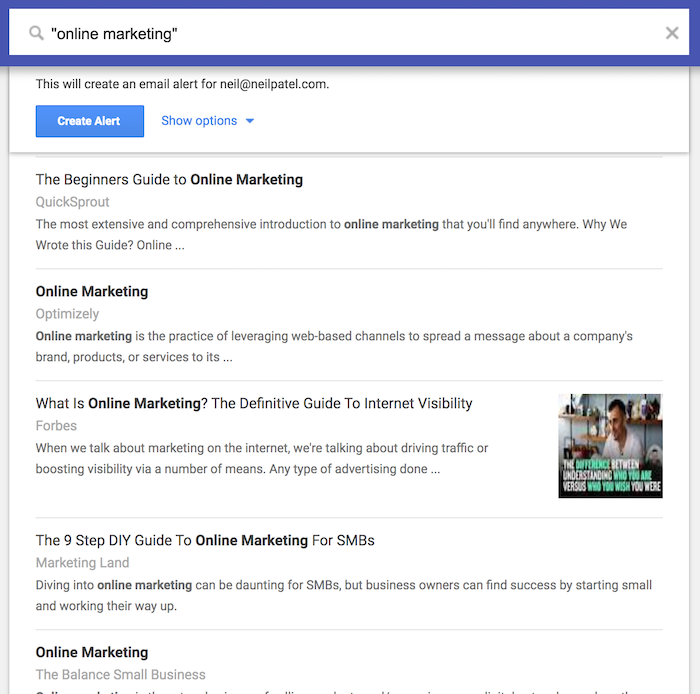
See the difference?
Getting links
Now that you have alerts set up, it is time to get links.
Keep in mind that when you get an alert email, someone could have already linked to you. So, not every alert will be a link building opportunity, but many will be.
Typically, more than half will be opportunities.
Depending on the alert type, some will be easier than others. So, let’s go over how to convert each opportunity into a link.
Your domain
You’ll find that a good portion of the mentions of your domain will contain a link back to your site.
For those, you don’t have to do anything as you’ve already got a link. 🙂
For the ones that aren’t linking to you, I want you to send the following email to the webmaster…
Subject: Did you make a mistake?
Hey [insert first name],
First off, I just wanted to say thanks for mentioning [insert your domain] in this article [insert a link to the URL that mentions your domain].
I know you are busy so I will just cut to the chase.
Would you mind hotlinking my domain to my website? I know it doesn’t seem like a big deal, but that extra traffic really helps small companies like mine.
Cheers,
[insert your name]
PS: Let me know if I can do anything for you.
Brand name
When it comes to brand names, it is a 50/50 shot. Roughly half the people will link to you when they mention your brand and the other half won’t.
For the ones that didn’t, send them this email:
Subject: You forgot to do this
Hey [insert first name],
I’m flattered.
Thank you for mentioning [insert your brand name] in your article on [insert the title of their article].
[insert the URL of their article]
You really made my day with that.
Again, thank you!
I feel bad doing this because you already mentioned us, but it would mean the world to me if you also linked our name to our site.
Would you mind doing that?
Sorry to bug you.
[insert your name]
PS: Let me know if I can do anything for you.
Product names
With product names, usually 70% to 80% of the websites will be linking back to you and the rest not. For the ones that don’t, send them an email similar to this:
Subject: Did you mean to do this?
Hey [insert their first name],
I just wanted to take a minute to tell you how much I appreciate that you mentioned [insert your brand name] here [insert the URL of the webpage that mentions your product].
Seriously, thank you!
Now, I feel bad doing this, but would you mind hotlinking [insert your product name] to this page on our website where people can find the product [insert the URL on your site that covers the product]?
Sorry to bug you.
And again, thank you for mentioning us. It really means a lot.
[insert your name]
PS: Let me know if I can do anything for you.
Your email address
Now this one is rare as most people won’t be publishing your email address.
And when they do, they usually aren’t linking to you.
