The Ultimate SEO Checklist for 2022
Does this topic sound a bit familiar? There’s a good reason for that.
Every year, there are new SEO trends every website owner should be aware of. Sometimes it might just be a fresh approach to a classic SEO tactic, and other times, it’s something new that could give your website an advantage over your competitors.
However, while these new trends and innovations emerge, many of the tried and tested SEO methods still play an important part in improving your website’s rank. Ultimately, isn’t that what every website owner wants?
To help you out, I’ve compiled the ultimate SEO checklist for 2022, an all-purpose tool for website owners to optimize their traffic.
First, though, let’s get started with a look at some emerging SEO trends.
What’s Happening in 2022 In SEO?
Voice search, mobile SEO, long-form content, local SEO, and user intent remain strong. They were around in 2021, they’ve been a constant for a long time before that, and they’re likely to remain a core part of your online marketing efforts for the foreseeable future.
Now I’ve got some of the mainstays of your SEO checklist out of the way; what’s new? Well, Hubspot points to tightened page headers for additional context, or Google’s snippet feature, People Also Ask, and using emotive headlines. I’m sure most of us have clicked on a headline just because it resonated with us, so we can all relate to that one. You know what I mean:
‘You Won’t Believe What This CEO Did To Save His Company’ or ‘How One Simple Change Can Transform Your Life’
Then there are some more innovative trends that we’re all set to see plenty more of. Many of you have heard of AI and its use in content creation. If you haven’t, you soon will. Other continuing trends for 2022 are:
- Core Web Vitals, which illustrate how your webpages perform.
- Content optimization software to help your content in the SERPs.
- Structured data, like schema markup/rich snippets.
- GPT-3, which is a language generator.
- Keyword clustering, which is the process of grouping related keywords together.
Your 2022 SEO Checklist
As I stated in the intro, regardless of new trends and advances, the major staples for SEO remain unchanged for 2022. However, even though you may be familiar with these SEO tactics, drawing up a clear strategy can seem like a challenge. It doesn’t have to be, though.
To help guide you, I’ve drawn up an SEO checklist to optimize your site. Just follow along, stage by stage, and see how your rankings can grow.
Let’s begin with the basics.
1. Set Up Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools
If you’re looking for a free way to monitor your site’s performance and traffic, enhance your website listing performance, and fix errors, then Google Search Console needs to be at the top of your SEO checklist.
Other benefits include:
- Monitoring which keywords are driving traffic
- Searching analytics for viewing impressions and clicks
- Checking which pages Google is indexing
- Understanding your website’s visibility
Sound good? Then you may want to set up an account by:
- Signing up for a Google account
- Adding your domain name or URL prefix to Google’s Search Console page
- Verifying your account
- Once verified, start viewing reports by clicking the ‘overview’ option.
Although Google is the king of search engines, that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t sign up for Bing or other competitors.
Bing Webmaster Tools can help you identify and fix any errors preventing your website from appearing higher in search results. Additionally, it’s a great resource for optimizing your website for Bing and improving your overall SEO health through identifying duplicate content issues and checking loading speeds.
If you’re new to Bing Webmaster Tools, follow these steps:
- Open an account or sign in. You can use your Microsoft, Google, or Facebook account details or sign up for a new Microsoft account.
- Add your site/s to your website by importing from your Google Search Console or manually adding your site/s.
- Verify your account by doing a DNS auto verification, an XML, or a Meta Tag authentication. Alternatively, add a CNAME record to DNS.
- Once Bing verifies your account, a green checkmark appears along with a message saying Bing has added your site to Webmaster Tools. A red cross indicates an error you must fix before trying again.
- Finally, you can upload a site map and develop a search optimization plan, but these steps are optional.
If you want some guidance for drawing up an SEO strategy, I’ve created a comprehensive list of resources.
2. Set Up Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a powerful tool used to track website traffic. It’s important to set up Google Analytics before you start publishing content so that you can track your website’s progress.
It’s hugely popular, and major companies such as Airbnb, Spotify, and Uber use it.
Here are the steps to get started with Google Analytics:
- Sign up for a Google Analytics account. Just select ‘Get started today.’ Alternatively, sign in to your existing account.
- Set up Google Analytics. You can use it on your website, app, or both. You can do this by selecting ‘admin’ in the account column and choosing ‘create account.’
- Add an account name and configure your data sharing options.