If you try to get them to link the email address, you will find it hard. But what’s easier is to get them to remove your email address and link to your contact page instead.
Here’s the email template I use for this.
Subject: Privacy issue
Hey [insert their first name],
I noticed you mentioned our email address, [insert your email address], on this page [insert the page they mentioned your email on].
Would you mind mentioning and linking to our contact page instead [insert your contact page URL]?
For privacy reasons, I would rather have people get in touch with us through that page instead of our email.
Thanks for your time.
[insert your name]
You also notice that in this template I didn’t include the PS at the bottom. The PS typically helps boost your success ratio, but when it comes to this email, you want to be a bit more firm as it is related to your privacy.
You ideally want the link and fewer people sharing your email because then you’ll have to deal with a ton of spam messages.
Industry terms
In almost all cases, alerts that contain industry terms won’t be linking to you. And this group will also be the largest number of results you get with each alert email.
You’ll have to go through each alert and look at the context of the web page.
If they are talking about something that you have already covered on your website and did more in-depth than they have, there is a good chance you can convince them to link to you.
For example, if there is an article about SEO and they mention how you need to build links, but they don’t go into how to build links, I would email the site owner pointing to this article as it breaks down how to build links.
Here is the type of email I would send:
Subject: Some feedback for you
Hey [insert their first name],
Love your article on [insert the topic of their article] [insert the URL of their article].
I just have one piece of feedback for you (hope you don’t get offended), but you mention [insert the subject they mention that you go more in-depth on within your own site], but you didn’t go too in-depth on it.
I think if you adjusted that it would provide a lot more value to your readers.
Or if you don’t have the time to, I already have an article on it here [insert the URL on your site where you go in-depth on that topic] that you could just link to.
Let me know your thoughts.
[insert your name]
PS: Let me know if I can do anything for you.
How do I get in touch?
Now that you know what kind of emails to send depending on the alert you receive, you’ll have to, of course, get in touch with the site owner.
So how do you find their email address?
Well, the simplest way is to go to their contact page and see if their email is there or if they have a contact form.
You can also check out their terms of service or privacy policy.
Another option is to use tools like Hunter. Just type in a domain name into Hunter and you’ll see a list of people you can contact.
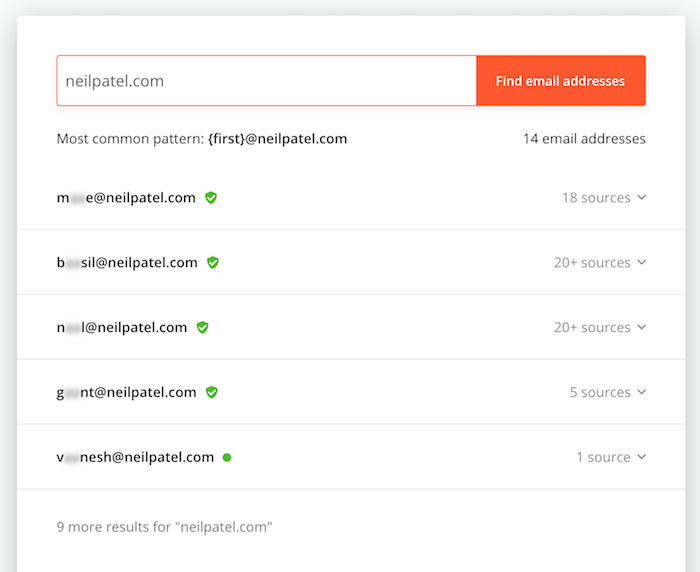
Their free plan allows 50 requests per month, which should be enough to get you started.
Conclusion
Google Alerts is an easy way to build links so I would start with that.
What’s beautiful about it is that you’ll get notified of opportunities. This will save you a lot of time.
And if you find yourself with a bit of extra time, I recommend one more strategy to build links.
Go here and put in your competition’s URL.