- Click ‘next’ to start adding your domains to your Analytics account.
- Google also provides a list of optional activities, including adding more users to Analytics and linking your Google Ads account.
3. Install an SEO Plugin if You’re on WordPress
WordPress users can easily optimize their sites by including a plugin as part of their SEO checklist.
There are many great SEO plugins available for WordPress, such as Yoast SEO or All in One SEO Pack. These plugins let you optimize your website for search engines, and they provide handy checklists so you can ensure you’re doing everything you can to improve your site’s visibility.
Other SEO plugins include:
- The SEO Framework. Free and paid options are available.
- SEO Press. (choose from freemium or premium packages).
- Rank Math, which has an extensive list of features.
- Nitropack. Free and paid plans are available.
Regardless of whichever keyword plugin you choose, look for one that:
- Is easy to use. The plugin should be easy to install and configure and should be intuitive to use.
- Can track all of your keywords, not just a few of them.
- Updates frequently for efficiency and security. Ideally, you’d want a plugin to update at least once weekly.
4. Create and Submit Your Sitemap
By creating and submitting a sitemap, you make it easier for crawlers to index your pages and identify any changes you’ve made since the last time the search engines crawled your site. Additionally, a site map increases visibility while aiding navigation and improving poor linking.
There are several different ways to create a sitemap, but the most common is an XML file. Once you’ve created your sitemap, submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools. They’ll crawl your site and add it to their indexes.
However, not every site needs a sitemap. According to Google, sitemaps work best if:
- You’ve got a large site
- Your site contains a substantial archive of isolated or poorly linked content pages.
- You’ve got a new site with limited external links
- Your site contains rich media, like video and photographs.
Now that you’ve done that, it’s time to set up a Robots.txt file.
5. Create a robots.txt File
When you’re creating or editing a website, don’t forget to add a robots.txt file! This file tells search engine bots which parts of your website they’re allowed to crawl and index.
The benefits of including robots.txt as part of your SEO checklist are:
- Helping improve your website’s load time by preventing unimportant pages from loading.
- Preventing search engines from indexing duplicate content on your site
- Blocking search engines from indexing spammy or low-quality pages
- Focusing your SEO efforts on the most important pages of your site
Here are things to consider when creating your robots.txt file:
- Which pages on your website do you want search engines to crawl and index?
- Which pages do you want to block from crawlers?
- What parameters do you want to set to crawl specific pages or sections of your website?
- How often should the robots.txt file be updated?
When it’s complete, your Robots.txt. might look like something like Nike’s.
6. Make Sure the Search Engines Can Crawl and Index Your Website
If you’re running a website, it’s vital to ensure the search engines can crawl and index it. After all, you want potential customers to find you online, right? Here are a few things to tick off your SEO checklist to help ensure the search engines can do just that.
- Check your site is accessible to crawlers. Search engines need access to all the pages on your website to index them. You can check this by using the URL Inspection Tool in the Google Search Console.
- Use keyword-rich titles and descriptions on your pages. This can improve your site’s ranking in search results.
- Add links to other related pages on your site, so search engines understand the topic of your page and rank it accordingly.
You should also consider the recent changes to Google’s scoring system: Now, Googlebot crawls and indexes just the first 15MB of your web content. Therefore, it’s imperative you place your most essential content first.
As part of its update, Google announced changes to its Product Structured Data Guidelines, so read all about those, too.
7. Be Sure Your Site Is Mobile-Friendly
Is your site mobile-friendly?
According to research, nine out of ten consumers have at least one mobile shopping app. The top reason people are using apps? Because of the superior user experience.
Visitors who have a negative user experience may not come back for more. Therefore, it’s well worth including this on your SEO checklist.
How do you do this? It’s easier than you think. You can:
- Use responsive design, so your site adapts to different screen sizes.
- Optimize images for mobile by resizing and compressing them. Imagify offers a free monthly plan for up to 200 images.
- Check your site on different browsers/devices. If you need a tool for this, here’s a list.
- Use Google Search Console to test your website performance and get tips to enhance it.
Here’s an example from Zappos:

Note its clear images and intuitive, highly visible search function.
8. Check for Oversized Image Files
It’s a simple enough equation: the larger your image files are, the longer they take to load.
To check for oversized image files, use a tool like ImageOptim or Google PageSpeed Insights. The PageSpeed tool checks for loading times and offers tips to improve them.