Once you hit “search” you’ll see a report that looks something like this:
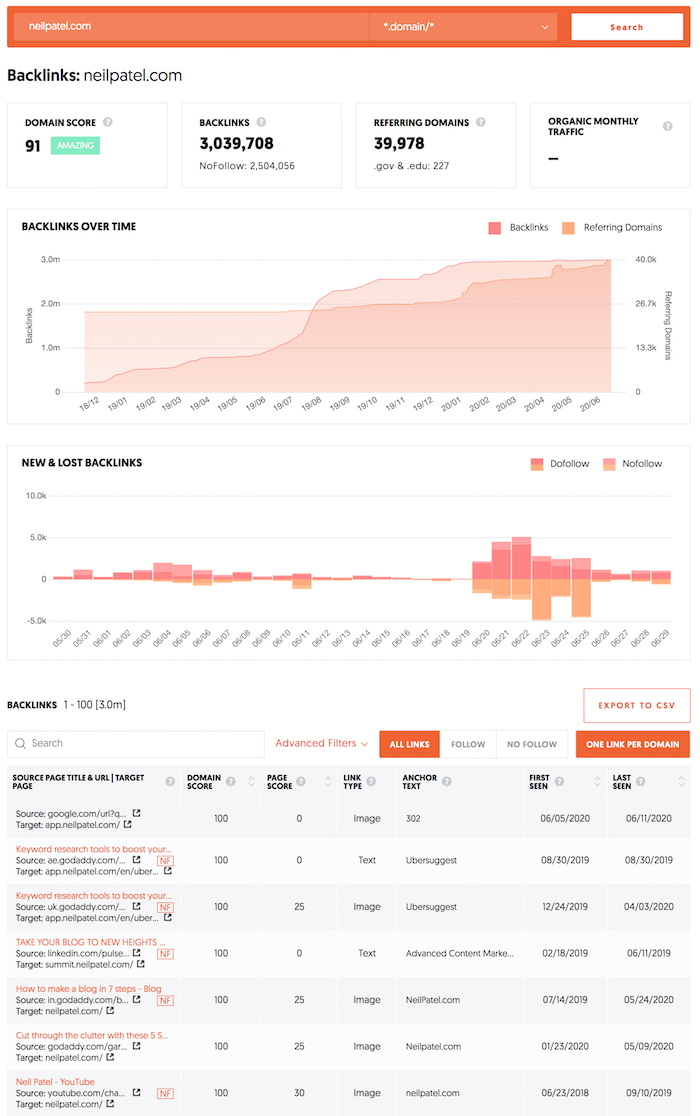
These are all of the websites linking to your competition. What’s interesting about this list is that it is sorted.
The results at the top have more authority, in which they typically boost SEO rankings more than the ones at the bottom of the list.
You’ll want to go through the list, click on each site, and see if it makes sense to reach out to that website and ask them to link to you.
Typically, if you have similar content to your competition that is more thorough, it’s possible to convince someone to link to you. You’ll have to send them emails like the one below…
Hey [insert their first name],
Question for you…
How do you think it makes you look to your readers when you link to another site that doesn’t really help them?
It kind of makes you look bad and maybe even lose a little bit of trust with your readers, right?
In this article [insert the URL on their site], you link out to [insert the competition’s URL].
The article you are linking to doesn’t cover [insert the areas the competition missed].
I actually have an article [insert your article URL] that covers [insert what you cover that the competition doesn’t and why it benefits readers more].
If you aren’t interested in linking to us no worries. I just know that you care about your readers and you want to do the best for them.
Cheers,
[insert your name]
PS: Let me know if I can do anything for you.
If you follow the steps above, you’ll start building links.
It isn’t that hard and you can do it. You just have to be willing to put in the time and not get discouraged if you send out a handful of emails and no one links back to you.
Just think of your email as a sales pitch and it may not be perfect the first time… so you may have to modify and adjust it.
If you have any questions on the steps or are confused about anything, just leave a comment below.
The post How to Build Links Using Google Alerts appeared first on Neil Patel.
5 Reasons Your Page Is Not Indexed On Google Search (+ Fix)
5 Ways to Get Your Page to Show on Search After hours of coding, writing, designing, and optimizing, finally you are ready to live your new web page. But hey, why is my blog post not showing on Google? What have I done wrong? Why does Google hate me? Now, now, we have all been … Continue reading 5 Reasons Your Page Is Not Indexed On Google Search (+ Fix)
3 Simple Steps to Get Your First 10,000 Visitors from Google
Today’s going to be fun.
I’m going to make a bet with you that if you follow the 3 steps below, and you really follow them, you can get 10,000 visitors from Google.
I promise it won’t be hard, but it will take time.
And if you follow my steps and don’t get the results, hit me up and I will personally help you with your marketing.
All I ask is you do it for 3 months straight. You may not get to 10,000 visitors from Google in 3 months as some niches are really tiny, but most of you should get there or be well on your way.
Again, if you prove to me that you followed everything below and you don’t achieve the results, you can get in touch and I will personally help you with your marketing for free.
Ready?
Step #1: Finding the right keywords
If you pick the wrong keywords, you’ll find yourself with little to no traffic and, even worse, you’ll find yourself with little to no sales.
So, before we get you on your way to more search traffic,
let’s find you the right keywords.
I want you to head to Ubersuggest and type in your
competitor’s domain name.
Now, I want you to click on the “Keywords” navigational
option in the sidebar.
This report will show you all of the keywords that your competition is ranking for.
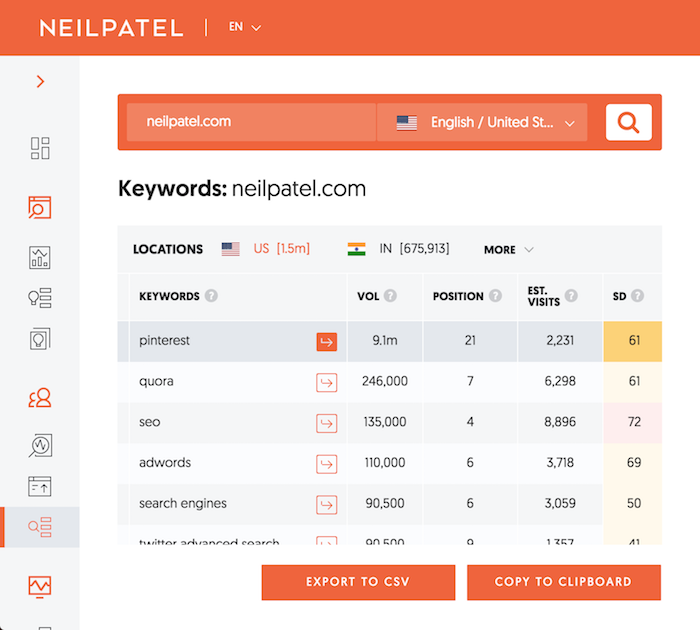
If you don’t see a list of thousands of keywords, that means you didn’t type in a big enough competitor. And if you don’t know who a big competitor is, just do a Google search for any major term related to your industry. The sites at the top are your major competitors.
I want you to go through the list of keywords and look for all of the keywords that are related to your business and have an SEO Difficulty (SD) score of 40 or less. The higher the number, the harder the keyword is to rank for. The lower the number, the easier it is to rank for.
In addition to an SD score of 40 or lower, I want you to look for keywords that have a volume of 500 or more.
Volume means the number of people that search for the keyword on a monthly basis. The higher the number, the more potential visitors that term will drive once you rank for it.
Next up, I want you to click on “Top Pages” in the
navigation.