ImageOptim compresses images without compromising quality; you can use it with Mac, Linux, and Windows.
These tools will analyze your images, tell you how large they are, and how you can optimize them for better performance.
9. Look for 404 Errors
Broken links and 404 errors can have a negative effect on your website’s SEO.
Not only do they create a poor user experience, but they can also impact your site’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). To avoid this, it’s imperative you regularly check for and fix broken website links.
To check for broken links and pages, use a tool like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console. These tools allow you to spot broken links and find pages that Google has yet to index.
When you’ve found a broken link, you’ve got a few options:
1) Edit the link so that it points to the correct page
2) Create a 301 redirect so that the broken link is redirected to another page on your website.
3) Remove the link from your website altogether.
10. Look For Duplicate Content and Keyword Cannibalization
If you use the same keyword phrase too many times, the search engines may penalize your site.
In addition, if you have multiple pages that target the same keyword phrase, the search engines may not know which page to rank higher. What does this mean for your website? It’s called keyword cannibalization, and it could mean lower search engine rankings for all your pages. That’s the last thing you want when you’ve worked hard to establish your website.
To avoid this, use an SEO checklist that details your keywords to ensure that you aren’t inadvertently optimizing your pages for the same keyword phrases.
In addition:
- Vary your keyword usage throughout your site. Don’t just focus on using them in your titles and headings; include them in the body of your text as well.
- Make sure each page has its own unique title tag and meta description.
- If you have several websites with similar content, ensure that you aren’t using the same keywords on all of them.
- Use Google Search Console to check for duplicate content and cannibalization issues.
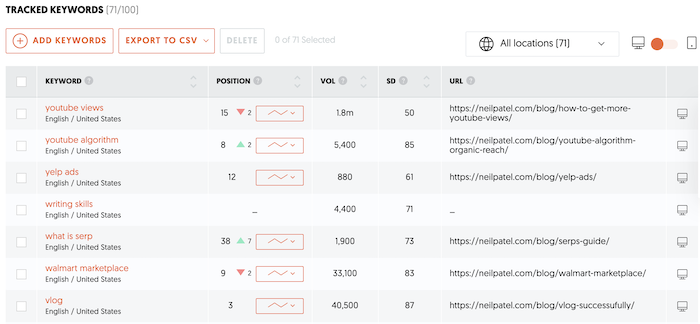
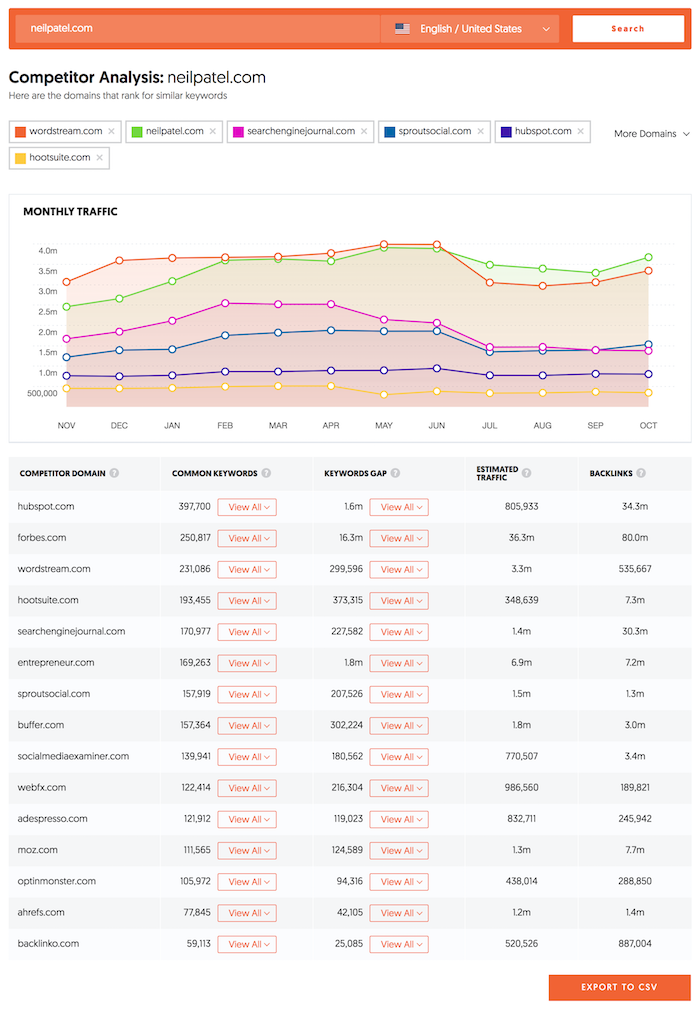
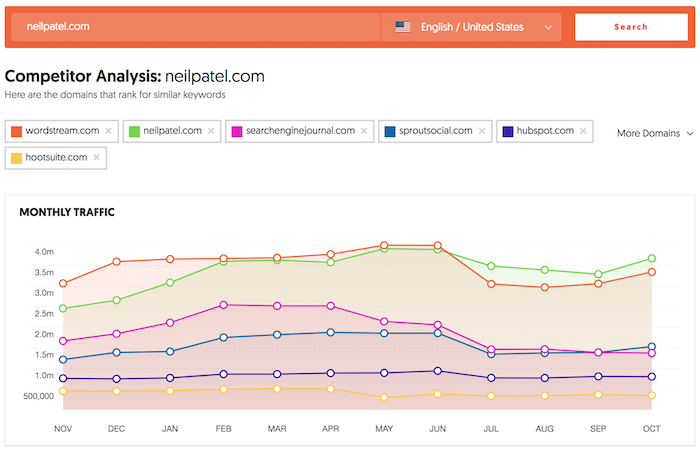
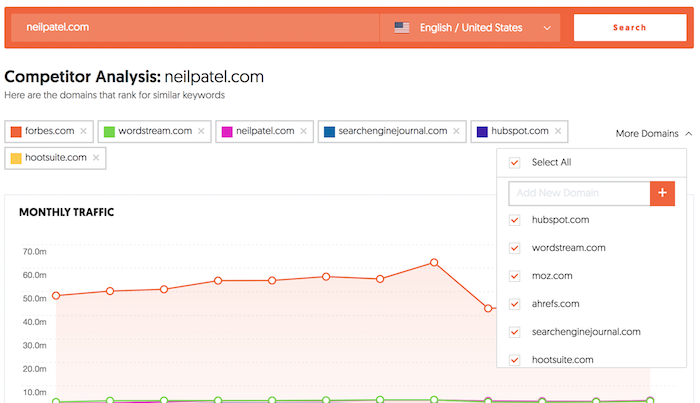
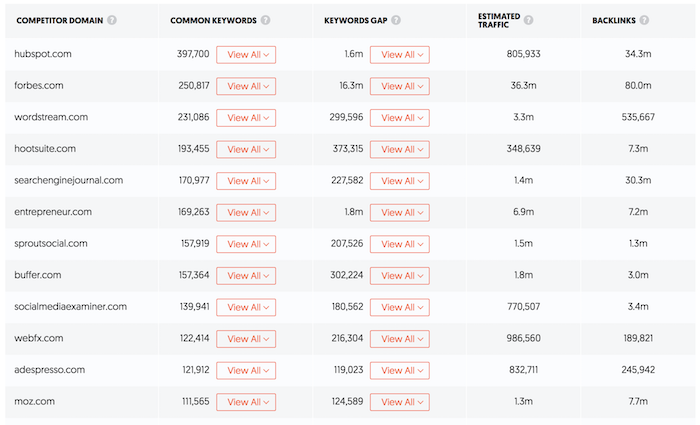
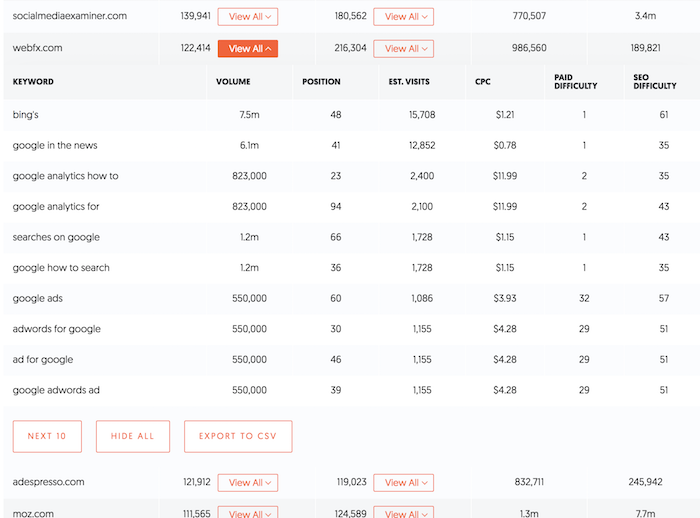
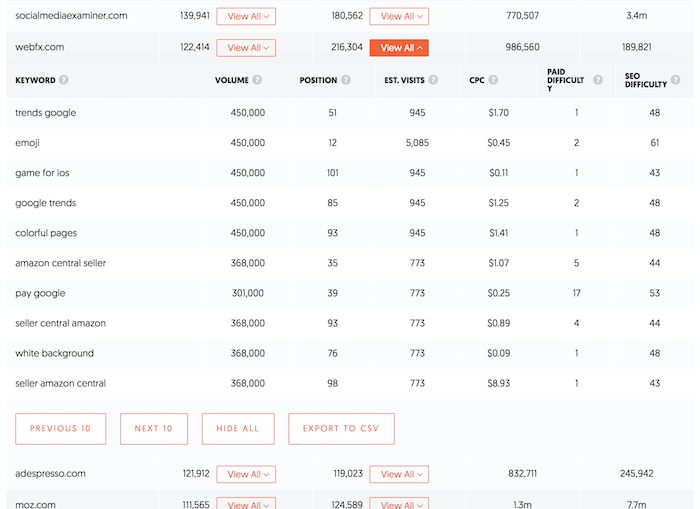