This will bring you to a report that looks like this:
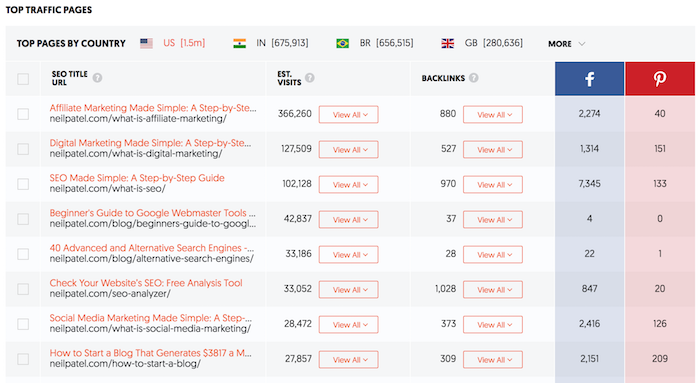
This report shows you the most popular pages on your
competitor’s site.
Now, under the Est. Visits (Estimated Visits) column, I want you to click on “view all” for the first few results.
Every time you do that it shows you all of the keywords that
drive traffic to that page.
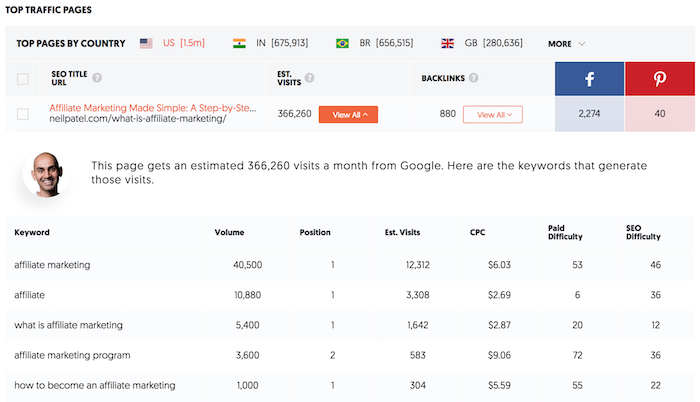
Just like you did with the keywords report, I want you to look at the keywords that have an SD of 40 or lower and a volume of 500 or more.
The one difference though, is that I want you to check out some of the URLs on the Top Pages report.
Click on over to the site so you can see the type of content they are writing. This is important because it will give you an idea of the types of content that Google likes to rank.
When you create similar pages (I will teach you how to do this shortly), it will allow you to get similar results to your competition over time.
Now that you have a handful of keywords, I want you to expand the list and find other related keywords.
In the navigation menu, click on “Keyword Ideas.”

When you type in one of the keywords you are thinking of going after in this report, it will give you a big list of other similar keywords.
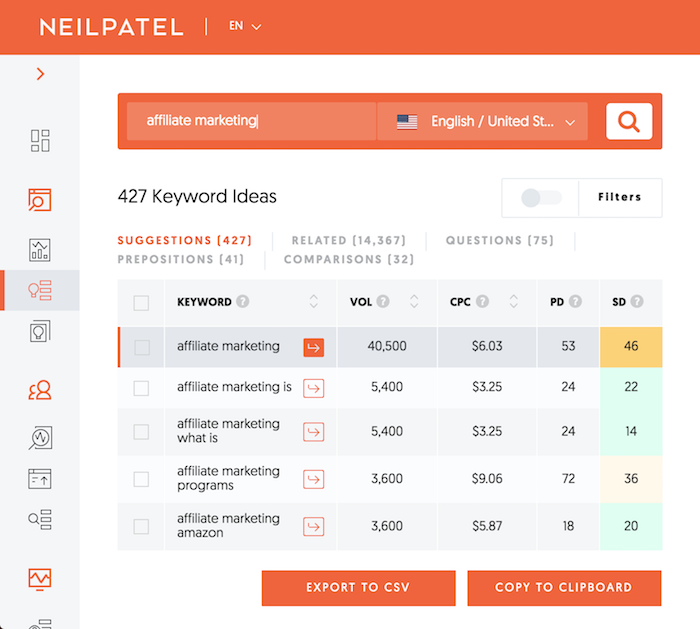
This is important because it will show you all of the
closely related terms.
For example, let’s say you came up with a list of keywords of a handful of keywords, such as:
- Dog food
- Cat food
- Dog bed
- How to clean your cat
- What do birds eat
You can’t just take all of those keywords and write one article and shove all the keywords in because they aren’t similar to each other. Someone looking for “dog beds” is probably not interested in reading about what birds eat.