11: Research Your Competitors’ Keyword Profiles
Just because you rank first for a particular keyword or set of keywords doesn’t mean that traffic and conversions automatically follow.
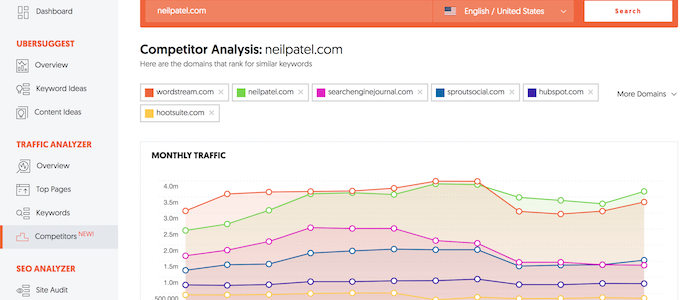
To truly optimize your website and its content for your target audience, you should research your competitors’ keyword profiles and understand what terms and phrases they are targeting.
By doing this research, you can get a good idea of the competition you’re up against, along with the terms and phrases that are most important to your target audience. Armed with this information, you can then begin targeting those same terms and phrases on your own website, helping to improve your rankings and visibility over time.
The result? They can be spectacular, helping you to rank higher, save money and maximize your ROI.
However, how do you find these keywords?
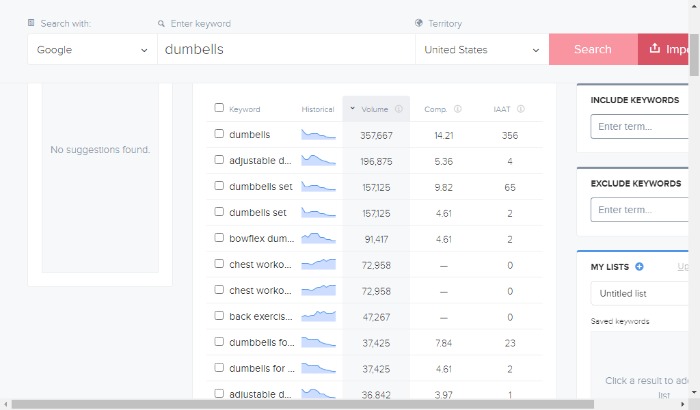
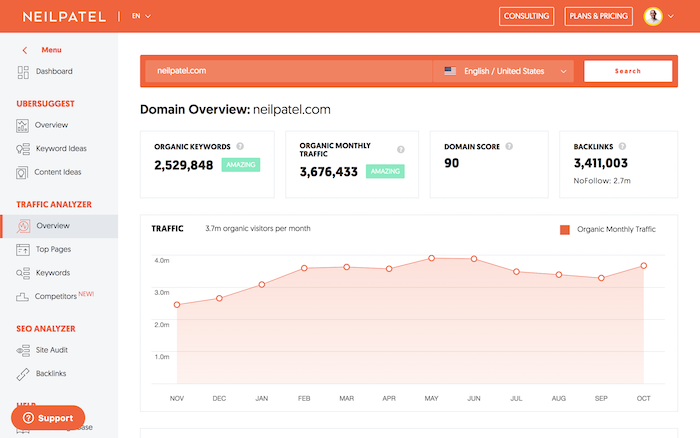
As a starting point, I’d recommend my tool, Ubersuggest, for finding competitor keywords. It’s easy to use. Just enter the URL, choose your country, and click ‘search’ to discover:
- Common keywords
- Keyword gaps
- Traffic over time.
12: See What Search Intent Your Primary Audience Has in Google
Search intent is one of the top factors for SEOs to consider. However, what do we mean when we’re talking about ‘search intent,’ and why should it be on your SEO checklist?
Well, first, search intent is a critical ranking factor, with many top SEOs basing their content strategies on this concept.
When you understand what the searcher wants, it enables you to create content that meets their needs and provides them with the information they’re looking for.
To find search intent, put yourself in the customer’s shoes and ask:
- What are your prospects typing into Google or whatever search engine they’re using? Google’s ‘People Also Ask’ feature is a great starting point for this.
- What questions are searchers trying to answer? Again, ‘People Also Ask’ can assist you with this.
Then:
- Use keyword research to determine popular keywords and phrases related to your topic.
- Look at SERPs and see what results appear (Keywords appear in bold).
13: Choose Focus and Secondary Keywords to Optimize For
Your primary keywords work best when you use them alongside focus and secondary words. Secondary keywords are words that relate to your primary keywords. When you use them in content, they can get it in front of a broader audience and help bolster your website rankings.
When selecting focus and secondary keywords, you should focus on a select few with the biggest impact. Here are some tips to help you do that:
- Choose keywords relevant to your business and audience.
- Make sure you target your keywords for your ideal customers, but also ensure they are popular enough that people actually use them in search engines.
- Use a mix of short-tail and long-tail keywords to get the most out of your SEO efforts.
- Research what your competitors are targeting and try to find gaps you can fill.
- Once you’ve selected your target keywords, make sure they appear throughout your website, including in the title tags, meta descriptions, header tags, and content.
14: Learn What it Takes To Rank for Your Chosen Keywords
This one should be on everyone’s SEO checklist, Your chosen keywords are no good to you if you’re not ranking for them. With that in mind, how do you rank for them? You can start by following these pointers:
- Understand data points, such as search volume, cost per click (CPC), SEO, and search difficulty.
- Draw up a list of content ideas.
- Then, carry out keyword research. You can either use Ubersuggest or any of the other keyword tools out there.
- Analyze the data to identify the best keywords. Again, Ubersuggest is your friend here.
- Optimize for featured snippets and meta descriptions.
- Include keywords in anchor text and use your main keywords strategically.
To help you out, I’ve published a comprehensive guide that talks you through all the above steps.
15: Be Sure to Create Useful, Actionable Content
Okay. Creating content is already on your SEO checklist. However, it can’t just be any content; it needs to be engaging, useful, and actionable. Why?
First, you need engaging content because you don’t want readers leaving part way through before they’ve got to the CTA or taken up your lead magnet offer. If your content is dull and uninspiring, and your reader isn’t doing what you want them to do, you’re wasting your time. Looking for some inspiration? Here’s a great infographic that tells you how to create epic content.
Next, it goes without saying that your content should be useful. You want readers to leave feeling like they’ve learned something.
Finally, write actionable content. You want readers to finish your article knowing what they can do to implement your ideas and get results.
Here are some tips for making your content actionable:
- Include how-tos and step-by-step instructions
- Ask questions and answer people’s pain points
- Add CTAs, so readers know what to do next
- Incorporate stats, storytelling, and images
- Get personal. Share your story and inspire readers
Just one last thing: when creating content, always keep Google’s guidelines in mind.
16: Make Sure You Have a Descriptive URL
Descriptive URLs assist with your SEO efforts and make it easier for customers to find your website. Also, by using descriptive URLs, it’s easier for searchers to understand what your content is about. Plus, it enables the search engines to deliver relevant content to the right people.
Additionally, more descriptive URLs can improve click-through rates, as users are more likely to click on a link that accurately reflects the page content.
To help craft more descriptive URLs, you can use tools like Ubersuggest, Google AdWords Keyword Planner, or Moz’s Keyword Explorer to find popular keywords related to your business. Then:
- Use clear, concise language that accurately reflects the page’s content.