So by typing in a keyword into the Keyword Ideas report, it will show you all of the other similar keywords that you can include in a single article.
When you are on the Keyword Ideas report you’ll notice some tabs: Suggestions, Related, Questions, Prepositions, and Comparisons.
I want you to go through each of those tabs. They will show you a different group of similar keywords that you may be able to include in your article (we will go over how to write the article in step 2).
Just take a look at the Questions tab:
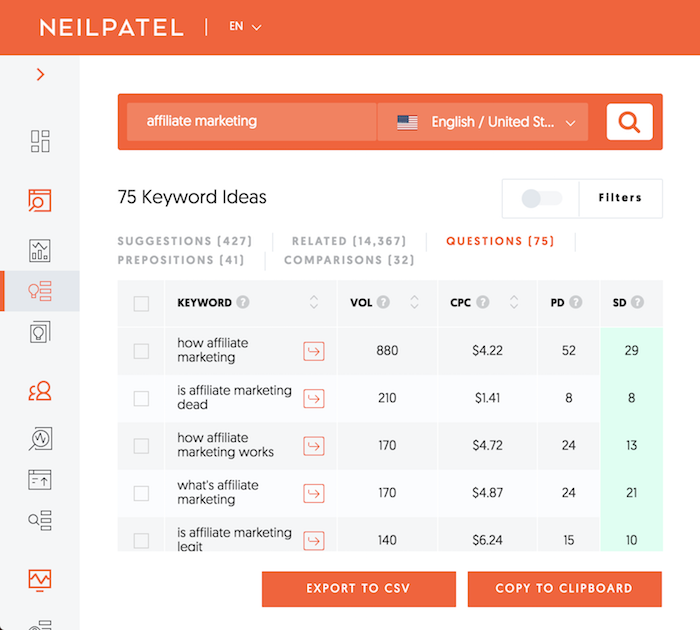
You can see the keywords are drastically different than the Related tab:
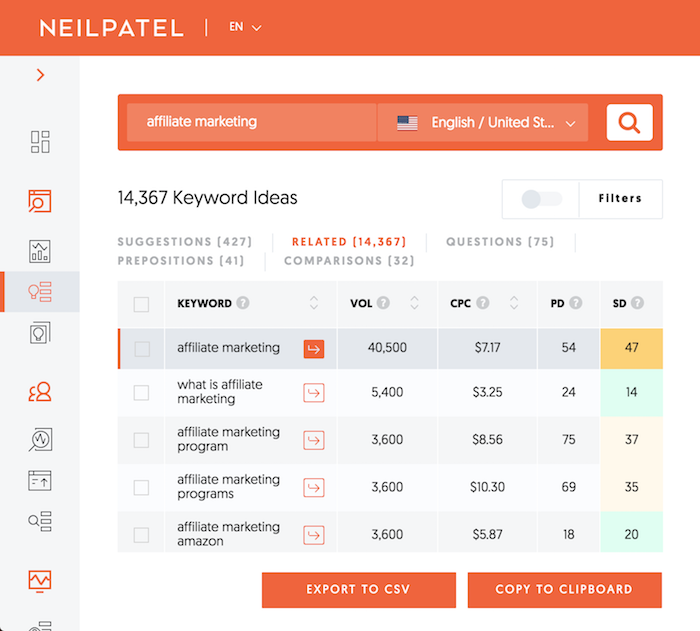
Again, you’ll want to look for all keywords that have an SD score of 40 or lower. But this report looks for keywords that have a volume above 200.
I know 200 may seem like a small number, but if you find 100
good keywords that all have a volume of 200 or more, that adds up to 20,000
potential visitors per month. Or better yet, 240,000 per year.
Now it’s rare that you are going to get all of those people
to come to your site, but you can get a portion of them. Even 10% would add up…
especially if you did this with a handful of articles.