- Do not use unnecessary words or symbols like & or %.
- Make sure each URL is unique and does not duplicate another page on your site.
- Keep URLs as short as possible without compromising readability.
17: Add Title Tags, Meta Descriptions, and Image Tags
One of the most important parts of an SEO checklist is adding title tags, meta descriptions, and image tags to your pages. These tags provide information about your page to search engines and can help them rank higher.
You see, title tags are one of the main factors search engines look at when determining a web page’s rank.
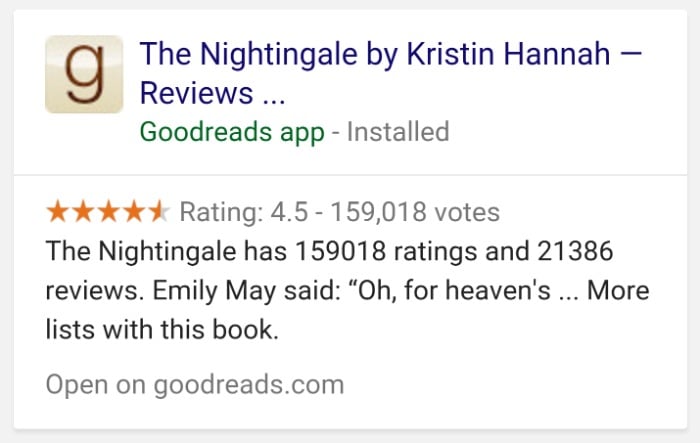
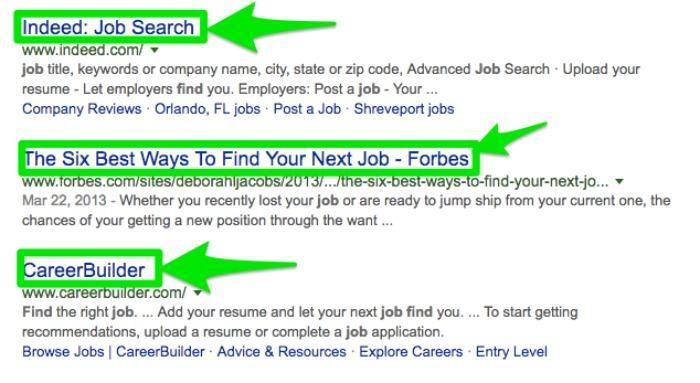
Then there are meta descriptions. You’ve all seen these before. They’re the short blurbs that appear under your title in search engine results pages (SERPs), and they’re your opportunity to persuade people to click through to your site.
They look like this:
Finally, adding image tags to your pictures is one of the simplest ways to improve your SEO. Image tags tell search engines what your image is about, which helps them rank your page higher in search results.
18: Use Schema Markup to Target Rich Snippets
One way to improve your website ranking is by using schema markup. Schema markup is code that you add to your website, which tells search engines what your content means. This can help the likes of Google better understand your content and rank it accordingly.
Rich snippets allow you to add extra information to your search results. Snippets come in different formats like movies, recipes, and maps:
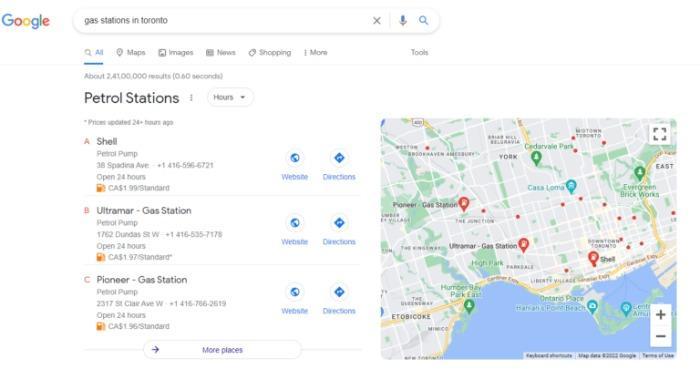
These rich snippets can help you stand out from the competition and attract more visitors to your site due to improved click-through rates (CTRs). This signals to the search engines that you have quality content and can ultimately help you rank higher in SERPs.
19: Have a Plan in Place to Report on Ranking Success
You’ve worked carefully on your SEO checklist but are you forgetting something? Like tracking your ranking success, maybe?
If you’ve made it this far, you’re doing awesome, but unless you’re tracking your progress (rankings), you don’t know that for sure.