Your goal should be to have a list of at least 100 keywords that are very similar. You’ll want to do this at least five times. For example, remember that list of five keywords I mentioned above wasn’t too similar to each other…
- Dog food
- Cat food
- Dog bed
- How to clean your cat
- What do birds eat
You’ll want to make sure that for each main keyword you use the Keyword Ideas report to find another 100 that can accompany each keyword.
Step #2: Write content
At this point, you should have a list of keywords. If your list of keywords isn’t at least 100 keywords per group, go back to step 1 and keep at it.
It’s not that hard to get to 100 similar keywords that you can include in one article. It just takes some time to continually search and find them.
In general, as a rule of thumb, I can find 100 keywords in
less than 8 minutes. It may take you a bit longer than me at first, but once
you get the hang of it, it’ll be easy.
With your newly found keywords, I want you to write an article.
All you have to do is follow this tutorial step-by-step to write your first article.
Or, if you prefer a video tutorial, watch this:
As for your keywords, naturally place them into the article when it makes sense.
What you’ll quickly learn is that you probably won’t be able
to “naturally” include all 100 keywords within your article. And that’s fine.
The last thing you want to do is stuff in keywords because you aren’t writing this article for just search engines, you are writing it for people… and the secondary benefit is that search engines will rank it because it contains the right keywords.
Before you make your article live on your site, I want you
to keep a few things in mind:
- Keep your URLs short – Google prefers shorter URLs.
- Include your main keyword in your headline – by having your main keyword in your headline, you’ll be more likely to rank higher.
- Include your three main keywords in your meta tags – whether it is your title tag or meta description, include at least three main keywords in them. You won’t fit as many in your title tag, and that’s fine, but you should be able to within your meta description tag.
There are a lot of other things you can do to optimize your articles for SEO, but my goal is to keep this simple. Again, if you just follow these three steps, you’ll hit the 10,000-visitor mark.
So, for now, let’s just keep things simple and once you hit
your goal, then you can get into the advanced stuff.
Step #3: Promoting your content
Writing content is only half the battle. Even if you include the right keywords in your article, if you don’t promote, it’s unlikely that it would be read or rank on Google.
So how do you make sure your content is read and ranks well?
Well, first you need to get social shares, and second, you need to get backlinks.
Yes, search engines don’t necessarily rank pages higher when
they get more Facebook shares or tweets, but the more eyeballs that see your
page the more likely you are to get backlinks.
And the more backlinks you get, generally, the higher you will rank.
So here’s how you get social shares…
First, I want you to go to Twitter and search for keywords related
to your article.
As you scroll down, you’ll see thousands of people tweeting about stuff related to your keywords. Some of them will just be general updates but look for the members sharing articles.
And…

Now what I want you to do is click on their profile and see if they mention their contact information or their website. If they mention their email you are good to go. If they mention their website, head to it, and try to find their contact information.
You won’t be able to find everyone’s contact information,
but for the people you do, I want you to send them this email:
Subject: [insert the keyword you searched for on Twitter]
Hey [insert their first name],
I saw that you tweeted out [insert the title of the article they tweeted]. I actually have an article that I recently released on that subject.
But mine covers [talk about what your article covers and how it is unique].
[insert link to your article]
If you like it, feel free to share it.
Cheers,
[insert your name]
PS: Let me know if you want me to share anything for you on Twitter or any other social network.
What you’ll find is a large percentage of the people will be willing to share your content because they already are sharing related content and, of course, you offered to share their content, which helps out too.
If you send out 30 to 40 emails like this, you’ll start
getting traction on the social web.
Now that you have social shares, it’s time to build backlinks. Instead of giving you tons of link building methods as there are many that work, I am just going to start you off with one that works very well.
I want you to head back to the Keyword Ideas report on
Ubersuggest.

Once you get there, type in some of the keywords that you are trying to go after.
On the right side of the report, you’ll see a list of sites that rank and the number of backlinks that each of the ranking URLs has.