When you create a report, it should cover things like:
- Your technical SEO efforts and overall technical health
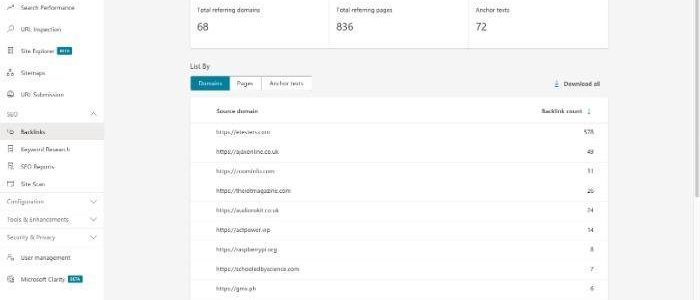
- Traffic
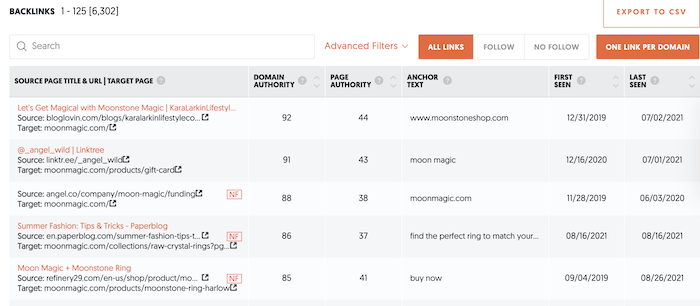
- Backlinks
- Conversions
However, you can include additional info, as pictured below:

To assist with tracking your efforts, Backlinko has a free SEO checklist/report template you can download.
20: Begin Planning a Link-Building Strategy for Finished Content
You’ve just about made it all the way through your SEO strategy checklist. Just one more thing, though.
Now, you want to start creating a link-building strategy for all your amazing content to further enhance your SERPs.
Where do you begin, and why is link building important? Hold on while I talk you through it.
Aside from the lift it can give your SEO, link building can increase organic search results and conversions. For example, one brand found that its revenues increased by 808.87 percent, and organic search sessions increased to 82.3 percent. Impressive, huh? And it all took was six months of off-site SEO.
Below are some simple tips you can use to start link building today:
- Create high-quality content and post it on authoritative blogs as guest posts
- Start a resource directory on your website
- Make sure your content is well-written, useful, and relevant to your target audience.
- Research which websites may want to link to your content, and reach out to them directly
- Link to authority sites in your articles, and reach out to authors/website owners to let them know
FAQs
What Are the Three Main Areas of SEO?
The three areas you should focus on are on-page, off-page, and technical SEO. This includes on-page optimization, link building, keyword research, title tag, meta description, headings, images, and other elements on the page.
What Are the Most Important Ranking Factors of SEO?
This depends on who you ask, but for many, the most important ranking factors are links, quality, content, and website authority. You should also focus on speed/mobile-friendliness, search intent, and usability.
However, Google often updates its guidelines, so ensure you keep up-to-date with these, too.
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “FAQPage”,
“mainEntity”: [
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What Are the Three Main Areas of SEO?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
The three areas you should focus on are on-page, off-page, and technical SEO. This includes on-page optimization, link building, keyword research, title tag, meta description, headings, images, and other elements on the page.
”
}
}
, {
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What Are the Most Important Ranking Factors of SEO?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: ”
This depends on who you ask, but for many, the most important ranking factors are links, quality, content, and website authority. You should also focus on speed/mobile-friendliness, search intent, and usability.
However, Google often updates its guidelines, so ensure you keep up-to-date with these, too.
”
}
}
]
}
Conclusion
A lot of stuff to cover, right?
It may seem overwhelming at first, but following these simple SEO tips can help your website rank higher in search engine results pages and improve your online visibility. Although this SEO checklist includes the mainstays of search optimization, it’s essential to stay up-to-date on the latest SEO trends to ensure your website continues to rank well.
While trends are changing, the constants like competitor keyword research, minimizing image size, optimizing for mobile, and using free tools like Ubersuggest paid tools to analyze keywords are all aspects on your SEO checklist that serve you well long term.
Use this article as your guide and remember that SEO is a long-term project, not a once-off. Keep working at it, and it’s likely your site is going to reap the rewards over time.
Which SEO tactics work well for you?