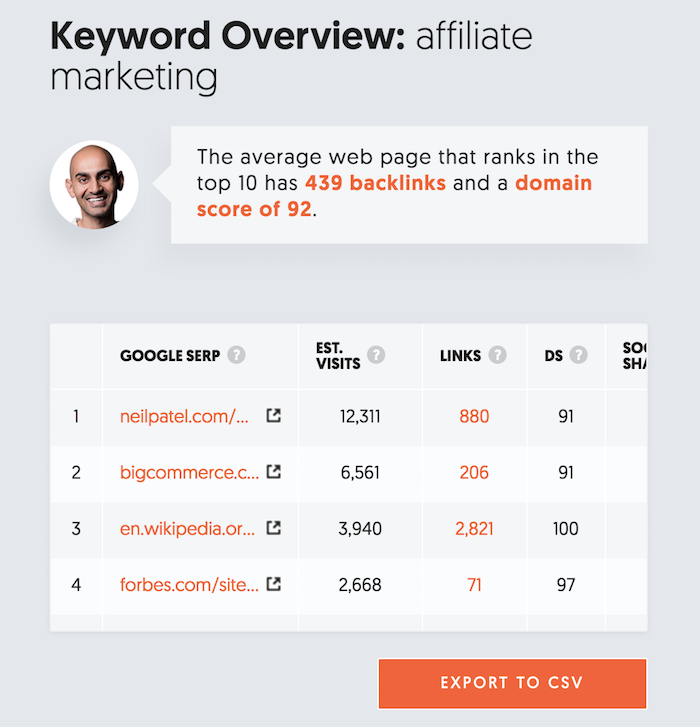
Click on the “Links” number. For each result, it will take you to the Backlinks report, which looks something like this:
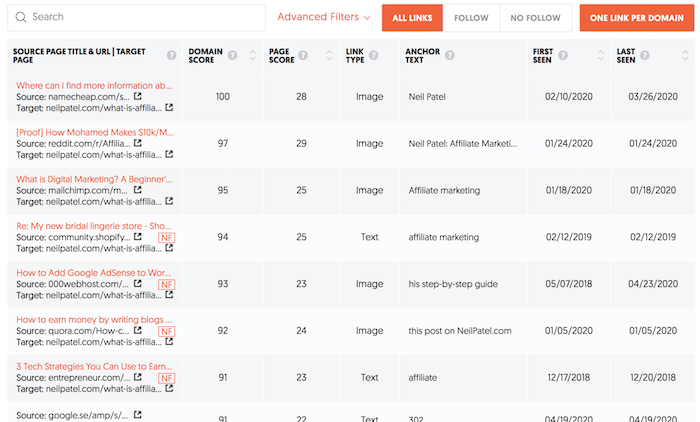
This will give you a list of all the sites linking to your
competitor’s article.
I want you to go to each of those URLs, find the site owner’s contact information, and shoot them an email that looks like this:
Subject: [name of their website]
Hey [insert their name],
I noticed something off with your website.
You linked to [insert your competitor that they linked to] on this page [insert the page on their site that they are linking to them from].
Now you may not see anything wrong with that, but the article you linked to isn’t helping out your website readers that much because it doesn’t cover:
[insert a few bullet points on how your article is better and different]
You should check out [insert your article] because it will provide a better experience for your readers.
If you enjoyed it, feel free to link to it.
Cheers,
[insert your name]
PS: If I can ever do anything to help you out, please let me know.
I want you to send out 100 of those emails for each article
you write.
Conclusion
Yes, it takes work to get 10,000 visitors but once you do it you’ll continually generate traffic and, more importantly, sales.
To achieve 10,000 visitors, I want you to do the steps above five times. In other words, you will be writing five pieces of new content following the steps above.
It’s actually not that bad because you can just do 1 a week.
So, within 5 weeks you would have done your job.
So, are you going to accept the challenge? If you do everything and don’t see the results over time, you can hit me up and I’ll help.
The post 3 Simple Steps to Get Your First 10,000 Visitors from Google appeared first on Neil Patel.